How Single Page Web Applications Actually Work
SPAs are all over the place but still prove a fairly controversial topic among web devs. Read on to get one developer's take on this matter.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Freesingle page web applications have come a long way since they first appeared around 2003. they have become an integral part of the modern javascript landscape .
but during my discussions with quite a few developers, i feel that there is still a lack of clarity about how single-page applications actually work. hence, i decided to roll up my sleeves (figuratively speaking) and provide my take on this very very interesting subject.
so, let's start from the beginning.
what are single page applications?
the best definition, in my humble opinion, is: a single page application is a type of web application that requires only a single page to be loaded into the browser.
you might be thinking, what does this even mean? how could an application with just a single-page be of use to anyone in the world?
the answer is simple. single page web applications are built around the concept of dynamically rewriting the contents of that single page. this is different from loading pre-rendered pages from the server.
and this is where the magic happens. by taking this approach, single page web applications avoid the interruption caused by rendering the pages on the server. this removes the biggest problem the web development world usually faces with regards to providing a seamless user experience.
sounds great already, right? i know! but let's just see how all of this works and i'm sure you'll be even more amazed.
how does the magic happen?
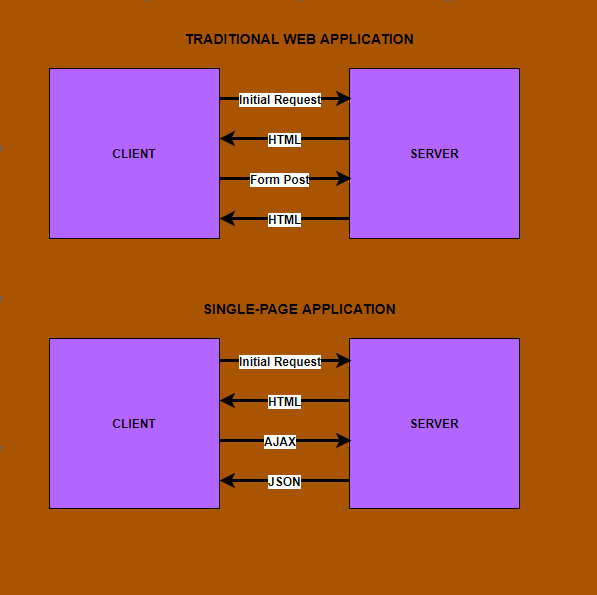
in single-page web applications, when the browser makes the first request to the server, the server sends back the index.html file. and that's basically it. that's the only time an html file is served. the html file has a script tag for the .js file which is going to take control of the index.html page. all subsequent calls return just the data, usually in json format. the application uses this json data to update the page dynamically. however, the page never reloads.
the client (and not the server) handles the job of transforming data to html once the application has started. basically, most of the modern spa frameworks have a templating-engine of sorts running in your browser to generate the html.
contrast this to a traditional web application. in a traditional application, every time the application calls the server, the server will render the entire html page. the client receives the rendered page and triggers a page refresh. in this case, the browser is the client.
the below illustration explains the difference between the two approaches:
what are the advantages?
- right off the bat, it's obvious that since we don't send any html over the network for every user interaction, it saves a lot of time and bandwidth. due to various opening and closing tags, the html version is usually larger. also, in the traditional approach, we also load a lot of duplicate html every time we made a request to the server. by following the spa approach, the application becomes much more responsive.
- no marks for guessing that faster data refresh and less bandwidth consumption leads to a better user experience. this is pretty useful on mobile devices and slower internet connections.
- there are arguments leveled against single page web applications saying that the javascript bundle size can become bloated. however, most of the good spa frameworks provide wonderful methods of code splitting. this keeps your bundle sizes in check and performs on-demand loading wherever applicable.
- a less obvious benefit is regarding the overall architecture of an spa. using json to send application data creates a sort of separation between the view layer (html) and the application layer. this decouples the presentation and application layer and allows developers to evolve each layer independently. you can potentially replace the html markup without changing the application logic. the client and server are also totally independent of one another.
- another overlooked benefit is production deployment of single page applications. spas are super easy to deploy. when you build an spa for production, you typically end up with one html file, one css bundle, and a javascript bundle. any static content server can host these files. good examples are nginx, amazon s3 bucket, apache, or firebase.
aren't there some disadvantages?
well, there are pros and cons to everything.
one of the biggest detractions leveled at single page web applications has been that they cannot be properly indexed by search engines like google. since there is no html markup except the initial index.html file, search engines cannot index the content because their crawlers cannot execute the javascript used to generate the html.
however, in an official announcement , google has stated that their search engine is now able to crawl ajax calls.
some of the criticisms leveled at spas are largely based on preference and complexity. however, in my opinion, they are largely subjective. the main point is that one should definitely look at the use-case while deciding on which approach best suits the application needs.
i would love to hear your comments on this in the comments section below.
Published at DZone with permission of Saurabh Dashora. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments