Low Code Approach for Building a Serverless REST API
In this article, we will build a REST-based service on AWS lambda, API gateway, and PostgreSQL database.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeBuilding REST-based services is pretty common when it comes to the backend world. When it comes to developing the service in a serverless world, it's a trend, but it comes with a lot of pain. For instance, we need to write a function in the language of our choice, then need to build a provisioning script like cloud formation or terraform to chain the set of services used for building the solution.
In this article, we will be building a REST-based service on AWS lambda, API gateway, and PostgreSQL database. The key part is that we will be developing it completely using a low code integration tooling and runtime framework, Kumologica.
Use Case
The customer registration portal of enterprise ABC Company requires a backend service to store the data. The portal will invoke the rest-based service to insert the customer information when the customer is registered. The admin page of the portal has features for listing customer records.

As per the design given above, the enterprise is using AWS cloud provider and its Lambda service for hosting the backend rest API service. The lambda function will be developed using Kumologica designer and runtime framework, which runs on Node.JS. The lambda function needs to connect with the PostgreSQL database hosted externally as managed service.
Pre-Requisites
1. Having an AWS cloud account with necessary IAM access or user having permissions (As prescribed during Kumologica designer installation).
2. AWS profile configured in your machine.
3. Install Kumologica Designer.
4. Create a Trial account in ElephantSQL (Managed service of PostgreSQL database).
5. Run the following SQL script to create the customer table.
CREATE TABLE CUSTOMER(
NAME CHAR(50) PRIMARY KEY NOT NULL,
EMAIL CHAR(50) NOT NULL,
AGE INT NOT NULL,
ADDRESS CHAR(50) NOT NULL
);Implementation
Let's get started implementing the solution by first opening the Kumologica Designer by using the command kl open via terminal or windows command line.
1. Create a new project by providing the Project name and customer service.
2. Install the SQL node in the workspace by opening a command line or terminal and going to the path of your project workspace (location of the project package.json). Enter the following npm command to install.
npm i @kumologica/kumologica-contrib-sqlFlow for Listing the Customers
3. Drag and drop the Event Listener node onto the designer canvas and provide the following configuration for the Event Listener node.
Display Name : [GET] /customers
Event Source : Amazon API Gateway
Verb : GET
URL : /customersThe above configuration is for flow that is listing all the customers.
4. Add a logger node from the palette to the canvas and wire the Event listener node to it. Provide the following log message.
Display Name : Log_Entry
Level : INFO
Message : Request received
Log format : String5. From the storage category in the palette, select the SQL node and drop it after the logger node. Provide the following configuration.
Display Name : GetCustomers
Provider : Postgres
Host : <<Hostname provided by elephant SQL platform>>
Port : 5432
Database : <<Database name provided by elephant SQL platform>>
Timeout : 10000
Username : <<Username provided by elephant SQL platform>>
Password : <<Password provided by elephant SQL platform>>
Query : SELECT * FROM CUSTOMER;6. Drag and drop an Eventlistener End node and wire it to the output of the SQL node. Provide the following configuration.
Display Name : Success
Response : Http Response
Status code : 200
Header > Content-Type : application/json
Payload : msg.payload.rows
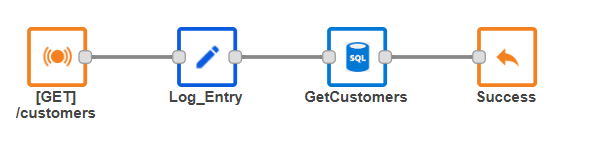
Final flow implementation for customer listing.
Flow for Adding Customer
1. Add the EventListner node with the following configuration.
Display Name : [POST] /customers
Event Source : Amazon API Gateway
Verb : POST
URL : /customers2. Add a JSON node and wire it to the EventListner node. Open the node and select "Always convert a JSON string to an object."
3. Add a logger and provide the following configuration. Wire the logger to the output of the JSON node.
Display Name : Log_Entry
Level : INFO
Message : msg.payload
Log format : JSON4. Add the SQL node and provide the following configuration. Wire the output of the logger to the SQL node.
Display Name : AddCustomer
Provider : Postgres
Host : <<Hostname provided by elephant SQL platform>>
Port : 5432
Database : <<Database name provided by elephant SQL platform>>
Timeout : 10000
Username : <<Username provided by elephant SQL platform>>
Password : <<Password provided by elephant SQL platform>>
Query : "INSERT INTO CUSTOMER( NAME, EMAIL , AGE , ADDRESS ) VALUES ('" & msg.payload.name & "','" & msg.payload.email & "'," & msg.payload.age & ",'" & msg.payload.address & "');"5. Wire an EventListener end node to the output of the SQL node and provide the following configuration.
Display Name : Success
Response : Http Response
Status code : 200
Header > Content-Type : application/json
Payload : msg.payload
Final flow implementation for customer listing.
Deploying to AWS
1. For deploying to AWS, select the AWS deployment icon from the right-hand side panel of the designer.
2. Select the AWS profile name you have created as part of the pre-requisite.
3. Click Deploy.
After deployment is completed, the complete REST endpoint URL for accessing the service will be displayed in the designer terminal. You can test the endpoint using any REST client of your choice.
Conclusion
When deploying the flow from Kumologica designer, the designer automatically packages the flow as a lambda zip along with the AWS cloud formation script. The script is generated by the deployment segment of the designer. The cloud formation script deploys the flow as a node.js-based AWS function and exposes the function via AWS API Gateway. As you can see, we have developed this serverless REST service with very minimal coding and zero scripting.
I hope you liked this article. Stay tuned for the next tutorial.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments