How to Add Social Media Authentication to ASP.NET Core
Today, I'd like to share how you can go about enabling social media authorization for an ASP.NET Core application very easily.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
adding social media authentication is easy with asp.net core. you start by creating another project, like you would with an asp.net core mvc project, and selecting individual user accounts as the authentication mode. this way the project template will add the database entities, controllers, and views to collect and store all the information needed to create a private site where users can register either directly (providing a username and password) or via oauth providers like facebook, twitter, google, microsoft, github, and others.
adding a social login is just a matter of adding the right nuget package and configuring the authentication provider in the
configureservice
method in the startup class. for example, to add a facebook login, add the nuget package, we'd use the following:
microsoft.aspnetcore.authentication.facebook
. then add the following lines of code in the
configureservice
method:
services.addauthentication().addfacebook(facebookoptions =>
{
facebookoptions.appid = configuration["authentication:facebook:appid"];
facebookoptions.appsecret = configuration["authentication:facebook:appsecret"];
});
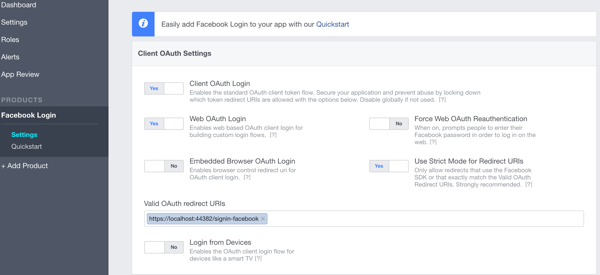
now you have to register a new application on the facebook developer portal in order to get the appid and appsecret needed to authenticate your application with facebook. go to the url https://developers.facebook.com/apps/ and click on the add a new app button and add the basic information for your app. once that's done, go to the settings and enter the url for the oauth redirect page, which is
/signin-facebook
(but you need to specify the absolute url,
http://localhost:nnn
). this route is added by the nuget package for the facebook authentication.
the last thing is to retrieve the
appid
and
appsecrets
needed for the application to work. for this, go to the dashboard inside the developer portal:
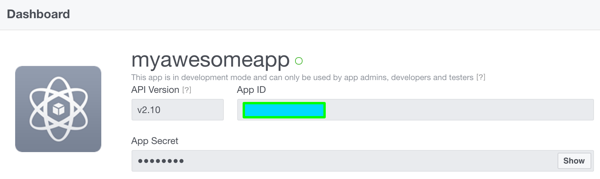
now that you have these values, you have to store them in the settings of your application. since this is sensitive data, you don't want to accidentally commit them to a public source repository, so it's better to store them in the user secrets.
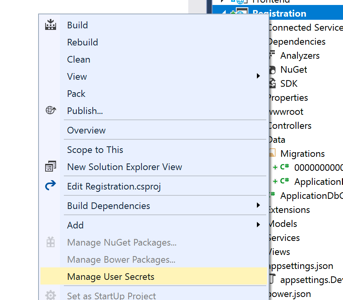
the file is stored in the user profile, which is still easily readable, but, in theory, only by its owner. the, in production, this information can be passed to the app in different ways, like shown when explaining the configuration of app settings inside the webhost .
{
"authentication": {
"facebook": {
"appid": "myappid",
"appsecret": "myappsecret"
}
}
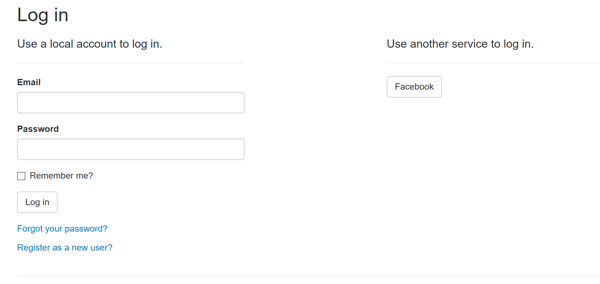
}now just launch the site and you'll see a new button to sign-in and log-in via facebook
Published at DZone with permission of Simone Chiaretta, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments