Distributed Tracing With Spring-cloud-Sleuth Kafka and Zipkin
In this post, you will learn to use Spring Cloud Sleuth for distributed tracing between Spring Boot microservices and Kafka with results displayed on the Zipkin server.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeDistributed Tracing introduction
As we are all living in the microservices world now, it is necessary and important to have a nice and easy way to trace the invocation from one service to another directly or via a message broker like Kafka.
So in this tutorial, you will see how to use Spring Cloud Sleuth to record distributed tracing between Spring Boot microservices and Kafka. Zipkin will be used as a tool to collect and visualize distributed tracing across services.
Demo Project Introduction
In this demo, there are 3 projects including:
- Customer-service which will receive request and then publish a message to Kafka topic. After that Kafka listener consumes the message then calling order-service.
- Order-service will call REST endpoint in product-service.
- Product-service receives calls from order-service.
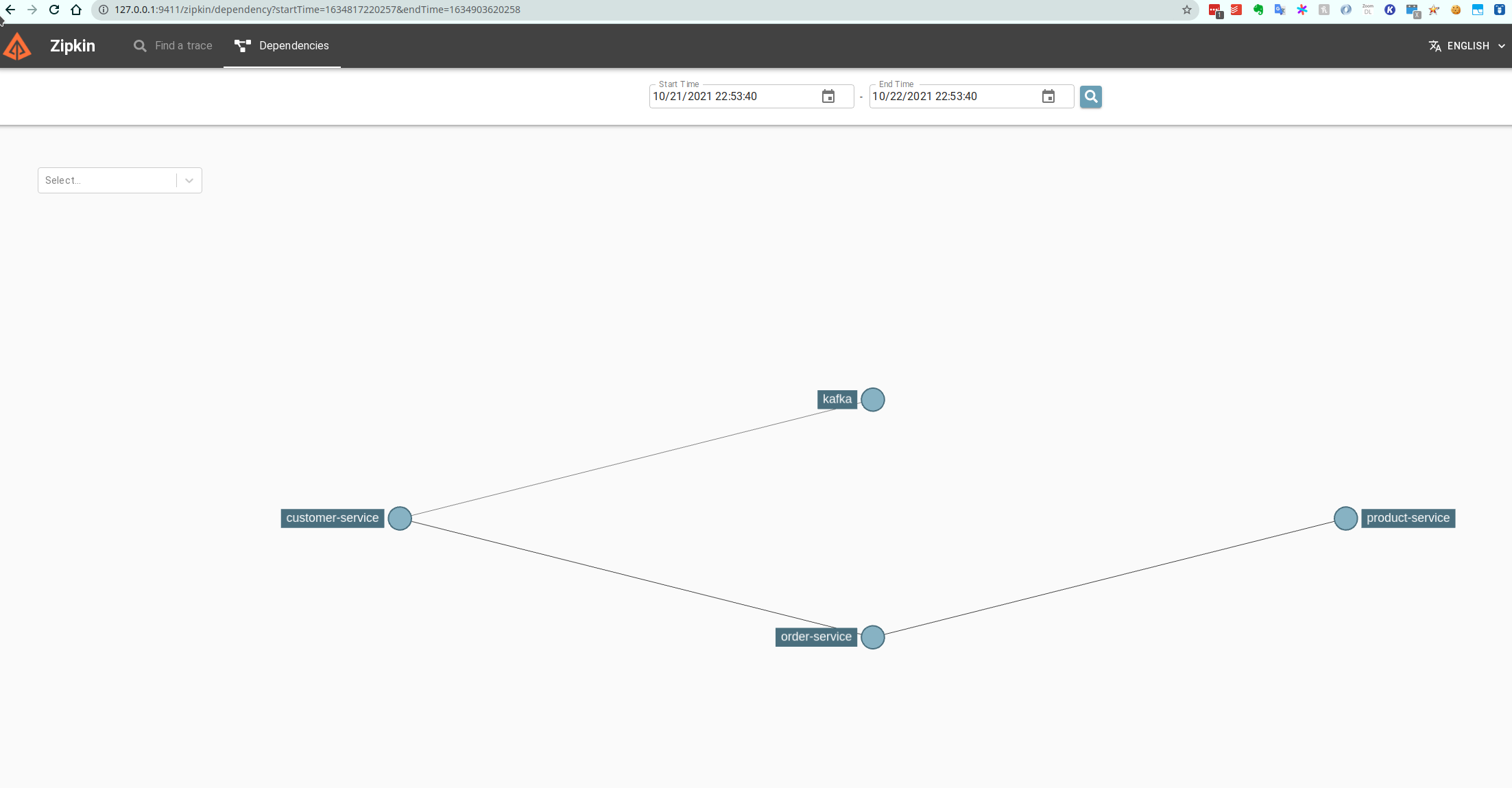
Here is the diagram regarding how they interact together.

Run Zipkin Server and Kafka
There are 3 ways to run the Zipkin server which you can find here but for the sake of simplicity in the article, we will use the docker option. Here is the docker compose file:
docker-compose.yml
version: '3'
services:
# Kafka service here
kafka-service:
image: landoop/fast-data-dev:latest
ports:
- "3030:3030"
- "9092:9092"
environment:
ADV_HOST: 127.0.0.1
BROKER_PORT: 9092
# Zipkin service here
zipkin-server:
image: openzipkin/zipkin
ports:
- "9411:9411"After this runs successfully, you can access the admin console of Zipkin and Kafka.
Zipkin Admin Console
Kafka Admin Console
Customer-service
customer-service will receive a HTTP GET request then publish a message into a Kafka topic. After that, a listener will consume the message and invoke order-service.
Here are the Maven pom.xml, application.properties and CustomerRestController.java. Furthermore, order-service and product-service are similar SpringBoot based project, so we will skip them here. But you can find the complete code here.
pom.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.4.11</version>
<relativePath/> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent>
<groupId>com.rvpnp</groupId>
<artifactId>customer-service</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>customer-service</name>
<properties>
<java.version>11</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2020.0.4</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.kafka</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-kafka</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-sleuth</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-sleuth-zipkin</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-configuration-processor</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
<optional>true</optional>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<excludes>
<exclude>
<groupId>org.projectlombok</groupId>
<artifactId>lombok</artifactId>
</exclude>
</excludes>
</configuration>
</plugin>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.apache.maven.plugins</groupId>
<artifactId>maven-compiler-plugin</artifactId>
<configuration>
<source>11</source>
<target>11</target>
</configuration>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build>
</project>Application.properties
server.port=9081
spring.application.name=customer-service
spring.zipkin.base-url=http://localhost:9411/
CustomerRestController.java
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
@RestController
@RequestMapping("/")
public class CustomerRestController {
private static final String ORDER_SERVICE_HOST = "http://localhost:9082";
private final KafkaTemplate<String, String> kafkaTemplate;
@GetMapping("/customer/11041032/orders")
public ResponseEntity<String> getOrderDetail() {
log.info("Calling webhook at customer-service");
kafkaTemplate.send(EVENT_TOPIC, "message-key", "message-body");
log.info("Publish message into topic {}", EVENT_TOPIC);
return ResponseEntity.ok("success");
}
}
Run Microservice
After clone the project, run mvn clean package and start these three services from the root as below:
java -jar customer-service/target/customer-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jarjava -jar order-service/target/order-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jarjava -jar product-service/target/product-service-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
In the terminal run command: curl 'http://localhost:9081/customer/11041032/orders'

After that, you will see logs appear like this:
2021-10-22 22:39:12.274 INFO [customer-service,00d6330df0dbc919,00d6330df0dbc919] 345215 --- [nio-9081-exec-1] c.r.customer.web.CustomerRestController : Publish message into topic event-topic
2021-10-22 22:39:12.317 INFO [customer-service,00d6330df0dbc919,13483035781266a4] 345215 --- [ntainer#0-0-C-1] c.r.customer.web.KafkaMessageListener : Receive message from topic event-topic with message message-body
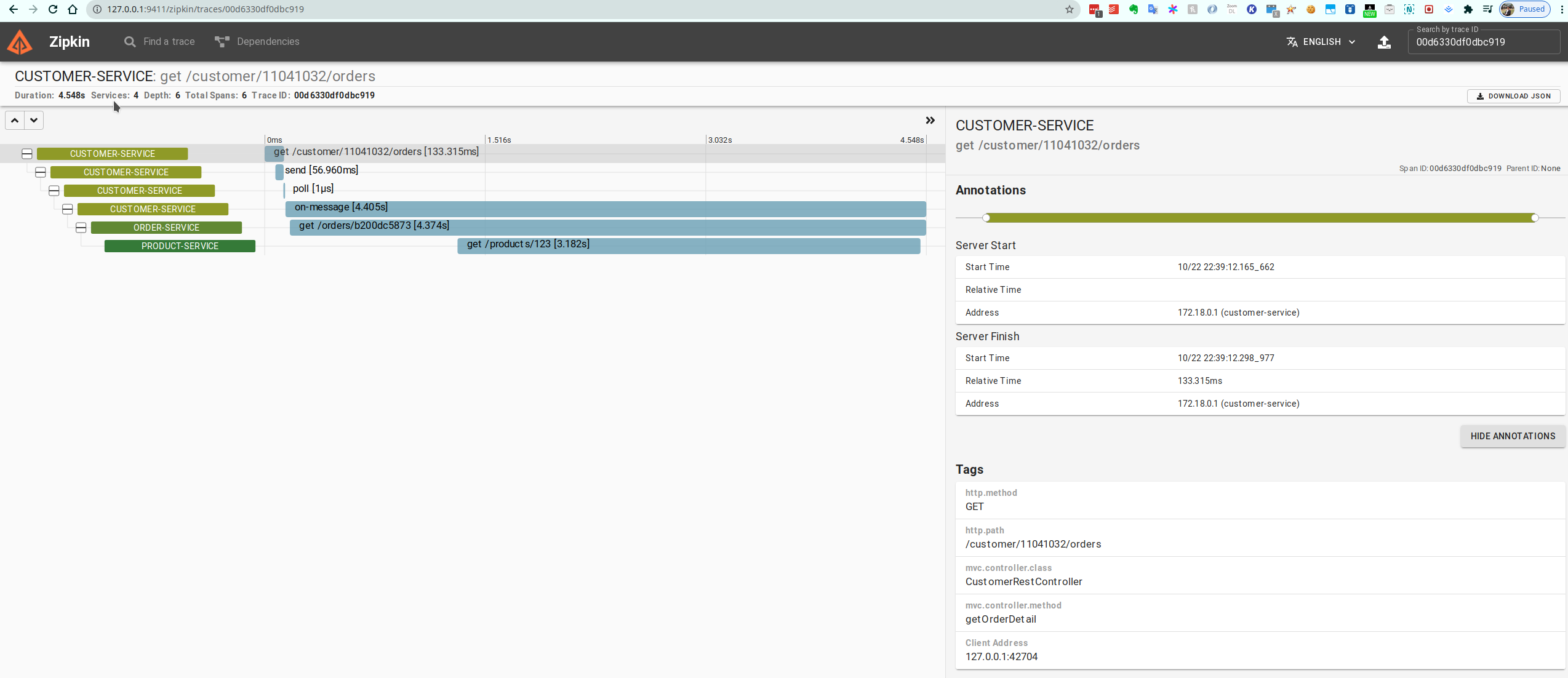
2021-10-22 22:39:16.713 INFO [customer-service,00d6330df0dbc919,13483035781266a4] 345215 --- [ntainer#0-0-C-1] c.r.customer.web.KafkaMessageListener : Call ORDER_SERVICE_HOST http://localhost:9082 from KafkaMessageListenerThen we can get traceId which is after a service name that is 00d6330df0dbc919 in this example.
Finally we can search in the Zipkin Admin UI and see tracing between microservices.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments