HLS Streaming With AVKit and Swift UI for iOS and tvOS
Upon reading the article, you will gain an understanding of the basic principles of HTTP Live Streaming and usage of AVKit and Swift UI to play HLS on iOS and tvOS.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeHLS (HTTP Live Streaming) is a popular video streaming protocol that is widely used for delivering video content over the internet. In this response, we'll discuss how to implement HLS streaming with AVKit and SwiftUI for iOS and tvOS.
What Is HLS?
HLS, which stands for HTTP Live Streaming, is an internet protocol that enables the delivery of video content. Developed by Apple Inc., it was first introduced in 2009 as part of their QuickTime X and iPhone software. Today, HLS is extensively used for streaming live and on-demand video to a broad range of devices and platforms, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and desktop computers. These systems can operate seamlessly with existing caching infrastructure, including Content Delivery Networks (CDNs), and can effectively navigate standard firewalls and routers.
How HLS Works
Similar to other adaptive streaming technologies, HLS operates by creating multiple files for distribution to the player, allowing for adaptive switching between streams to optimize playback. Being an HTTP-based technology, it doesn't require a streaming server, and all switching logic is handled by the player. To achieve this, HLS breaks down the video stream into small chunks with varying durations, usually lasting between 2 and 10 seconds, and loads them onto an HTTP server alongside a text-based manifest file with an .M3U8 extension.
These chunks are then encoded at different bitrates and made available for download over HTTP. When a client device, such as a smartphone, requests playback, it selects the best bitrate based on the available bandwidth and device capabilities, downloads the chunks, and plays them back sequentially.
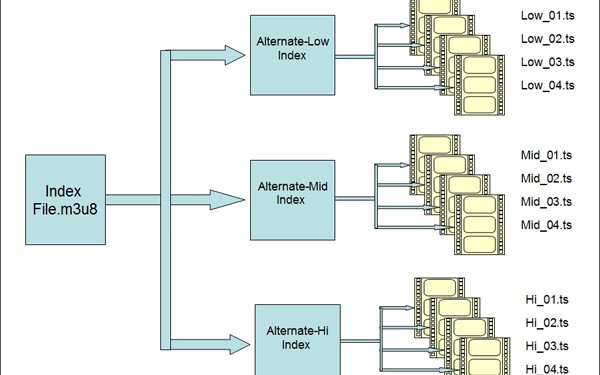
Playlist Relationship
HLS is a highly versatile streaming protocol that has become an industry standard for streaming high-quality video content over the internet.
Why HLS
HLS has become a popular choice for streaming video content over the internet due to several factors.
Efficient and Reliable
It is based on HTTP, which allows it to leverage existing web infrastructure like CDNs for efficient and reliable delivery of video content with minimal buffering or interruptions.
Adaptive Bitrate
HLS incorporates adaptive bitrate streaming, allowing it to dynamically adjust the video quality in real time based on the viewer's internet speed and device capabilities. This ensures uninterrupted playback, even under varying network conditions.
Compatibility
HLS is compatible with a broad range of devices and platforms, including smartphones, tablets, smart TVs, and desktop computers, making it an adaptable option for content creators to reach a large audience.
Content Protection
HLS offers robust and flexible DRM (digital rights management) options that enable content creators to protect their content from piracy and unauthorized access.
Also, provides more advantages like
- Closed Captions and Subtitles
- Fast Forward and Reverse Playback
- Alternate Audio and Video Renditions
- Fallback with Stream Alternates
- Timed Metadata
- Ad Insertion
Playing HLS Stream in iOS / tvOS Apps Using AVKit and SwiftUI
The AVKit framework offers all the essential components required to create interfaces for media playback, transport controls, and other functionalities to play media files in iOS, tvOS and macOS apps. Additionally, it includes a VideoPlayer with a standard native user interface for SwiftUI that shows media content and provides playback control.
AVPlayer is a class provided by Apple's AVFoundation framework that allows you to play a single media file, such as an audio or video file. You can initialize an AVPlayer instance by providing it with either an AVPlayerItem object or a URL that references the media file you want to play.
AVQueuePlayer, on the other hand, is used to play a sequence of media items, which can include audio or video files. It allows you to add multiple AVPlayerItem objects to a queue and play them sequentially. This can be useful in scenarios where you want to play a playlist or a sequence of video clips.
When it comes to creating a video player in SwiftUI, you can use AVPlayer to play a single video file by providing a URL to the video asset. UIViewControllerRepresentable protocol can be used, which allows you to expose a UIKit view to a SwiftUI View.
Here's an example of how you can create a simple video player in SwiftUI:
struct VideoPlayerView: UIViewControllerRepresentable {
var videoURL: URL
func makeUIViewController(context: Context) -> AVPlayerViewController {
let player = AVPlayer(url: videoURL)
let playerController = AVPlayerViewController()
playerController.player = player
player.play()
return playerController
}
func updateUIViewController(_ uiViewController: AVPlayerViewController, context: Context) {}
}
struct ContentView: View {
var body: some View {
VideoPlayerView(videoURL: URL(string: "https://test-streams.mux.dev/x36xhzz/x36xhzz.m3u8")!)
.frame(height: 300)
}
}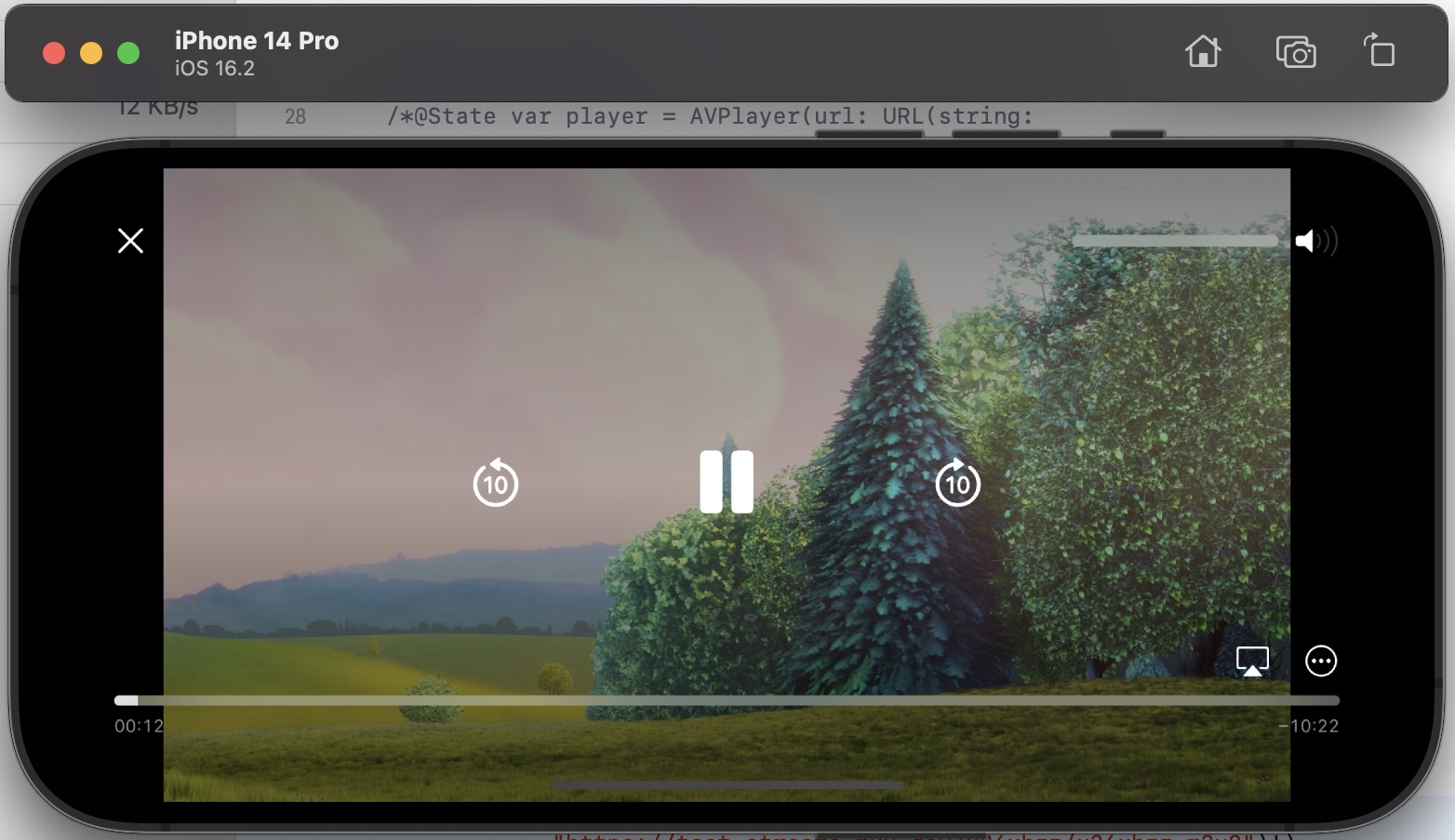
The above code snippet demonstrates how to create a custom view in SwiftUI that plays a video using AVPlayer. We define a struct called VideoPlayerView that conforms to the UIViewControllerRepresentable protocol. This allows us to wrap an existing UIKit view controller, AVPlayerViewController, and use it in our SwiftUI view hierarchy.
Inside the makeUIViewController method, we create an AVPlayer instance and initialize it with the URL of the video we want to play. We then create an instance of AVPlayerViewController and set its player property to the AVPlayer instance we just created.
Finally, we add the VideoPlayerView to our SwiftUI view hierarchy by instantiating it and setting its videoURL property to the URL (HLS stream, in this case) of the video we want to play. We also set the frame height to 300 points to ensure that the video player is visible.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments