Getting Started With Kubernetes 1.4 using Spring Boot and Couchbase
Here's a look at containerized microservices using Kubernetes to host a Java Spring Boot application, accessing Couchbase with the newest Kubernetes platform.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeKubernetes 1.4 was released earlier this week. Read the blog announcement and CHANGELOG. There are quite a few new features in this release, but the key ones that I'm excited about are:
- Install Kubernetes using the
kubeadmcommand. This is in addition to the usual mechanism of downloading from https://github.com/kubernetes/kubernetes/releases. Thekubeadm initandkubeadm joincommands look very similar todocker swarm initanddocker swarm joinfor Docker Swarm Mode. - Federated Replica Sets.
- ScheduledJob allows to run batch jobs at regular intervals.
- Constraining pods to a node and affinity and anti-affinity of pods.
- Priority scheduling of pods.
- Nice looking Kubernetes Dashboard (more on this later).
This blog will show how to:
- Create a Kubernetes cluster using Amazon Web Services.
- Create a Couchbase service.
- Run a Spring Boot application that stores a JSON document in Couchbase.
All the resource description files in this blog are at github.com/arun-gupta/kubernetes-java-sample/tree/master/maven.
Start the Kubernetes Cluster
Download binary and extract. Include kubernetes/cluster in PATH. Start a two-node Kubernetes cluster:
NUM_NODES=2 NODE_SIZE=m3.medium KUBERNETES_PROVIDER=aws kube-up.shThe log will be shown as:
... Starting cluster in us-west-2a using provider aws
... calling verify-prereqs
... calling kube-up
Starting cluster using os distro: jessie
Uploading to Amazon S3
+++ Staging server tars to S3 Storage: kubernetes-staging-0eaf81fbc51209dd47c13b6d8b424149/devel
upload: ../../../../../var/folders/81/ttv4n16x7p390cttrm_675y00000gn/T/kubernetes.XXXXXX.bCmvLbtK/s3/bootstrap-script to s3://kubernetes-staging-0eaf81fbc51209dd47c13b6d8b424149/devel/bootstrap-script
Uploaded server tars:
SERVER_BINARY_TAR_URL: https://s3.amazonaws.com/kubernetes-staging-0eaf81fbc51209dd47c13b6d8b424149/devel/kubernetes-server-linux-amd64.tar.gz
SALT_TAR_URL: https://s3.amazonaws.com/kubernetes-staging-0eaf81fbc51209dd47c13b6d8b424149/devel/kubernetes-salt.tar.gz
BOOTSTRAP_SCRIPT_URL: https://s3.amazonaws.com/kubernetes-staging-0eaf81fbc51209dd47c13b6d8b424149/devel/bootstrap-script
INSTANCEPROFILE arn:aws:iam::598307997273:instance-profile/kubernetes-master 2016-07-29T15:13:35Z AIPAJF3XKLNKOXOTQOCT4 kubernetes-master /
ROLES arn:aws:iam::598307997273:role/kubernetes-master 2016-07-29T15:13:33Z / AROAI3Q2KFBD5PCKRXCRM kubernetes-master
ASSUMEROLEPOLICYDOCUMENT 2012-10-17
STATEMENT sts:AssumeRole Allow
PRINCIPAL ec2.amazonaws.com
INSTANCEPROFILE arn:aws:iam::598307997273:instance-profile/kubernetes-minion 2016-07-29T15:13:39Z AIPAIYSH5DJA4UPQIP4BE kubernetes-minion /
ROLES arn:aws:iam::598307997273:role/kubernetes-minion 2016-07-29T15:13:37Z / AROAIQ57MPQYSHRPQCT2Q kubernetes-minion
ASSUMEROLEPOLICYDOCUMENT 2012-10-17
STATEMENT sts:AssumeRole Allow
PRINCIPAL ec2.amazonaws.com
Using SSH key with (AWS) fingerprint: SHA256:dX/5wpWuUxYar2NFuGwiZuRiydiZCyx4DGoZ5/jL/j8
Creating vpc.
Adding tag to vpc-6b5b4b0f: Name=kubernetes-vpc
Adding tag to vpc-6b5b4b0f: KubernetesCluster=kubernetes
Using VPC vpc-6b5b4b0f
Adding tag to dopt-8fe770eb: Name=kubernetes-dhcp-option-set
Adding tag to dopt-8fe770eb: KubernetesCluster=kubernetes
Using DHCP option set dopt-8fe770eb
Creating subnet.
Adding tag to subnet-623a0206: KubernetesCluster=kubernetes
Using subnet subnet-623a0206
Creating Internet Gateway.
Using Internet Gateway igw-251eab41
Associating route table.
Creating route table
Adding tag to rtb-d43cedb3: KubernetesCluster=kubernetes
Associating route table rtb-d43cedb3 to subnet subnet-623a0206
Adding route to route table rtb-d43cedb3
Using Route Table rtb-d43cedb3
Creating master security group.
Creating security group kubernetes-master-kubernetes.
Adding tag to sg-d20ca0ab: KubernetesCluster=kubernetes
Creating minion security group.
Creating security group kubernetes-minion-kubernetes.
Adding tag to sg-cd0ca0b4: KubernetesCluster=kubernetes
Using master security group: kubernetes-master-kubernetes sg-d20ca0ab
Using minion security group: kubernetes-minion-kubernetes sg-cd0ca0b4
Creating master disk: size 20GB, type gp2
Adding tag to vol-99a30b11: Name=kubernetes-master-pd
Adding tag to vol-99a30b11: KubernetesCluster=kubernetes
Allocated Elastic IP for master: 52.40.9.27
Adding tag to vol-99a30b11: kubernetes.io/master-ip=52.40.9.27
Generating certs for alternate-names: IP:52.40.9.27,IP:172.20.0.9,IP:10.0.0.1,DNS:kubernetes,DNS:kubernetes.default,DNS:kubernetes.default.svc,DNS:kubernetes.default.svc.cluster.local,DNS:kubernetes-master
Starting Master
Adding tag to i-f95bdae1: Name=kubernetes-master
Adding tag to i-f95bdae1: Role=kubernetes-master
Adding tag to i-f95bdae1: KubernetesCluster=kubernetes
Waiting for master to be ready
Attempt 1 to check for master nodeWaiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be running (currently pending)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be running (currently pending)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
[master running]
Attaching IP 52.40.9.27 to instance i-f95bdae1
Attaching persistent data volume (vol-99a30b11) to master
2016-09-29T05:14:28.098Z /dev/sdb i-f95bdae1 attaching vol-99a30b11
cluster "aws_kubernetes" set.
user "aws_kubernetes" set.
context "aws_kubernetes" set.
switched to context "aws_kubernetes".
user "aws_kubernetes-basic-auth" set.
Wrote config for aws_kubernetes to /Users/arungupta/.kube/config
Creating minion configuration
Creating autoscaling group
0 minions started; waiting
0 minions started; waiting
0 minions started; waiting
0 minions started; waiting
2 minions started; ready
Waiting for cluster initialization.
This will continually check to see if the API for kubernetes is reachable.
This might loop forever if there was some uncaught error during start
up.
..............................................................................................................................................................................................................................Kubernetes cluster created.
Sanity checking cluster...
Attempt 1 to check Docker on node @ 54.70.225.33 ...working
Attempt 1 to check Docker on node @ 54.71.36.48 ...working
Kubernetes cluster is running. The master is running at:
https://52.40.9.27
The user name and password to use is located in /Users/arungupta/.kube/config.
... calling validate-cluster
Waiting for 2 ready nodes. 0 ready nodes, 0 registered. Retrying.
Waiting for 2 ready nodes. 0 ready nodes, 0 registered. Retrying.
Waiting for 2 ready nodes. 0 ready nodes, 0 registered. Retrying.
Waiting for 2 ready nodes. 0 ready nodes, 2 registered. Retrying.
Waiting for 2 ready nodes. 0 ready nodes, 2 registered. Retrying.
Found 2 node(s).
NAME STATUS AGE
ip-172-20-0-111.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready 39s
ip-172-20-0-112.us-west-2.compute.internal Ready 42s
Validate output:
NAME STATUS MESSAGE ERROR
scheduler Healthy ok
controller-manager Healthy ok
etcd-0 Healthy {"health": "true"}
etcd-1 Healthy {"health": "true"}
Cluster validation succeeded
Done, listing cluster services:
Kubernetes master is running at https://52.40.9.27
Elasticsearch is running at https://52.40.9.27/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/elasticsearch-logging
Heapster is running at https://52.40.9.27/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/heapster
Kibana is running at https://52.40.9.27/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/kibana-logging
KubeDNS is running at https://52.40.9.27/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/kube-dns
kubernetes-dashboard is running at https://52.40.9.27/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/kubernetes-dashboard
Grafana is running at https://52.40.9.27/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/monitoring-grafana
InfluxDB is running at https://52.40.9.27/api/v1/proxy/namespaces/kube-system/services/monitoring-influxdb
To further debug and diagnose cluster problems, use 'kubectl cluster-info dump'.This shows that the Kubernetes cluster has started successfully.
Deploy Couchbase
Create a Couchbase service and replication controller:
kubectl.sh create -f couchbase-service.yml
service "couchbase-service" created
replicationcontroller "couchbase-rc" createdThe configuration file is here. This creates a Couchbase service and the backing replication controller. The name of the service is couchbase-service. This will be used later by the Spring Boot application to communicate with the database. Check the status of pods:
kubectl.sh get -w pods
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
couchbase-rc-gu9gl 0/1 ContainerCreating 0 6s
NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE
couchbase-rc-gu9gl 1/1 Running 0 2m
Note how the pod status changes from ContainerCreating to Running. The image is downloaded and started in the meanwhile.
Run Spring Boot
Run the application:
kubectl.sh create -f bootiful-couchbase.yml
pod "bootiful-couchbase" createdThe configuration file is here. In this service, COUCHBASE_URI environment variable value is set to couchbase-service. This is the service name created earlier. Docker image used for this service is arungupta/bootiful-couchbase and is created using the fabric8-maven-plugin as shown here. Specifically, the command for the Docker image is:
java -Dspring.couchbase.bootstrap-hosts=$COUCHBASE_URI -jar /maven/${project.artifactId}.jarThis ensures that the COUCHBASE_URI environment variable is overriding spring.couchbase.bootstrap-hosts property as defined in application.properties in the Spring Boot application. Get the logs:
kubectl.sh logs -f bootiful-couchbase
. ____ _ __ _ _
/\\ / ___'_ __ _ _(_)_ __ __ _ \ \ \ \
( ( )\___ | '_ | '_| | '_ \/ _` | \ \ \ \
\\/ ___)| |_)| | | | | || (_| | ) ) ) )
' |____| .__|_| |_|_| |_\__, | / / / /
=========|_|==============|___/=/_/_/_/
:: Spring Boot :: (v1.4.0.RELEASE)
2016-09-29 05:37:29.227 INFO 5 --- [ main] org.example.webapp.Application : Starting Application v1.0-SNAPSHOT on bootiful-couchbase with PID 5 (/maven/bootiful-couchbase.jar started by root in /)
2016-09-29 05:37:29.259 INFO 5 --- [ main] org.example.webapp.Application : No active profile set, falling back to default profiles: default
2016-09-29 05:37:29.696 INFO 5 --- [ main] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Refreshing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4ccabbaa: startup date [Thu Sep 29 05:37:29 UTC 2016]; root of context hierarchy
2016-09-29 05:37:34.375 INFO 5 --- [ main] c.c.client.core.env.CoreEnvironment : ioPoolSize is less than 3 (1), setting to: 3
2016-09-29 05:37:34.376 INFO 5 --- [ main] c.c.client.core.env.CoreEnvironment : computationPoolSize is less than 3 (1), setting to: 3
2016-09-29 05:37:35.026 INFO 5 --- [ main] com.couchbase.client.core.CouchbaseCore : CouchbaseEnvironment: {sslEnabled=false, sslKeystoreFile='null', sslKeystorePassword='null', queryEnabled=false, queryPort=8093, bootstrapHttpEnabled=true, bootstrapCarrierEnabled=true, bootstrapHttpDirectPort=8091, bootstrapHttpSslPort=18091, bootstrapCarrierDirectPort=11210, bootstrapCarrierSslPort=11207, ioPoolSize=3, computationPoolSize=3, responseBufferSize=16384, requestBufferSize=16384, kvServiceEndpoints=1, viewServiceEndpoints=1, queryServiceEndpoints=1, searchServiceEndpoints=1, ioPool=NioEventLoopGroup, coreScheduler=CoreScheduler, eventBus=DefaultEventBus, packageNameAndVersion=couchbase-java-client/2.2.8 (git: 2.2.8, core: 1.2.9), dcpEnabled=false, retryStrategy=BestEffort, maxRequestLifetime=75000, retryDelay=ExponentialDelay{growBy 1.0 MICROSECONDS, powers of 2; lower=100, upper=100000}, reconnectDelay=ExponentialDelay{growBy 1.0 MILLISECONDS, powers of 2; lower=32, upper=4096}, observeIntervalDelay=ExponentialDelay{growBy 1.0 MICROSECONDS, powers of 2; lower=10, upper=100000}, keepAliveInterval=30000, autoreleaseAfter=2000, bufferPoolingEnabled=true, tcpNodelayEnabled=true, mutationTokensEnabled=false, socketConnectTimeout=1000, dcpConnectionBufferSize=20971520, dcpConnectionBufferAckThreshold=0.2, dcpConnectionName=dcp/core-io, callbacksOnIoPool=false, queryTimeout=7500, viewTimeout=7500, kvTimeout=2500, connectTimeout=5000, disconnectTimeout=25000, dnsSrvEnabled=false}
2016-09-29 05:37:36.063 INFO 5 --- [ cb-io-1-1] com.couchbase.client.core.node.Node : Connected to Node couchbase-service
2016-09-29 05:37:36.256 INFO 5 --- [ cb-io-1-1] com.couchbase.client.core.node.Node : Disconnected from Node couchbase-service
2016-09-29 05:37:37.727 INFO 5 --- [ cb-io-1-2] com.couchbase.client.core.node.Node : Connected to Node couchbase-service
2016-09-29 05:37:38.316 INFO 5 --- [-computations-3] c.c.c.core.config.ConfigurationProvider : Opened bucket books
2016-09-29 05:37:40.655 INFO 5 --- [ main] o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter : Registering beans for JMX exposure on startup
Book{isbn=978-1-4919-1889-0, name=Minecraft Modding with Forge, cost=29.99}
2016-09-29 05:37:41.497 INFO 5 --- [ main] org.example.webapp.Application : Started Application in 14.64 seconds (JVM running for 16.631)
2016-09-29 05:37:41.514 INFO 5 --- [ Thread-5] s.c.a.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext : Closing org.springframework.context.annotation.AnnotationConfigApplicationContext@4ccabbaa: startup date [Thu Sep 29 05:37:29 UTC 2016]; root of context hierarchy
2016-09-29 05:37:41.528 INFO 5 --- [ Thread-5] o.s.j.e.a.AnnotationMBeanExporter : Unregistering JMX-exposed beans on shutdown
2016-09-29 05:37:41.577 INFO 5 --- [ cb-io-1-2] com.couchbase.client.core.node.Node : Disconnected from Node couchbase-service
2016-09-29 05:37:41.578 INFO 5 --- [ Thread-5] c.c.c.core.config.ConfigurationProvider : Closed bucket booksThe main output statement to look in this is
Book{isbn=978-1-4919-1889-0, name=Minecraft Modding with Forge, cost=29.99}This indicates that the JSON document is upserted (either inserted or updated) in the Couchbase database.
Kubernetes Dashboard
Kubernetes Dashboard is looking more comprehensive and claimed to have 90% parity with the CLI. Use the kubectl.sh config view command to view the configuration information about the cluster. It looks like:
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: REDACTED
server: https://52.40.9.27
name: aws_kubernetes
contexts:
- context:
cluster: aws_kubernetes
user: aws_kubernetes
name: aws_kubernetes
current-context: aws_kubernetes
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: aws_kubernetes
user:
client-certificate-data: REDACTED
client-key-data: REDACTED
token: 3GuTCLvFnINHed9dWICICidlrSv8C0kg
- name: aws_kubernetes-basic-auth
user:
password: 8pxC121Oj7kN0nCa
username: adminThe clusters.cluster.server property value shows the location of Kubernetes master. The users property shows two users that can be used to access the dashboard. The second one uses basic authentication, so copy the username and password property value. In our case, the Dashboard UI is accessible at https://52.40.9.27/ui. 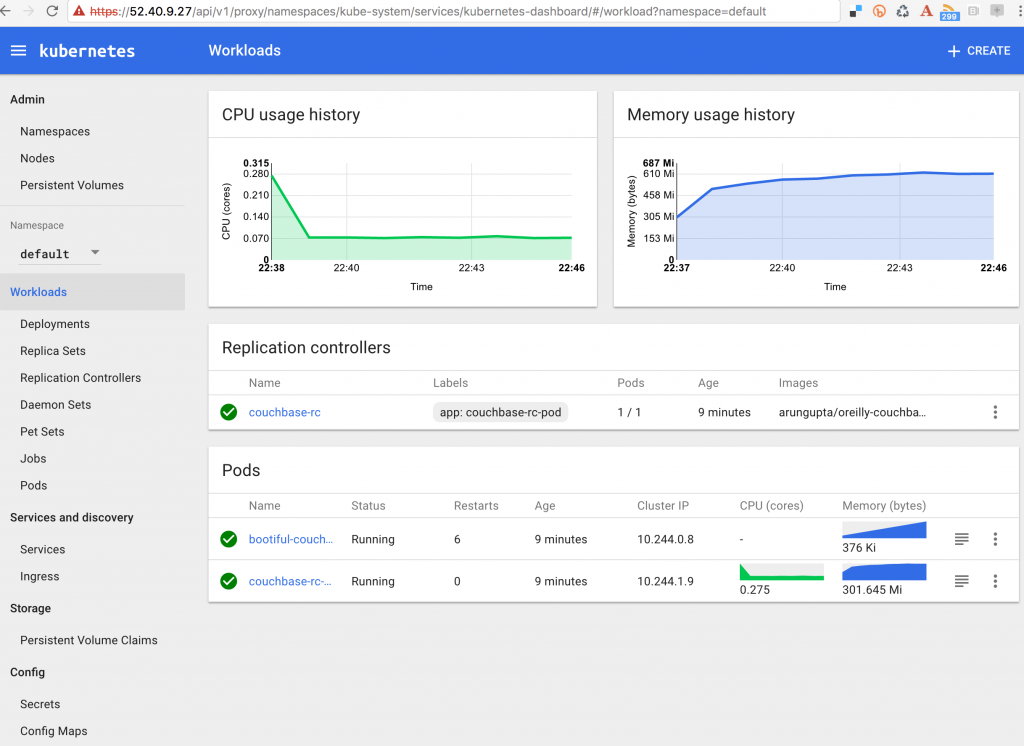
All the Kubernetes resources can be easily seen in this fancy dashboard.
Shutdown Kubernetes Cluster
Finally, shut down the Kubernetes cluster:
kube-down.sh
Bringing down cluster using provider: aws
Deleting instances in VPC: vpc-6b5b4b0f
Deleting auto-scaling group: kubernetes-minion-group-us-west-2a
Deleting auto-scaling launch configuration: kubernetes-minion-group-us-west-2a
Deleting auto-scaling group: kubernetes-minion-group-us-west-2a
Waiting for instances to be deleted
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
Waiting for instance i-f95bdae1 to be terminated (currently shutting-down)
Sleeping for 3 seconds...
All instances deleted
Releasing Elastic IP: 52.40.9.27
Deleting volume vol-99a30b11
Cleaning up resources in VPC: vpc-6b5b4b0f
Cleaning up security group: sg-cd0ca0b4
Cleaning up security group: sg-d20ca0ab
Deleting security group: sg-cd0ca0b4
Deleting security group: sg-d20ca0ab
Deleting VPC: vpc-6b5b4b0f
DoneCheck out couchbase.com/containers, which provides more details about running Couchbase using different orchestration frameworks.
Related Refcard:
Published at DZone with permission of Arun Gupta, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments