Building a RESTful API With AWS Lambda and Express
Build a RESTful API using AWS Lambda and Express.js with this quick and easy-to-follow tutorial. Deploy your RESTful API with confidence using Node.js.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAWS Lambda is a serverless computing service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS) that allows you to run code without provisioning or managing servers. Node.js is a JavaScript runtime built on Chrome’s V8 JavaScript engine. Together, AWS Lambda and Node.js can be used to create a RESTful API that can be triggered by events such as an HTTP request.
Prerequisites
Before building a RESTful API with Express.js, you should have the following in place:
- As Express.js is a JavaScript framework, you’ll need Node.js installed to run it. You can download Node.js from the official website.
- Text Editor or Integrated Development Environment (IDE): To write and edit your API code, you will need a text editor or IDE. Examples of popular text editors are Sublime Text and Visual Studio Code, while popular IDEs are WebStorm and Visual Studio.
- In order to write your API, you should have a basic understanding of JavaScript, since Express.js is written in JavaScript.
- A familiarity with Express.js: Express.js is a web framework for Node.js that helps you build web applications and APIs quickly and easily.
- The RESTful APIs use HTTP for communication, so you should be familiar with the protocol. It is necessary to have a basic understanding of HTTP methods (GET, POST, PUT, DELETE) and their intended uses, status codes, and the format of HTTP requests and responses.
- For keeping track of changes to your codebase, familiarity with version control systems (VCS) like Git is helpful.
As soon as you have these prerequisites in place, you can start building your RESTful API with Express.js.
Adding in The Code
1. Create an AWS_Node folder using the mkdir command in the terminal and cd into the directory.
mkdir aws-lambda-express-demo
cd aws-lambda-express-demo
2. Create an app.js file in your AWS_Node folder.
touch app.js
Libraries
1. We’ll use npm to download the latest version of the express package from the npm registry and store it in the node_modules folder in your project’s root directory. The package’s dependencies will also be installed and stored there as well.
npm install express
2. Next we’ll install a middleware-compatible framework called serverless-http, a library for creating serverless applications. AWS Lambda allows you to write your application normally, and then wrap it around a function that is exported and executed using an HTTP request. Aside from Azure, Google Cloud, and others, it is also compatible with serverless providers.
npm install serverless-http
You can install the package globally by running npm install -g serverless-http.
Here’s an example of a RESTful API implemented using Node.js with the Express.js framework that implements the GET, POST, DELETE, and PUT methods:
This code creates an Express.js app and adds routes for the GET, POST, DELETE, and PUT methods. It uses an in-memory items array to store data and uses the find and findIndex methods to retrieve and update items based on the id provided in the URL. Note that for the POST and PUT routes, you will have to parse the body of the request, which you can do with middleware such as body-parser.
const express = require('express');
const app = express();
const serverless = require('serverless-http');
const users = [ { id: 1, name: 'John', company: "ABC Company" }, { id: 2, name: 'Frank', company: "XYZ Inc." }, { id: 3, name: 'Ashley', company: "123 Company" }, ];app.get('/users', (req, res) => { res.json(users); });app.get('/users/:id', (req, res) => { const user = users.find(user => user.id === parseInt(req.params.id)); if (!user) res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' }); res.json(user); });app.post('/users', (req, res) => { const user = { id: users.length + 1, name: req.body.name, company: req.body.company, }; users.push(user); res.json(user); });app.delete('/users/:id', (req, res) => { const userIndex = users.findIndex(user => user.id === parseInt(req.params.id)); if (userIndex === -1) res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' }); users.splice(userIndex, 1); res.json({ message: 'User deleted' }); });app.put('/users/:id', (req, res) => { let user = users.find(user => user.id === parseInt(req.params.id)); if (!user) res.status(404).json({ message: 'User not found' }); user.name = req.body.name; user.company = req.body.company; res.json(user); }); const handler = serverless(app);const startServer = async () => { app.listen(3000, () => { console.log("listening on port 3000!"); }); }startServer();module.exports.handler = (event, context, callback) => { const response = handler(event, context, callback); return response; };
We’ll write the line console.log("listening on port 3000!"); to indicate that your API is up and running. Finally, module.exports.handler is a function that takes in event, context, and callback arguments, and calls the handler function passing in the event, context, and callback arguments.
Running and Testing the Code
Start the server by running the following:
node app.js
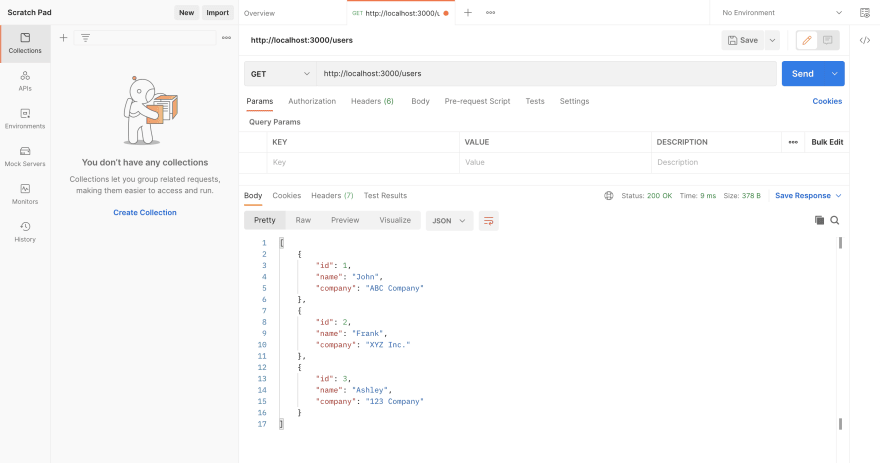
Now, our API is up and running. You can send a test HTTP request through Postman. By sending a request to localhost:3000/users, you should see a 200 OK status code. For this test, no request body is needed for the incoming request.
Published at DZone with permission of Preet Kaur. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments