How Event-Driven Ansible Works for Configuration Monitoring
Monitor configuration files with event-driven Ansible to detect changes, automate responses, and ensure security, compliance, and reliability in IT systems.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeConfiguration files control how applications, systems, and security policies work, making them crucial for keeping systems reliable and secure. If these files are changed accidentally or without permission, it can cause system failures, security risks, or compliance issues. Manually checking configuration files takes a lot of time, is prone to mistakes, and isn’t reliable, especially in complex IT systems.
Event-driven Ansible offers a way to automatically monitor and manage configuration files. It reacts to changes as they happen, quickly detects them, takes automated actions, and works seamlessly with the tools and systems you already use.
In this article, I will demonstrate how to use Ansible to monitor the Nginx configuration file and trigger specific actions if the file is modified. In the example below, I use the Ansible debug module to print the message to the host. However, this setup can be integrated with various Ansible modules depending on the organization's requirements.
About the Module
The ansible.eda.file_watch module is a part of event-driven Ansible and is used to monitor changes in specified files or directories. It can detect events such as file creation, modification, or deletion and trigger automated workflows based on predefined rules. This module is particularly useful for tasks like configuration file monitoring and ensuring real-time responses to critical file changes.
Step 1
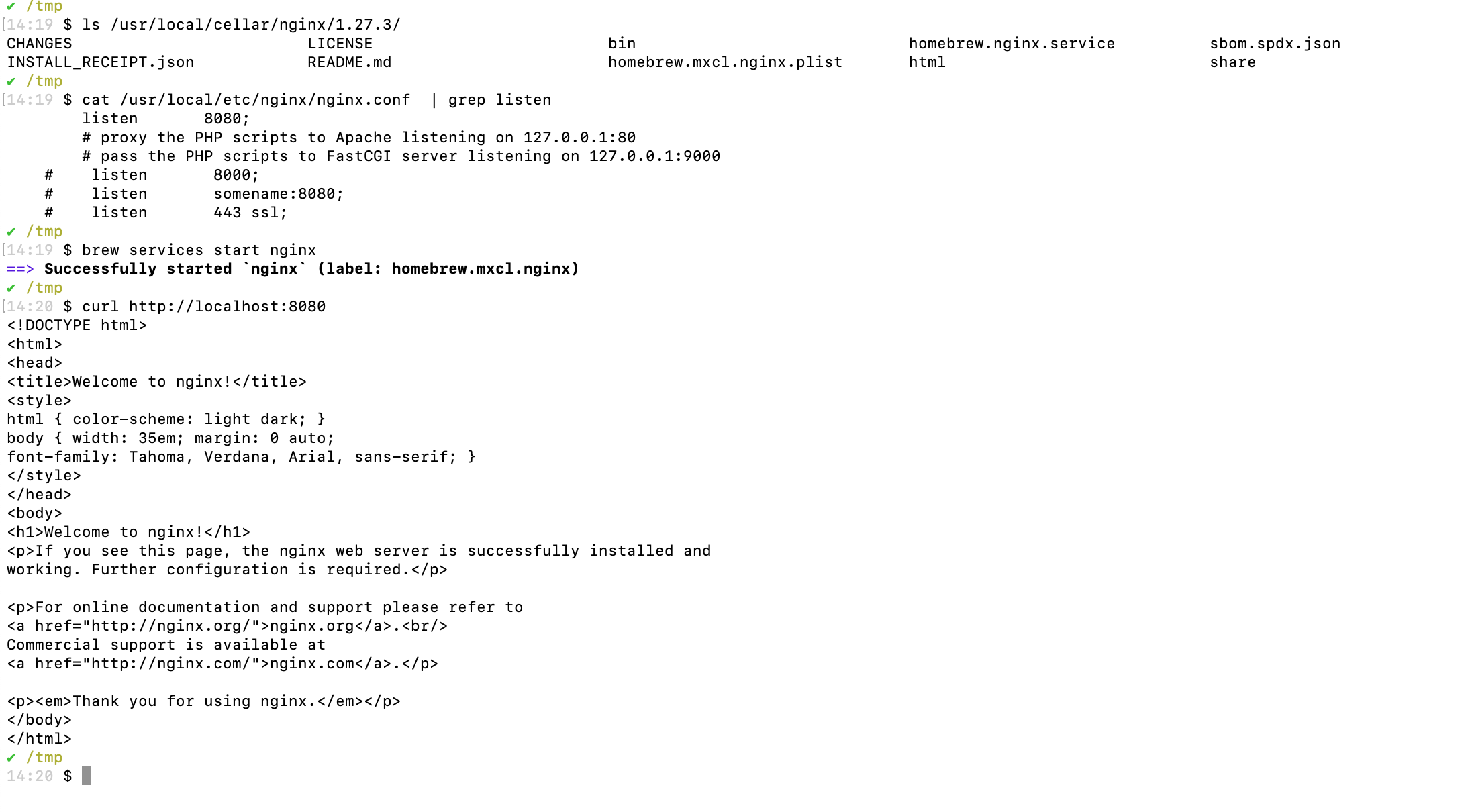
To install Nginx on macOS using Homebrew, run the command brew install nginx, which will automatically download and install Nginx along with its dependencies. By default, Homebrew places Nginx in the directory /usr/local/Cellar/nginx/ and configures it for use on macOS systems.
After installation, edit the configuration file at /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf to set the listen directive to listen 8080;, then start the Nginx service with brew services start nginx.
To confirm that Nginx is running, execute the command curl http://localhost:8080/ in the terminal. If Nginx is properly configured, you will receive an HTTP response indicating that it is successfully serving content on port 8080.
Step 2
In the example below, the configwatch.yml playbook is used to monitor the Nginx configuration file at /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf. It continuously observes the file for any changes. When a modification is detected, the rule triggers an event that executes the print-console-message.yaml playbook.
---
- name: Check if the nginx config file is modified
hosts: localhost
sources:
- name: file_watch
ansible.eda.file_watch:
path: /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf
recursive: true
rules:
- name: Run the action if the /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf is modified
condition: event.change == "modified"
action:
run_playbook:
name: print-console-message.ymlThis second playbook performs a task to print a debug message to the console. Together, these playbooks provide automated monitoring and instant feedback whenever the configuration file is altered.
---
- name: Playbook for printing the message in console
hosts: localhost
connection: local
gather_facts: false
tasks:
- name: Error message in the console
debug:
msg: "Server config altered"Demo
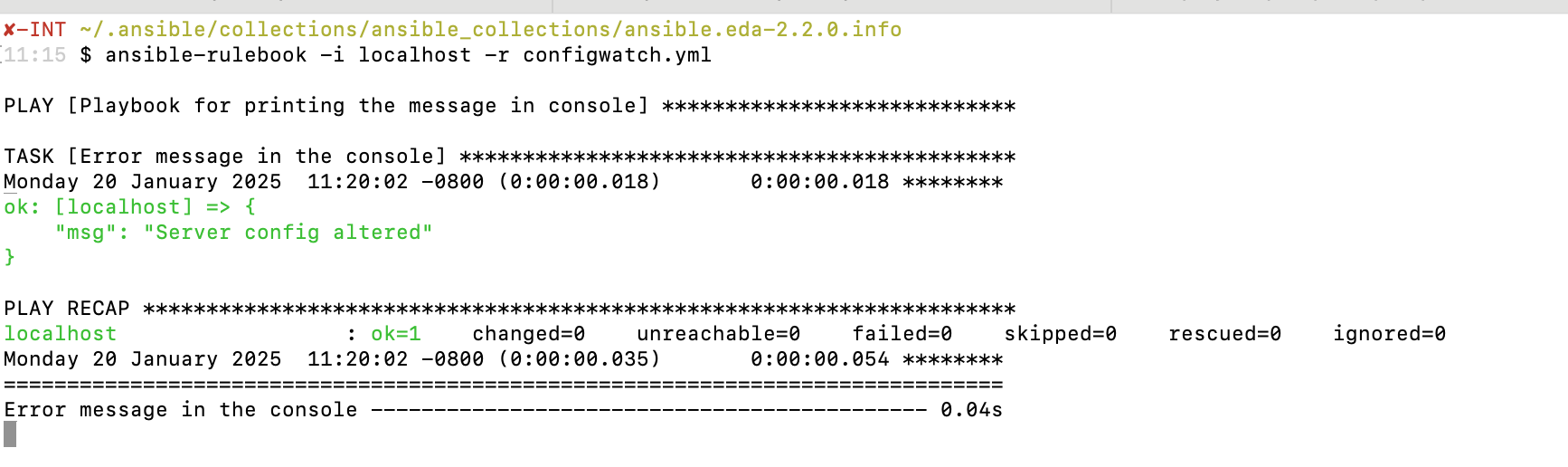
To monitor the Nginx configuration file for changes, execute the command ansible-rulebook -i localhost -r configwatch.yml, where -i localhost specifies the inventory as the local system, and -r configwatch.yml points to the rulebook file that defines the monitoring rules and actions. This command will initiate the monitoring process, enabling Ansible to continuously watch the specified Nginx configuration file for any modifications. When changes are detected, the rules in the configwatch.yml file will trigger the action to run the print-console-message.yaml playbook.
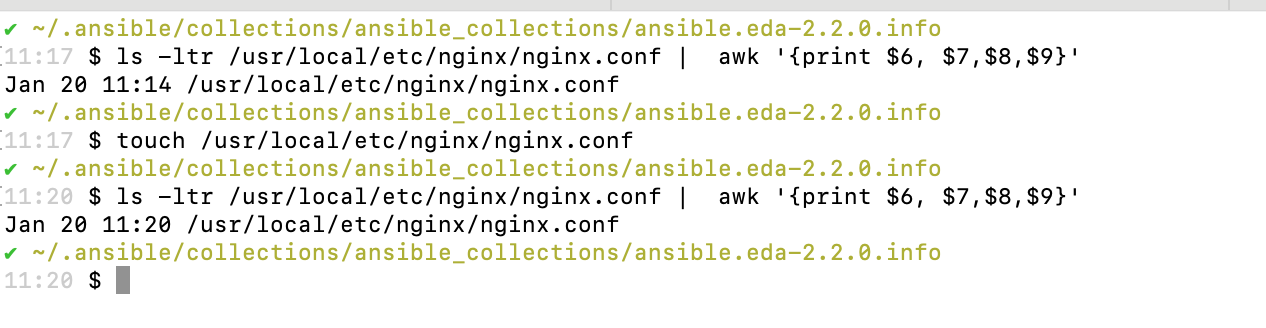
Check the last modified time of /usr/local/etc/nginx/nginx.conf by running the ls command.

Use the touch command to update the last modified timestamp, followed by the ls command to display the output in the console.
The output of the ansible-rulebook -i localhost -r configwatch.yml command, it detected the file timestamp modification change and triggered the corresponding action.
Benefits of Event-Driven Ansible for Configuration Monitoring
Event-driven Ansible simplifies configuration monitoring by instantly detecting changes and responding immediately. Organizations can extend the functionality to automatically fix issues without manual intervention, enhancing security by preventing unauthorized modifications. It also supports compliance by maintaining records and adhering to regulations while efficiently managing large and complex environments.
Use Cases
The Event-Driven Ansible File Watch module can serve as a security compliance tool by monitoring critical configuration files, such as SSH or firewall settings, to ensure they align with organizational policies. It can also act as a disaster recovery solution, automatically restoring corrupted or deleted configuration files from predefined backups. Additionally, it can be used as a multi-environment management tool, ensuring consistency across deployments by synchronizing configurations.
Conclusion
Event-driven Ansible is a reliable and flexible tool for monitoring configuration files in real time. It automatically detects, helping organizations keep systems secure and compliant. As systems become more complex, it offers a modern and easy-to-adapt way to manage configurations effectively.
Note: The views expressed on this blog are my own and do not necessarily reflect the views of Oracle.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments