Fix Active Directory Corrupted (NTDS ISAM Database Corruption Errors in Event Log)
Active Directory might seem simple but it's a very complex and delicate system. Follow this tutorial to fix active directory corruption errors in event log.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeActive Directory might seem simple but it’s a very complex and delicate system. Active Directory is the holder of all your policies, users, and schemas. Also, several applications depend on the system. To your dismay, on a fine day, you encounter the below issue while changing something in user details or a simple reset of password.
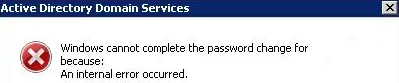
In such a case, the first thing to do is not to panic. Otherwise, you may end up changing stuff and applying fixes without carefully evaluating the situation and possibly making it worst.
The next thing is to get some clues about the reasons for such a situation. The first place to look for clues is the Event Viewer. For this, expand the Applications and Services Logs and then click on the Directory Services.
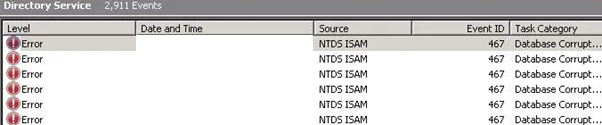
If you see the NTDS ISAM source with event ID 467, it means that the ntds.dit database is corrupt.
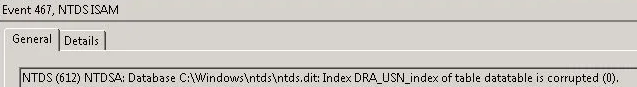
You may notice some other error events, which also refer to the same issue. These can be,
- NTDS Replication Event ID: 1084 Replication Error
- NTDS Replication Event ID: 2108 Replication Error
- NTDS General Internal Event ID: 1173 Processing Warning
Now you need to look for solutions before any more damage occurs. There are two solutions, depending on your architecture. If you have just one Active Directory, you can try a repair or restore from backup. If you have more than one Domain Controller, you can rebuild the faulty server. Let’s explore both solutions.
1. Repair Active Directory by Using ESENTUTL
Restart the faulty domain controller in Directory Restore Mode (DSRM). There are different ways to do this. Importunately, you need to remember your DSRM password, which was created when you promoted the server as a domain controller or when you have set up the forest in the beginning.
Note: If you don’t have the DSRM password and you only have one domain controller, then you would need to rebuild the forest from scratch, join the computer to the new domain and set up everything from the beginning.
- Option 1 – F8
Reboot the machine and press F8 during start-up and wait for the prompt to select DSRM. Of course, you would either need physical or console access to perform this. - Option 2 – MSConfig
Open MSConfig.msc, go to the Boot tab, click Safeboot, and ActiveDirectoryRepair. - Option 3 - Command-Line
From a command-line window type, the bcdedit /set safeboot dsrepair
Once the server has rebooted in DSRM mode, click the Start button and open a command-line window by using the cmd.
It is important to take a backup of the database by saving a copy of the file elsewhere. For example, in c:\scripts.
You need to run an integrity check of the database first. This can be done by executing the following command:
esentutl /g c:\windows\ntds\ntds.dit
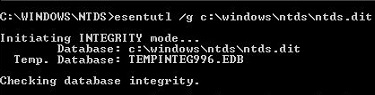
If the result shows ‘CORRUPTED’, then you need to run the repair switch and try to repair the database. This can be done by the example below:
esentutl /p c:\windows\ntds\ntds.dit
After the operation is complete, you will need to clear the log files, if exist, from C:\Windows\ntds folder.
After this is complete, remove the DSRM option and reboot the server. If all goes well, the issue should be resolved.
Rebuilding the Domain Controller In Case of More Than One AD Servers
The first thing is to remove the faulty Active Directory server from your forest by switching it off. The next step is to run DCPromo /ForceRemoval. If this is not executed from the Active Directory users and computers, you can remove the server by right-clicking on the server and then click on Delete.
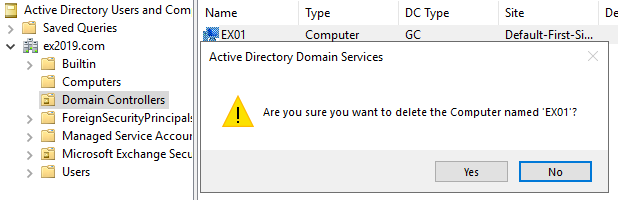
The second step is to seize the roles from the faulty domain controller if any roles were installed on it. There are five FSMO roles,
- Schema Master (Forest)
- Domain Naming Master (Forest)
- Infrastructure Master (Domain)
- Relative ID (RID) Master (Domain)
- PDC Emulator (Domain)
Now, when we execute the dcpromo /forceremoval command, this leaves the FSMO roles of the faulty server in an invalid state, until a new owner has been assigned.
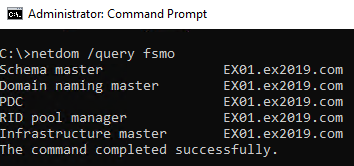
On a healthy domain controller, run netdom /query fsmo to get the current owner of each role.
- Type ntdsutil and press Enter
- Type roles and press Enter
- Type connections and press Enter
- Type connect to server <computer name> and press Enter. The computer name is the domain controller, where you are transferring the roles.
- Type quit and press Enter
Now, to seize the roles, you need to type the following:
- seize schema master and press Enter
- seize naming master and press Enter
- seize rid master and press Enter
- seize pdc and press Enter
- seize infrastructure master and press Enter
- Finally, when ready, enter quit and press Enter
Final Thoughts and Considerations
It is highly suggested to have more than one Active Directory server in your infrastructure for high availability and disaster recovery. Take a full backup, by using an application that is application-aware of the whole VM or physical server. Although there is nothing wrong with having a physical server, it is recommended to implement a virtual environment such as VMWare or Hyper-V. It’s better to split the FSMO owners between domain controllers. The last suggestion is to leave the Active Directory servers as clean as possible so that if something like this happens and you need to rebuild the server, you do not need to worry about moving other services.
As discussed, some applications such as Exchange server will be impacted which depends on the Active Directory. In case the server is rescued, there might not be so many issues. However, if the Domain Controller was the only one and reconstructed, Exchange will fail to work as it’s a different domain with different GUID for the user and other things. In both cases, you will end up having issues with your Exchange Server. Since it’s dependent on the Active Directory, you need to rebuild the Exchange Server, with a lot of issues to restore the data. You have already passed through the trouble and long hours to reconstruct a new Active Directory and to work on the Exchange Server as well, it would be a massive overhead in the situation.
In such cases, Stellar Repair for Exchange can come in handy for a painless and fast resolution to the problem. With the application, you can attach the EDB file and simply export all the mailboxes directly to the live database of your newly created Exchange Server. It’s the ideal companion application for any Exchange Server Admin as it requires less effort and exports all the data with no repercussions.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments