Generating Laplace Distributed Random Values
Although it's simple to generate Laplacian random values, the Laplace distribution is not always one of the built-in options for random number generation libraries.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeDifferential privacy adds Laplace-distributed random noise to data to protect individual privacy. (More on that here.) Although it's simple to generate Laplacian random values, the Laplace distribution is not always one of the built-in options for random number generation libraries.
The Laplace distribution with scale β has density:
The Laplace distribution is also called the double exponential because it looks like two mirror-image exponential distributions glued together.
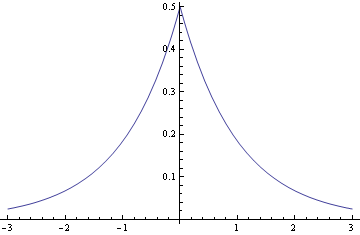
Note that the scale β is not the standard deviation. The standard deviation is √2 β.
To generate samples from a Laplace distribution with scale β, generate two independent exponential samples with mean β and return their difference.
If you don't have an API for generating exponential random values, generate uniform random values and return the negative of the log. That will produce exponential values with mean 1. To make random values with mean β, just multiply the results by β.
If you want to generate Laplace values in Python, you could simply use the laplace function in scipy.stats. But I'll write a generator from scratch just to show what you might do in another environment where you didn't have exponential or Laplace generators.
from math import log
from random import random
def exp_sample(mean):
return -mean*log(random())
def laplace(scale):
e1 = exp_sample(scale)
e2 = exp_sample(scale)
return e1 - e2
Related: Stand-alone numerical code is useful when you need a few common mathematical functions but are in an environment that doesn't provide them or when you want to avoid adding a library to your project.
Published at DZone with permission of John Cook, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments