Connect Oracle SQL Developer to Amazon Redshift
This guide will walk you through the process of setting up a PostgreSQL JDBC driver and an SSL connection.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
If you have used Oracle SQL Developer, you might have struggled to connect to databases other than Oracle. This is especially true for Oracle SQL Developer users that want to connect to Amazon Redshift. There is a lot of piecemeal documentation out there, some of which is outdated or inaccurate.
We thought a cohesive step-by-step guide on how to connect Oracle SQL Developer to Redshift was needed.
Typical Challenges
If you try to use JDBC drivers provided by Amazon Redshift, you will quickly find that Oracle SQL Developer doesn’t support those. You must use PostgreSQL JDBC drivers instead.
Also, if Redshift forces SSL connections, this can be a roadblock. The connection parameters need to be explicitly set for SSL. Without setting SSL, the connection will fail.
Our guide will walk you through the process of setting up a PostgreSQL JDBC driver and an SSL connection.
How to Connect Amazon Redshift to Oracle SQL Developer With Postgres JDBC Driver
Step 1: Download PostgreSQL JDBC Driver
Download the PostgreSQL JDBC driver from this URL: https://jdbc.postgresql.org/download.html. Find the most recent version of the driver and click the link to download it. After that, save the resulting .jar file on your computer to a location where you can easily find it.
Step 2: Establish a Connection From Oracle SQL Developer UI
1. In Oracle SQL Developer, click Tools then Preferences from the top menu bar:
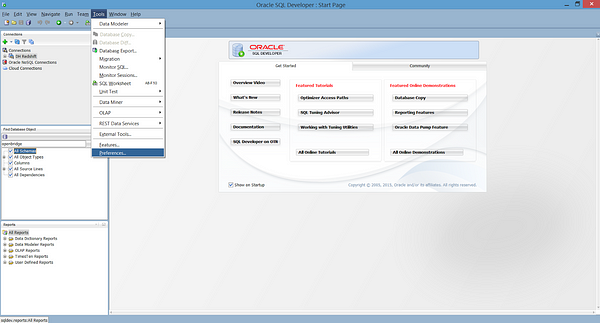
2. Under Database, select Third Party JDBC Drivers.

3. Click Add Entry, and in the Select Path Entry Window, click on the .jar file you saved in Step 1 and click Select.
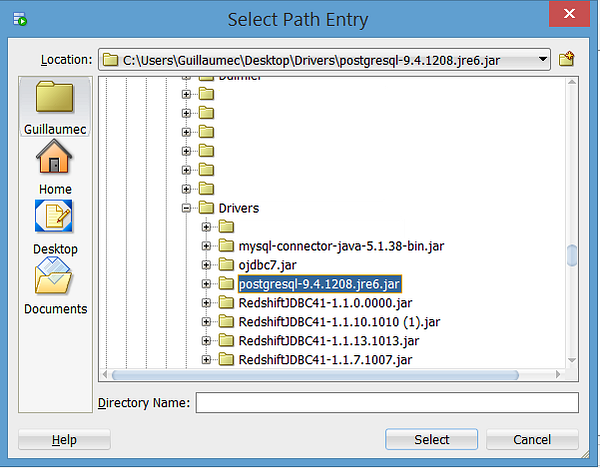
4. Click OK in the Preferences window
5. Now when you click New Connection, you will see a PostgreSQL tab
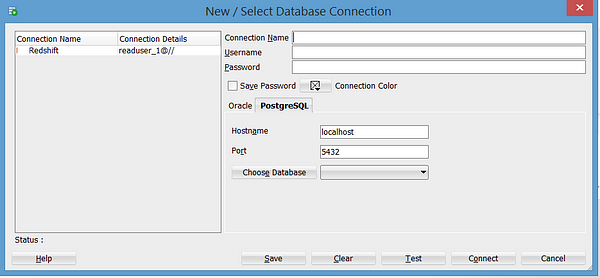
6. Enter a Connection Name and the Username and Password.
7. In the Hostname box, replace:
localhostwith your connection string containing the SSL parameters:
yourhost.redshift.openbridge.io:5439/openbridge?ssl=true&sslfactory=org.postgresql.ssl.NonValidatingFactory&What if you are not using SSL? Simply remove those SSL parameters:
yourhost.redshift.openbridge.io:5439/openbridge?8. You can delete what is in the Port Box and leave it blank. The post is part of the connection string. Also, leave Choose Database as is.
9. Click Save and then click Connect. If everything went according to plan, you should be connected to Redshift! However, don’t celebrate just yet. Time to test.
Step 3: Test
Once you have connected, run this quick test to make sure queries run properly. It should list all the tables for a given database and schema:
SELECT DISTINCT tablename FROM pg_table_def WHERE schemaname = ‘replacewithschemaname’ ORDER BY tablename;Run the query. If you see a list of tables, awesome! If you don’t, check your permissions or run a different test query based on your access/permissions.
Let me know your thoughts in the comments.
Published at DZone with permission of Anna Shmelkova. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments