Geo What? A Quick Introduction to Geo-Distributed Apps
This is the first post documenting an experience building a geo-distributed app in Java from scratch. Follow to learn wins, tips, tricks, struggles, and more.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeHave you heard of geo-distributed apps? According to my statistics around 50% of us haven’t!
Microsoft defines a geo-distributed app as an app that spans multiple geographic locations for high availability and resiliency. "Geo-distributed" is a relatively new term, coined around the time when many of us jumped on the cloud bandwagon and started building cloud-native apps like crazy.
Dealing with geo-distributed apps is now my daily duty. While I reside on the data layer side of things in my work with YugabyteDB, I'm a proponent of the "eat your own dog food" approach! Many developers use YugabyteDB as the database component in geo-distributed apps. However, the database is just a piece of the puzzle. There are many more layers to take care of: middleware, backend, API, networking, frontend, and global cloud load balancer, to name just a few.
This article is the first in my journal, where I'll be documenting my experience of building a geo-distributed app in Java from scratch. I know it’s going to be tough, but it’s going to be a completely open and uncensored story. It will include wins, tips and tricks, struggles, and things to avoid.
This story may last a few months, or might even take a bit longer. The one thing I know for sure is that I'll finish the project much faster than Stephen King who worked on the Dark Tower series for 34 years!
So if you’re with me, then, as the pirates used to say: “All Hand Hoy!” which means, “Everyone on deck!"

Clarifying the Definition of Geo-Distributed Apps
Personally, I would expand Microsoft’s definition of geo-distributed apps by adding a couple of extra words: an app that spans multiple geographic locations for high availability, resiliency, compliance, and performance. Now that’s too many buzzwords, right? So, let’s break it into pieces because, frankly, the definition is accurate and concise if you know the full context.
The high-availability/resiliency characteristic implies that the app can withstand all types of cloud outages, including major incidents. A typical cloud environment comes with abundant resources and services, but you shouldn’t expect all those resources to be available 100% of the time. Starting in 2011, AWS alone had a major outage at least once a year. It took an average of four hours to recover. Minor outages happen all the time. The purpose of geo-distributed apps is to remain available and resilient even in the event of major cloud incidents.
So, what does compliance mean in relation to the geo-distributed apps? This one is simpler. Remember GDPR and similar data residency requirements? That’s about it. Suppose you create an app for US-based users, and it becomes a big success. The next milestone is to offer the same service in Europe. Is your architecture ready for that? Or do you need to postpone the launch because the app is not yet GDPR-ready? With a geo-distributed app it happens naturally and as quickly as you like, as long as those apps are capable of keeping users’ personal data in the countries of their origin.
Finally, we’ve got to the performance characteristic of the apps. Let’s use some visuals for this:
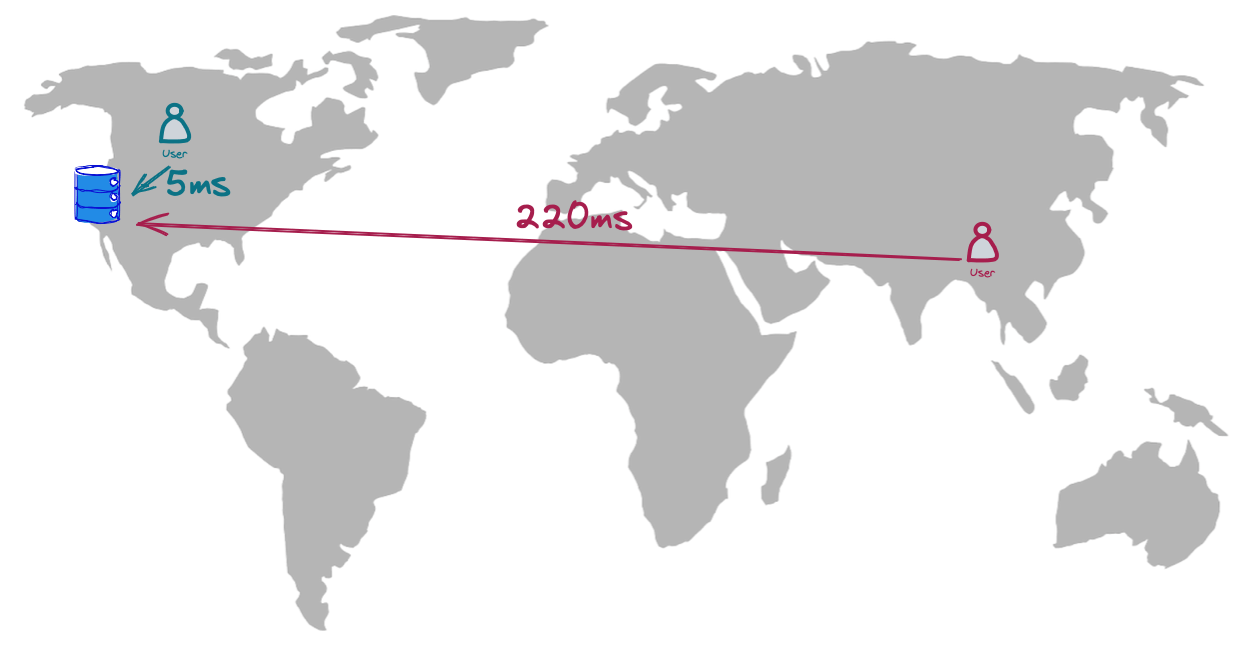
Suppose an app’s data resides in a single cloud region, like the US West. Users who live nearby can experience a latency as low as 5ms (Google Cloud strives to deliver 5ms roundtrip latencies between availability zones within a region). However, if the user interacts with the app from South Asia, latency might be 40x higher (~220ms in Google Cloud because the traffic needs to travel through cables under the ocean surface).
The geo-distributed app’s promise and requirement are to compete against the laws of physics and brutal reality (such as the cables in the ocean) in a way that allows the user from South Asia to experience the same (or comparable) latency as the user from the US:
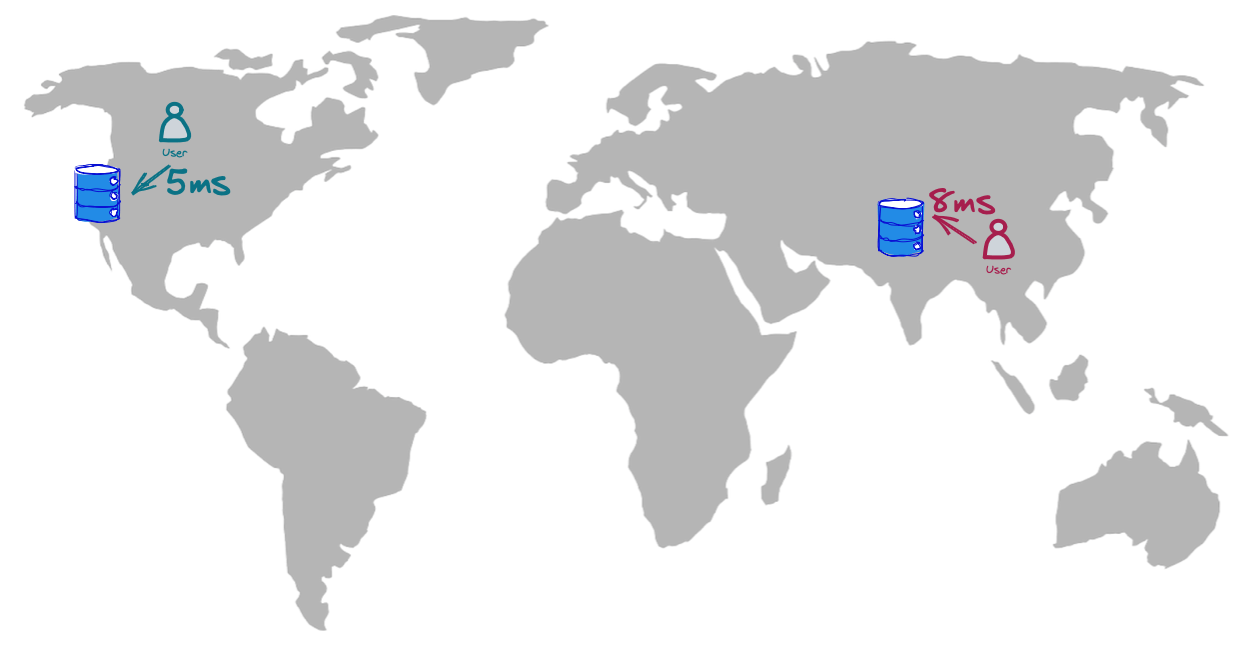
In the next articles, I’ll dive into how to drop latency from 220ms to 8ms for folks in South Asia. In the meantime, as the picture shows, let me add a database instance to that region, which is a bare minimum.
With those examples in place, the definition of a geo-distributed app should make more sense to you:
A geo-distributed app is an app that spans multiple geographic locations for high availability, resiliency, compliance and performance.
Still confused or do you have any questions on the above? Nudge me in the comments and we’ll get things sorted together!
What’s on the Horizon?
Alright, that’s enough for my opening chapter. What do we have on the horizon?
In the next chapters, I’ll introduce you to the typical building blocks of geo-distributed apps (aka architecture) and share the results of the prototype I’ve developed over the last four days. The prototype is promising, but, arrrgghh, the performance sucks, and the UI is as ugly as...
Published at DZone with permission of Denis Magda. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments