How Spring Boot Initializes the Spring MVC Application Context
In this article, we use Spring Boot which has been bootstrapped in order to enable and use the web services functionality Spring provides.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeWhen the Spring Boot is bootstrapped using the below code, it loads the Spring MVC configuration automatically.
package hello;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
}Under the hood of @SpringBootApplication, when the above code is executed, it adds the below annotation.
@Configuration tags the class as a source of bean definitions for the application context.
@EnableAutoConfiguration tells Spring Boot to start adding beans based on classpath settings, other beans, and various property settings.
Normally you would add @EnableWebMvc for a Spring MVC app (explicit declaration ), but Spring Boot adds it automatically when it sees spring-webmvc on the classpath. This flags the application as a web application and activates key behaviors such as setting up a DispatcherServlet.
@ComponentScan tells Spring to look for other components, configurations, and services in the hello package, allowing it to find the controllers.
Here are some different options you can use to initialize the Spring MVC context if you're NOT using Spring Boot.
@EnableWebMvc + extending WebMvcConfigurerAdapter and customizing some of the default configurations. With this mechanism, you are basically doing some autoconfiguration provided by @EnableWebMvc.
Just extend WebMvcConfigurationSupport and customize the default configuration.
If you're using Spring Boot, add @EnableAutoConfiguration annotation and extend WebMvcConfigurerAdapter. No need to use @EnableMvc.
So option 3 is more generic.
Below is a chart I created to illustrate the difference between WebMvcConfigurerAdapter and WebMvcConfigurationSupport.
WebMvcConfigurerAdapter |
WebMvcConfigurationSupport |
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurerAdapter class. |
org.springframework.web.servlet.config.annotation.WebMvcConfigurationSupport class |
implements WebMvcConfigurer. |
Implements: Aware, ApplicationContextAware, ServletContextAware |
Main purpose is to customize the default configuration. |
This is the main class providing the configuration behind the MVC Java config. As we see it implements the *Aware interfaces. |
The whole process is manual. |
It works under the hood of |
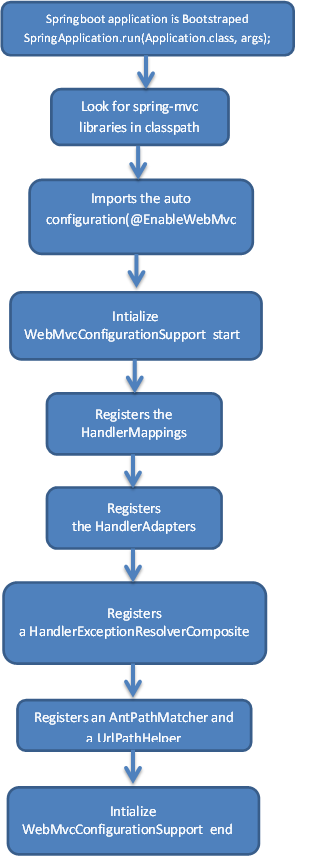
So Spring Boot initializes WebMvcConfigurationSupport for you. If you see the Java API doc. It done the following –
This is the main class providing the configuration behind the MVC Java config. It is typically imported by adding @EnableWebMvc to an application's @Configuration class. An alternative, more advanced, option is to extend directly from this class and override methods as necessary, remembering to add @Configuration to the subclass and @Bean to overridden @Bean methods. For more details, see the Java doc of @EnableWebMvc.
1. This class registers the following HandlerMappings:
RequestMappingHandlerMapping - ordered at 0 for mapping requests to annotated controller methods.
HandlerMapping - ordered at 1 to map URL paths directly to view names.
2. Registers these HandlerAdapters:
- RequestMappingHandlerAdapter - for processing requests with annotated controller methods.
- HttpRequestHandlerAdapter - for processing requests with HttpRequestHandler.
- SimpleControllerHandlerAdapter - for processing requests with interface-based Controllers.
3.Registers a HandlerExceptionResolverComposite with this chain of exception resolvers:
ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver - for handling exceptions through @ExceptionHandler methods.
ResponseStatusExceptionResolver - for exceptions annotated with @ResponseStatus.
DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver - for resolving known Spring exception types.
4.Registers an AntPathMatcher and a UrlPathHelper to be used by:
The RequestMappingHandlerMapping.
The HandlerMapping for ViewControllers.
The HandlerMapping for serving resources.
Note that those beans can be configured with a PathMatchConfigurer.
Both the RequestMappingHandlerAdapter and the ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver are configured with default instances of the following by default:
A ContentNegotiationManager.
A DefaultFormattingConversionService.
An OptionalValidatorFactoryBean if a JSR-303 implementation is available on the classpath.
A range of HttpMessageConverters depending on the third-party libraries available on the classpath.
The flow diagram looks like below:
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments