Containerize Gradle Apps and Deploy to Kubernetes With JKube Kubernetes Gradle Plugin
Eclipse JKube now supports Gradle!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article is a follow-up to my previous post, Deploy Maven Apps to Kubernetes With JKube Kubernetes Maven Plugin.
Eclipse JKube is a collection of tools and libraries which ease a Java developer's workflow working with Docker and Kubernetes. It is the successor to the famous Fabric8 Maven Plugin.
Eclipse JKube brings a set of tools focused on bridging the gap between traditional Java development and modern cloud-native development. Till v1.4.0, Eclipse JKube only supported Maven Plugins; but recently their team also has added Gradle Plugins.
We will be taking a look at Eclipse JKube Kubernetes Gradle Plugin to see how it provides a similar developer experience while working with Docker and Kubernetes like you usually have with your popular application frameworks:
Setting Up Your Gradle Project
If you already have access to a grade, project you can skip this step. If not, you can create a Spring Boot-based project from start.spring.io or use one of the Eclipse JKube Gradle Quickstarts.
You can find latest version of Eclipse JKube on Maven Central. You'll need to specify mavenCentral() in your settings.gradle and build.gradle to tell gradle to look into maven central repositories while searching for plugin:
settings.gradle:
pluginManagement {
repositories {
gradlePluginPortal()
mavenCentral()
}
}build.gradle:
repositories {
mavenCentral()
}
To add Eclipse JKube Kubernetes Gradle Plugin to your project, you can simply add it to your build.gradle like this:
plugins {
id 'org.eclipse.jkube.kubernetes' version '1.5.1'
}Let's take a look at tasks available with Kubernetes Gradle Plugin:
| Task Name | Description |
k8sBuild |
Build Container Images |
k8sResource |
Generate Kubernetes Manifests |
k8sApply |
Apply generated Manifests to Kubernetes |
k8sPush |
Push Container Image to container registry |
k8sHelm |
Generate Helm Charts |
k8sDebug |
Debug application in Kubernetes Cluster |
k8sLog |
Get Logs of the application running in Kubernetes |
k8sUndeploy |
Cleanup: Delete all resources deployed in Kubernetes |
1. Containerizing Your Application
Kubernetes Gradle Plugin makes containerizing your Gradle applications extremely easy. It allows building Docker images without providing any configuration with the help of it’s opinionated defaults. Of course, you can customize this very easily by allowing customization of image via Groovy DSL or by providing your own Dockerfile.
To build Docker image of your application, just run the k8sBuild task (Default strategy for building images Is Docker so It requires access to a docker daemon):
gradle k8sBuildThis will create a Docker Image in the daemon you performed this task against. You can check the image build using docker images command. If you don’t have access to docker daemon, you can change build strategy to JIB like this:
gradle k8sBuild -Djkube.build.strategy=jibIt will generate a tar file for your image which can be copied and loaded in any other docker daemon.
2. Pushing Image to Container Registry
Once you’ve built an image, you might want to push it to a remote registry like DockerHub or Quay. You can easily achieve this with Kubernetes Gradle Plugin. Before doing it, you need to make sure that the image you’ve built is in the correct ${registry}/${user}/${image-name}:${tag} format. If you’re providing your own Groovy DSL Configuration for building image, you can simply change the image name by changing the name section like this:
kubernetes {
images {
name = 'quay.io/rohankanojia/helloapp:1.0.0'
alias = 'hello-world'
build {
from = 'openjdk:latest'
cmd {
exec = ["java", "-jar", "/deployments/${project.name}-${project.version}.jar"]
}
}
}
}If you’re using Kubernetes Gradle Plugin’s Zero Configuration, you need to change default image name generated by Kubernetes Gradle Plugin by providing this property:
jkube.generator.name = quay.io/rohankanojia/helloapp:1.0.0For registry authentication, Kubernetes Gradle Plugin automatically detects credentials from these locations:
~/.docker/config.json(docker login config file)- In
authsection in plugin configuration
You can check these in detail in Kubernetes Gradle Plugin Authentication Docs.
In order to push image to specified registry, you can go ahead and use k8sPush task:
gradle k8sPushOr if you had built your image with JIB build strategy, you can do:
gradle k8sPush -Djkube.build.strategy=jib3. Generate Kubernetes Manifests
Kubernetes Gradle Plugin also automatically generates opinionated Kubernetes Manifests by inspecting your project’s dependencies. Of course, it can easily be customized by providing your own manifests or small portions of YAML in src/main/jkube directory, For more information check out plugin documentation about Resource Fragments.
In order to generate Kubernetes Manifests, you just need to run k8sResource task:
gradle k8sResourceThis would generate Kubernetes manifests which would be available in build/ directory, as shown in listing below:
$ tree build/classes/java/main/META-INF/jkube/
build/classes/java/main/META-INF/jkube/
├── kubernetes
│ ├── eclipse-jkube-demo-project-gradle-deployment.yml
│ └── eclipse-jkube-demo-project-gradle-service.yml
└── kubernetes.yml
1 directory, 3 files
4. Deploying To Kubernetes
You can use Kubernetes Gradle Plugin’s apply task in order to apply the Kubernetes YAML manifests generated in previous step on top of Kubernetes Cluster. You just need to be logged into a Kubernetes cluster.
Then you can deploy your application in just one step using k8sApply task:
gradle k8sApplyTo remove your application from Kubernetes, just use the k8sUndeploy task:
gradle k8sUndeploy5. Inspect Logs
Once your application has been deployed into Kubernetes using Kubernetes Gradle Plugin; you might want to inspect its logs. You can use k8sLog task which would output logs for your application running inside Kubernetes:
gradle k8sLogUse Ctrl+C to stop tailing the log
If you wish to get the log of the app and then terminate immediately then use this option:
gradle k8sLog -Djkube.log.follow=false6. Live Debugging App Running Inside Kubernetes
To debug your application deployed using the k8sApply task, just run the k8sDebug task:
gradle k8sDebugThis will use the default Java remote debugging port of 5005. You can also specify a different port if you want:
gradle k8sDebug -Djkube.debug.port=8000Once task is up and running, a debug port would be opened on your laptop(localhost) which then connects using Kubernetes Pod Port forwarding to your latest application Pod.
You can add a debug execution in IntelliJ like this:
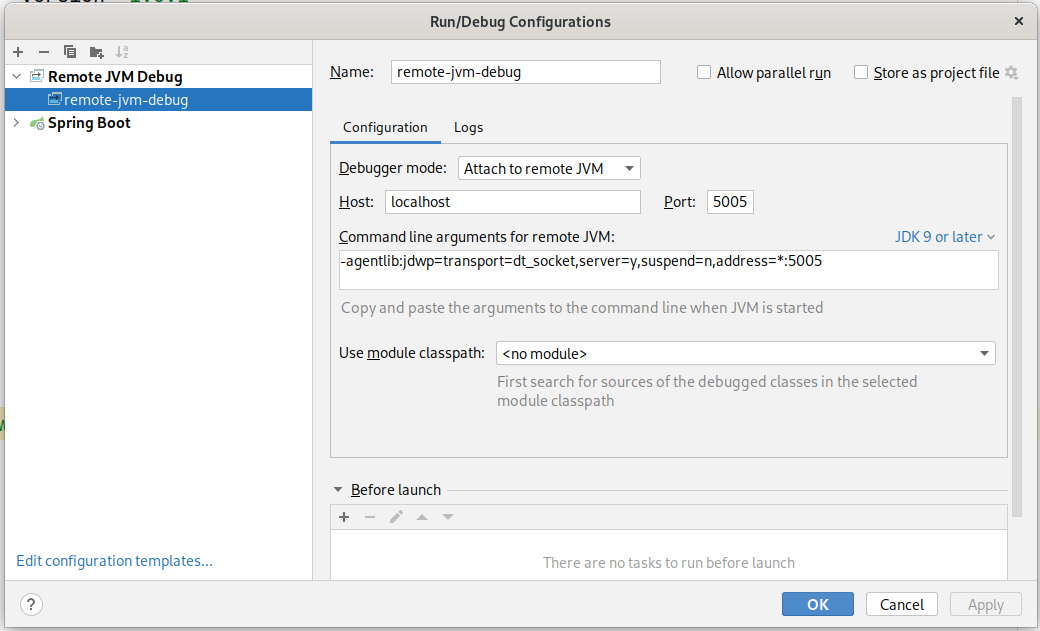
7. Generating Helm Charts
If you're familiar with helm, Eclipse JKube also provides support for generating and publishing helm charts. You can generate helm charts using the k8sHelm task provided by Kubernetes Gradle Plugin. This helm chart would include all the resources generated by k8sResource task.
gradle k8sHelmNote that it's required to run k8sResource before running this task.
After executing the task, you can apply this helm chart via helm CLI like this:
$ helm install build/jkube/helm/eclipse-jkube-demo-project-gradle/kubernetes/ --generate-name
NAME: kubernetes-1635508429
LAST DEPLOYED: Fri Oct 29 17:23:49 2021
NAMESPACE: default
STATUS: deployed
REVISION: 1
TEST SUITE: None
$ helm list
NAME NAMESPACE REVISION UPDATED STATUS CHART APP VERSION
kubernetes-1635508429 default 1 2021-10-29 17:23:49.888358544 +0530 IST deployed eclipse-jkube-demo-project-gradle-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT Conclusion
Please try out the Kubernetes Gradle Plugin and let us know via Community or via Issue Tracker. Are you interested in joining us to make this project better? Don’t be shy about joining our welcoming community:
- Provide feedback on GitHub
- Craft code and push a pull request to the Eclipse JKube repository.
- Interact with the Eclipse JKube team on Gitter and the JKube mailing list .
- Ask questions and get answers on Stack Overflow.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments