An Overview of Cloud Cryptography
This article gives details about the need for Cloud Cryptography, the various techniques and algorithms used, and its benefits.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeCloud Cryptography refers to a set of techniques used to secure data stored and processed in the cloud environment and is essential for protecting sensitive information. By using encryption and secure key management techniques, Cloud Cryptography provides the following security:
- Data Privacy
- Data Confidentiality
- Data Integrity
The three common methods used in Cloud Cryptography are as follows:
1. Symmetric Encryption: uses the same key for encryption and decryption of data.
2. Asymmetric Encryption: uses a public key for encryption and a private key for decryption.
3. Hash functions: creates a unique version of a message to maintain its integrity.
Cloud Cryptography protects the data by adding a layer of protection to avoid the data being breached, affected by malware, or hacked. The data stored in the cloud are secured by encryption, allowing the users to access cloud services conveniently and safely. Also, it provides security without delaying the delivery of information.
How Does Cloud Cryptography Work?
Cloud Cryptography is based on encryption algorithms that convert the text into ciphertext. This ciphertext is then converted into plain text through an encryption key.
There are two types of Cloud Cryptography for protection:
- Data-in-transit
- Data-at-rest
Data-in-transit is encrypted when a user visits a site on the internet. Encryption is done by using the data transfer protocol ‘HTTPS.’ HTTPS protects the data by providing a layer of encryption around it.
Data-at-rest can be encrypted and decrypted using encryption and decryption keys, making it impossible for anyone to hack the information. Data is encrypted at both sender’s and receiver’s ends.
How Is Cloud Cryptography Implemented?
Physical control over the data in the cloud is impossible. Cloud data encryption helps in protecting confidential information and ensures faster data transfer.
The following cryptography techniques are employed for Cloud data security.
1. Symmetric Algorithm
The Symmetric algorithm decrypts using the same key used for encryption. This technique requires fewer computing resources and performs well in encryption. Two-way keys are used in the symmetric algorithm to ensure validation and approval. The encrypted data is stored in the Cloud and can be decrypted only when the client knows the key.
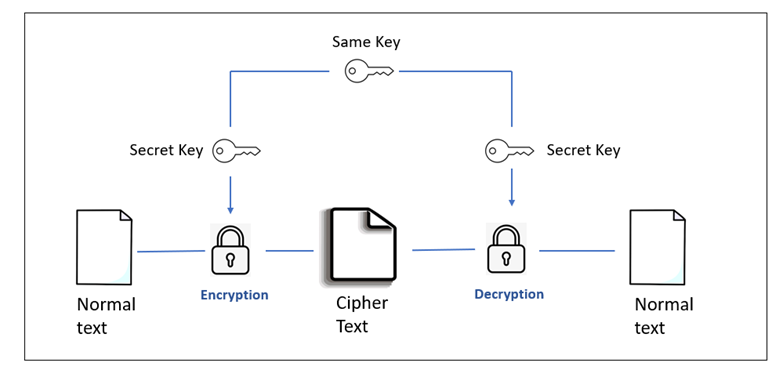
Image 1: Symmetric Cryptography
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES), Data Encryption Standard (DES), Blowfish, and Triple DES are some of the widely used symmetric algorithm techniques.
Advanced Encryption Standard (AES): This technique encrypts digital data in industries like finance, telecommunication, and the public sector. Encryption and decryption use the same key. A block of ciphertext repeats itself after each mentioned step. The key size can be 128, 192, and 256 bits, with a block size of 128.
Data Encryption Standard (DES): This technique uses a 64-bit secret key, out of which the first 56 bits are generated at random, and the other 8 bits are used for detecting errors and maintaining data integrity. DES is mostly used on hardware for encryption by single users, such as encrypted information saved on a hard drive.
2. Asymmetric Algorithm
The asymmetric algorithm encrypts and decrypts data using different keys. Each recipient of the data needs to have a decoding key. This is also called as Recipient’s private key. Any organization or individual is the owner of the encryption key. Since this algorithm requires both encryption and decryption keys to access any information, this algorithm is considered the safest.

Image 2: Asymmetric Cryptography
Digital Signature Algorithm (DSA), Rivest Shamir Adleman Algorithm (RSA), Elliptic Curve Cryptography (ECC), and Diffie-Hellman algorithm are some of the asymmetric algorithms used for encrypting data in the cloud.
Rivest Shamir Adleman Algorithm (RSA): It is a de facto encryption standard that is used for encryption in a wide range of systems. It employs different keys for encryption and decryption. The public key is known to everyone, but only an authorized individual can decrypt it with the private key.
Elliptic Curve Encryption (ECC): It is a contemporary public-key cryptography that generates a small key using mathematical elliptic curves and a number concept. Because of its short key size, ECC is most used by security experts.
3. Hashing
Hashing is the most important element of blockchain security. When a data block is added to the chain, a unique code or hash is assigned to it. Hashing makes data retrieval faster, and this technique is mostly used for indexing.
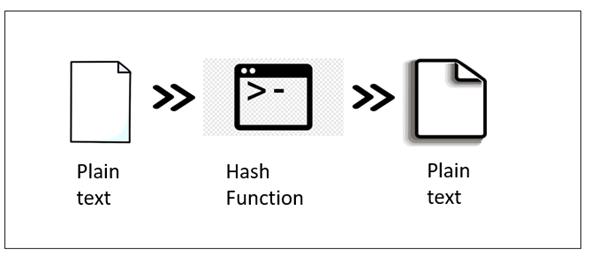
Image 3: Hashing Algorithm
Benefits of Cloud Cryptography
- Cryptography is undoubtedly the safest technique for storing and transferring data in the cloud since it adheres to the constraints imposed by standards such as FIPS, HIPAA, and FISMA.
- Since the client’s information is kept confidential, Cloud cryptography reduces cybercrime.
- Cloud encryption enables organizations to be proactive in their defense against data breaches and cyber-attacks which is necessary in today’s data-driven world.
Disadvantages of Cloud Cryptography
- Cloud cryptography needs highly advanced systems to maintain encrypted data.
- Overprotective measures can cause difficulties for organizations when recovering data.
Conclusion
Organizations must follow a data-centric strategy in this complex and evolving world of virtualization and cloud services to protect information against attacks. Organizations must implement security measures to protect sensitive data, like encryption and cryptographic key management for cloud data.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments