Exploring Shadow DOM With Examples Using Cypress
In this blog, we'll delve into Shadow DOM and explore how Cypress can help us interact with components encapsulated within Shadow DOM with detailed examples.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe idea of componentization has completely changed how we design and maintain user interfaces in the field of web development. The advent of Shadow DOM is one of the pillars of this movement. Shadow DOM empowers developers to encapsulate styles, scripts, and markup within components, shielding them from the global scope and preventing unintended interference.
In this blog, we'll delve into the fascinating realm of Shadow DOM and explore how Cypress, a powerful end-to-end testing framework, can help us interact with components encapsulated within Shadow DOM with detailed examples.
Let's quickly review the definition of DOM before grasping the idea of Shadow DOM.
What Is DOM?
Document Object Model, or DOM for short, is a programming interface and illustration of a web page's structure that enables applications and scripts to dynamically access and modify a document's content, structure, and appearance. The DOM essentially acts as an abstraction of the document's layout and content, giving scripts a structured interface through which to interact with and alter the webpage.
When a web page is loaded, the browser creates a Document Object Model of the page. The HTML DOM model is constructed of a tree of objects.

Each branch of the tree ends in a node, and each node contains objects. DOM methods allow programmatic access to the tree. With them, you can change the document’s structure, style, or content. Nodes can also have event handlers attached to them. Once an event is triggered, the event handlers get executed.
Let us consider a very simple example of an HTML page:
<html lang="en">
<head>
<title>A simple web page</title>
</head>
<body>
<h1>Hello talet500</h1>
<p>How are you talent500</p>
</body>
</html>As mentioned in the above-mentioned definition, a logical tree of this HTML structure would look like this;

What Is Shadow DOM?
Shadow DOM is a feature of the DOM that allows developers to create a shadow tree, which is a separate DOM tree that is nested inside of the main DOM tree. The shadow tree is isolated from the main DOM tree, which means that its elements and styles cannot be accessed from the main DOM tree.
Let's build a firm understanding of Shadow DOM before moving on to the integration of Cypress with it. Shadow DOM is fundamentally a browser feature that makes it possible to build independent web components. In order to protect them from the styling and behavior of the rest of the document, these components may have their own encapsulated HTML, CSS, and JavaScript.
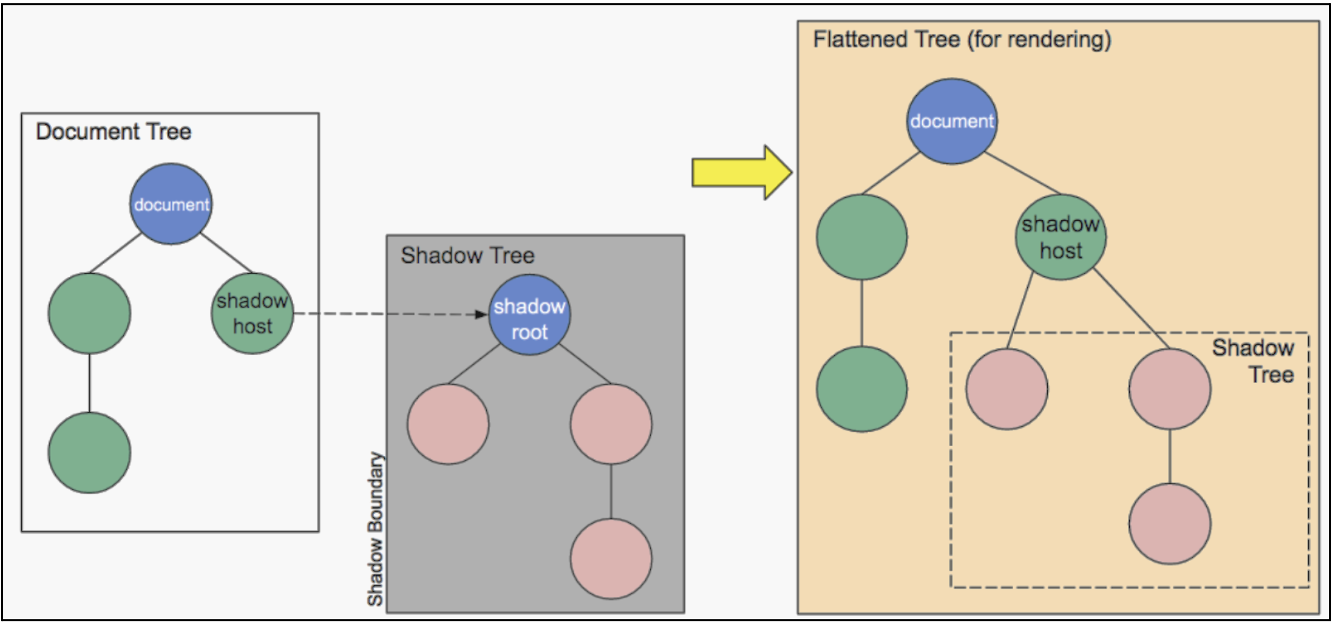
Sourced from Mozilla’s Shadow DOM documentation
Shadow DOM works by creating a boundary around a web component. This boundary separates the component's internals from the surrounding document. This isolation ensures that the styles and behaviors defined within the component do not affect or get affected by the styles and behavior of the parent document.
Benefits of Shadow DOM
Here are some key benefits of using Shadow DOM:
Encapsulation and Isolation: Shadow DOM allows web components to encapsulate their internal structure, styling, and behavior. This isolation prevents external styles and scripts from affecting the component's internals and vice versa. This ensures that the component's functionality remains consistent regardless of its context on a webpage.
Styling Encapsulation: With Shadow DOM, components can have their own scoped styles. This prevents global styles from unintentionally affecting the component's appearance. Developers can create components with predefined styles that won't interfere with the rest of the page's styling.
Avoiding Style Clashes: By encapsulating styles within the Shadow DOM, you reduce the risk of style clashes and conflicts between different components or between components and the surrounding page.
Shadow DOM Terminology To Be Aware Of
Shadow DOM: A web standard that enables encapsulation of a DOM subtree, along with its associated styles and functionality, inside a web component. It provides a separate scope for a component's internals, preventing external styles and scripts from affecting them.
Shadow Host: The element in the main DOM to which a Shadow DOM is attached. It serves as the entry point for the Shadow DOM's encapsulated content.
Shadow Tree: The DOM tree inside the Shadow DOM, separate from the main DOM. It contains the encapsulated elements and nodes defined within the Shadow DOM.
Shadow Boundary: The boundary that separates the Shadow DOM from the main DOM. It prevents styles and scripts from the main DOM from leaking into the Shadow DOM and vice versa.
Shadow Root: The root node of the Shadow DOM's internal tree. It's where encapsulated content is attached and contained. The Shadow Root can be accessed using the shadowRoot property of the Shadow Host element.
The Problem in Direct Accessing Shadow DOM Elements Using Cypress
Before explaining how we can handle the Shadow DOM element. Let’s first see what the problem is when we try to access the Shadow DOM elements using Cypress.
Use Case 1
Let me take an example of the site.
- Open the URL
- Enter Some Value in the Text Box, e.g., “Math”
- Search the entered data
- Verify that the URL contains the text ‘Math’
Let's inspect the text box. We can see we have a locator [id="input"] for the text box field.
In the below screenshot, we can see the text field (where we have to enter the data) is inside the Shadow DOM.
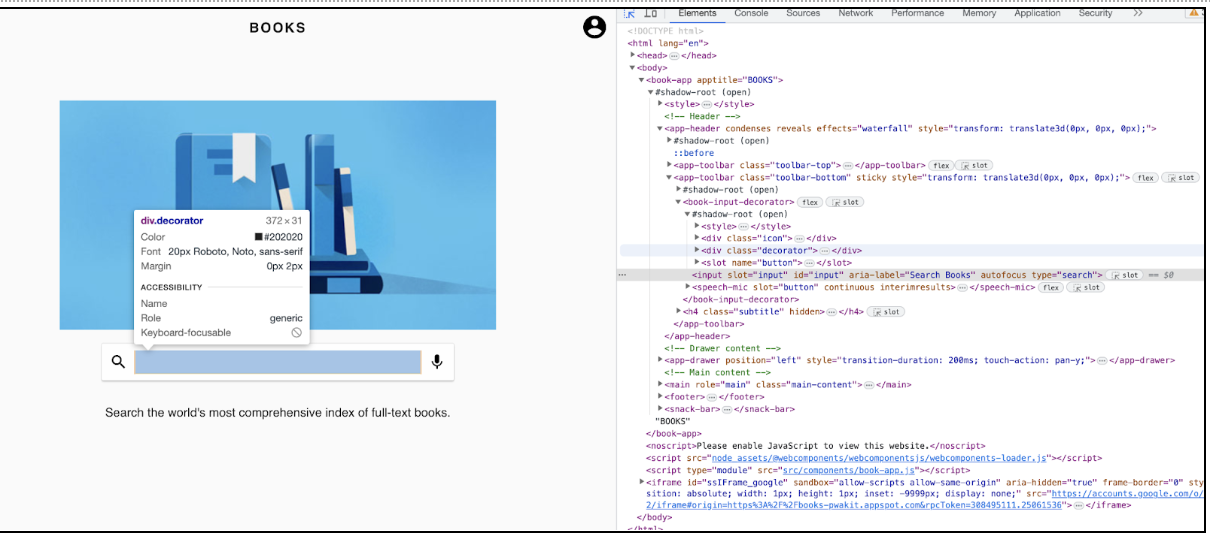
Let’s write Cypress code to enter data in this text field:
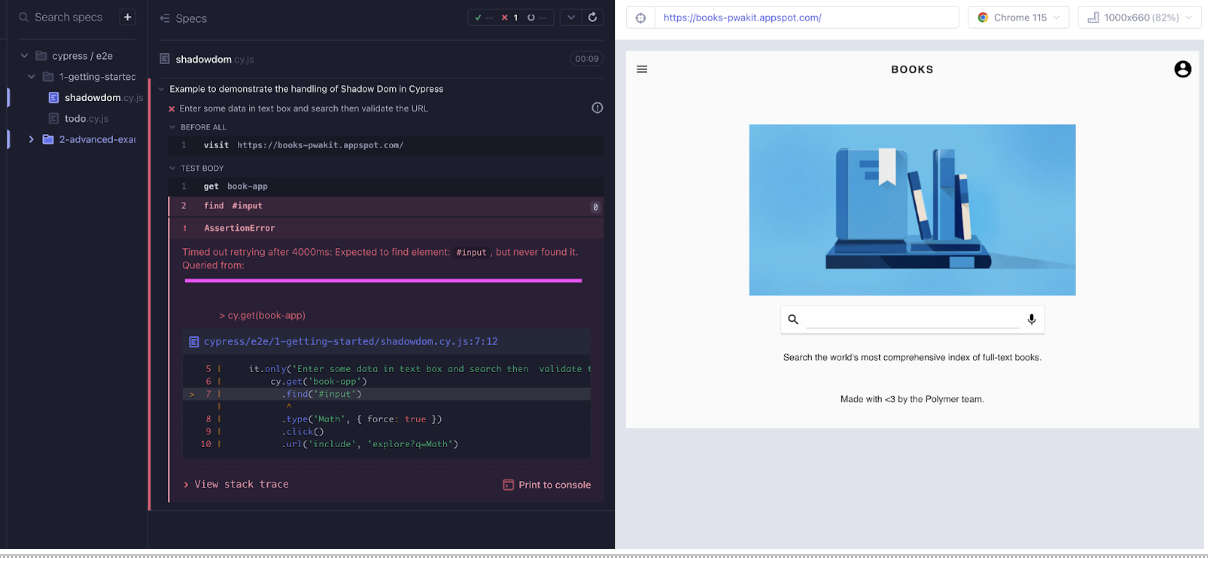
it('Enter some data in text box and search it then validate the URL', () => {
cy.get('book-app')
.find('#input')
.type('Math', { force: true })
.click()
.url('include', 'explore?q=Math')
}As we run the above code in the screenshot below, you can see the Error “Expected to find element: #input, but never found it. Queried from:”.
Use Case 2
Let's see another use case where the user is trying to enter the data in a field inside the Shadow DOM;
- Open the URL
- Enter Some Value in Text Box e.g. “Upload the File”
Let's inspect the text box. We can see we have a locator [type="text"]:
![locator [type="text"]](https://dz2cdn1.dzone.com/storage/temp/17132941-screenshot-2023-08-11-at-35351-pm.png)
Let’s write Cypress code to enter data in this text field:
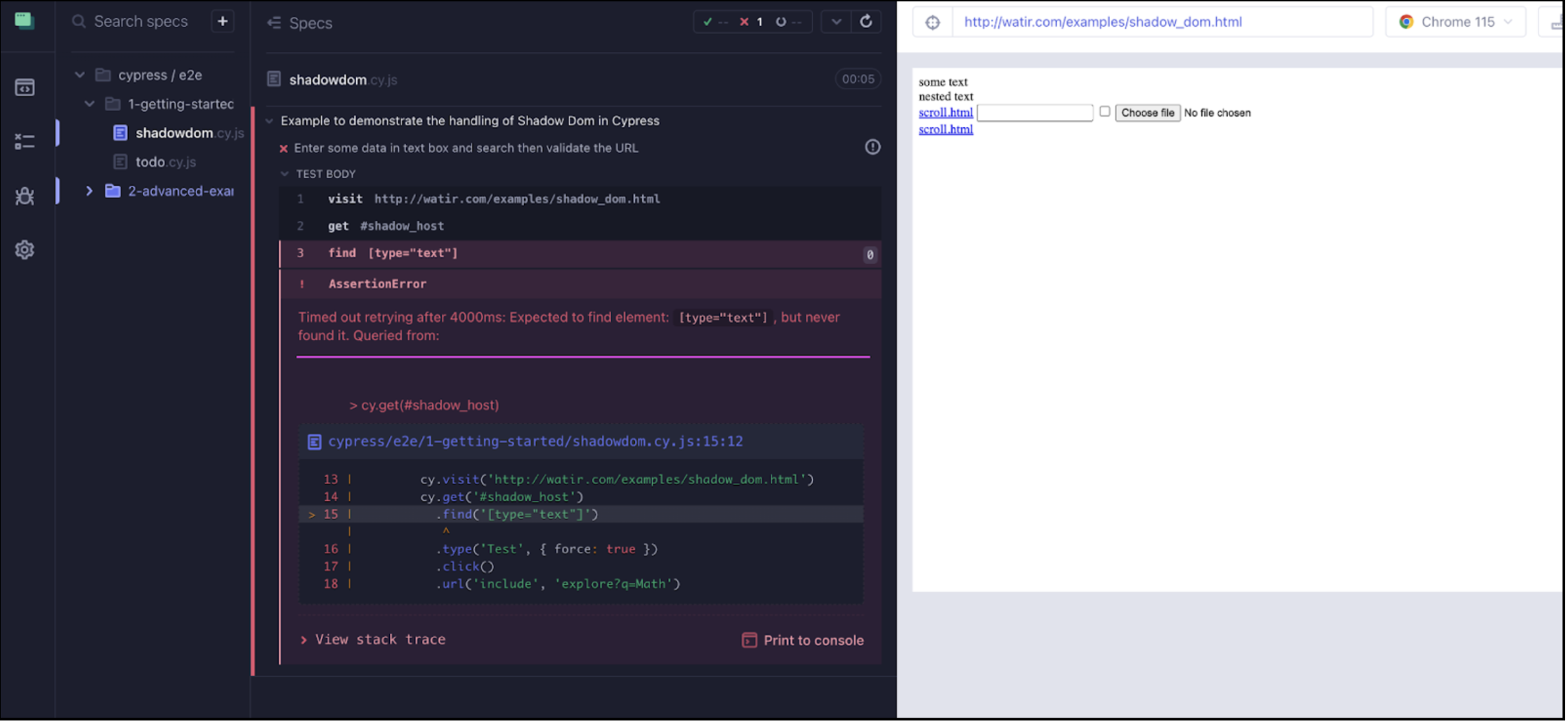
it('Enter some data in text box and search then validate the URL', () => {
cy.visit('http://watir.com/examples/shadow_dom.html')
cy.get('#shadow_host')
.find('[type="text"]')
.type('Upload the File', { force: true })
.click()
.url('include', 'explore?q=Math')
})As we run the above code in the screenshot below, you can see Error “Expected to find element: #input, but never found it. Queried from:” .
Solve Problem: Accessing Elements Inside Shadow DOM
We have seen it's not easy to access the element which is inside the Shadow DOM.
Cypress is a popular end-to-end testing framework that's commonly used for testing web applications. When dealing with Shadow DOM in your web application using Cypress, there are a few different approaches you can take.
Approach 1: Using the shadow() Command
The shadow() command allows you to access Shadow DOM elements by their CSS selector. For example, the following code will access the input element inside the Shadow DOM of the #my-element element:
Let me take an example of the site.
- Open the URL
- Enter Some Value in Text Box e.g., “Math”
- Search the entered data
- Verify the URL contains text ‘Math’
Let’s write Cypress code to enter data in this text field:
describe('Example Of How To Handle Shadow Dom in Cypress', () => {
before(() => {
cy.visit('https://books-pwakit.appspot.com/')
})
it('Enter some data in text box and search then validate the URL', () => {
cy.get('book-app')
.shadow()
.find('app-header')
.find('.toolbar-bottom')
.find('book-input-decorator')
.find('#input')
.type('Math', { force: true })
.click()
.url('contains', 'explore?q=Math')
})
})Code Walkthrough of Script Step by Step:
Describe Block: This is the outermost block that describes the test suite.
before() Hook: This hook runs before any test cases within the suite. It's used here to visit the specified URL before starting the tests.
it() Block: This block represents a single test case. The purpose of this test case is to enter data into a text box, search, and then validate the resulting URL.
Inside the test case:
cy.get('book-app'): This command attempts to select a book-app element on the webpage..shadow(): The.shadow()function is used to interact with Shadow DOM elements. It essentially allows you to traverse into the Shadow DOM of the selected element..find('app-header'): This command is used to find an element with the tag app-header within the Shadow DOM of the previously selected ‘book-app’ element..find('.toolbar-bottom'): Similar to the previous command, this command finds an element with the class toolbar-bottom within the ‘app-header’ element..find('book-input-decorator'): Again, this command searches for an element with the tag book-input-decorator within the previous element..find('#input'): This command targets an element with the ID input within the book-input-decorator element..type('Math'): It simulates typing the text "Math" into the selected input field..click(): This command simulates a click action on the same input field, which might trigger a search action..url('contains', 'explore?q=Math'): This asserts that the current URL should contain the substring 'explore?q=Math', indicating that the search was performed successfully.
Approach 2: Using the includeShadowDom Flag in Config
The ‘includeShadowDom’ config option tells Cypress to automatically traverse through Shadow DOM when searching for elements.
This flag tells Cypress to automatically traverse through Shadow DOM when you use the get() or find() commands. To use this flag, add the following line to your cypress.config.js file:
"includeShadowDom": true
cypress.config.js looks like attached below
const { defineConfig } = require("cypress");
module.exports = defineConfig({
"includeShadowDom": true,
e2e: {
setupNodeEvents(on, config) {
// implement node event listeners here
},
},
});Write Cypress code to enter data in this text field without shadow() command:
describe('Example Of How To Handle Shadow Dom in Cypress with Flag : "includeShadowDom": true', () => {
before(() => {
cy.visit('https://books-pwakit.appspot.com/')
})
it('Enter some data in text box and search then validate the URL', () => {
cy.get('book-app')
.find('app-header')
.find('.toolbar-bottom')
.find('book-input-decorator')
.find('#input')
.type('Math')
.click()
.url('contains', 'explore?q=Math')
})
})Wrapping Up
In this blog post, we have explored how to use Cypress to interact with Shadow DOM. We have looked at different ways to access elements inside the Shadow DOM: Using the shadow() command Using the includeShadowDom flag.URL.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments