How to Configure HAProxy as a Proxy and Load Balancer
Learn how to configure HAProxy and look into some basic concepts such as ACLs, backends, and frontends in HAProxy Configuration.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeHAProxy (High-Availability Proxy) is a free, very fast, and reliable solution written in C that offers high-availability load balancing and proxying for TCP- and HTTP-based applications.
Before we move to configure the proxy, let's look into some of the basic concepts such as ACLs, backends, and frontends in HAProxy Configuration.
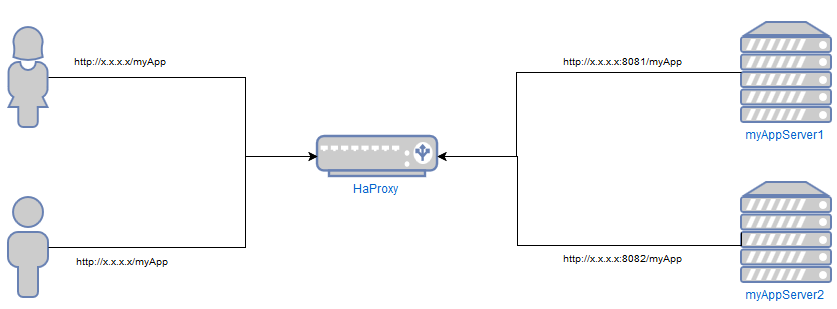
HAProxy as proxying and load balancing server.
ACL
Access Control List (ACL) is a test condition. Actions are performed based on the result of the test conditions, for example, selecting the server to forward the request. The syntax of ACL is acl <aclname> <criterion> [flags] [operator] [<value>] ..., as demonstrated below.
acl acl_myApp path_sub myAppacl_myapp: The name of the ACL.path_sub: A function that validates if the request URL has myApp as a substring.
For more details, please see here.
Backend
This is a set of servers that actually processes the forwarded requests. The backend consists of a load balancing algorithm and a list of servers with ports.
The basic syntax of the backend is:
backend <backendname>
balance <loadbalancing algorithm>
server <name of the server> <ip>:<port> check
....
server <name of the server> <ip>:<port> checkHere's an example with all of the details filled in:
backend myAppBackend
balance roundrobin
server myAppServer1 172.21.28.1:8080 check
server myAppServer2 172.21.28.2:8080 checkmyAppBackend: The name of the backend to which the ACL will forward the request.roundrobin: The name of the load balancing algorithm.myAppServer,myAppServer1: The name of the server.172.21.28.1,172.21.28.2: IP addresses of servers.8080: The port on which server listens.check: Specifies to check the health of the server.
Frontend
The frontend defines how requests are forwarded to backends. It is composed of set of IP addresses, a port, ACLs, and use_backend rules.
The syntax is:
frontend <frontend name>
bind <IPs or wild card>:80
acl <aclname> <criterion> [flags] [operator] [<value>] ...
use_backend <backend name> if <aclname>Here's an example with all of the details filled in:
frontend myAppFrontEnd
bind *:80
acl acl_myApp path_sub myApp
use_backend myAppBackend if acl_myAppmyAppFrontEnd: Name of the frontend.
The frontend listens on port 80 to all the interfaces * available in server. If the URL has myApp as a substring, the request is forwarded to myAppBackend. Otherwise, you will get no service available exception.
Statistics (Optional)
The tatistics report of HAProxy will show the status of the servers, the number of connections, etc. This can be enabled easily by adding the following configuration to the config file:
listen stats
bind *:<Port>
stats enable
stats hide-version
stats uri </url>
stats auth <username>:<password>Here's an example with all of the details filled in:
listen stats
bind *:9999
stats enable
stats hide-version
stats uri /stats
stats auth admin:admin@1239999: Listens on port 9999 for statistics report requests./stats: The URL of the statistics page (i.e. localhost:9999/stats).admin/admin@123: The username and password to access the statistics page.
The complete content of the configuration file haproxy.cfg is as follows:
#HA Proxy Config
global
daemon
maxconn 256
defaults
mode http
timeout connect 5000ms
timeout client 50000ms
timeout server 50000ms
listen stats
bind *:9999
stats enable
stats hide-version
stats uri /stats
stats auth admin:admin@123
frontend myApp
bind *:80
acl acl_myApp path_sub myApp
use_backend myAppBackEnd if acl_myApp
backend myAppBackEnd
balance roundrobin
server myAppServer1 127.0.0.1:8081 check
server myAppServer2 127.0.0.1:8082 checkHow to Deploy on Linux
Unzip the file into the desired location
tar xvzf haproxy-1.8-dev1.tar.gz.Compile the source code using:
Create config file
haproxy.cfgwith the configuration detailsStart the haproxy with
./haproxy -f haproxy.cfg.Access the status page on http:localhost:9999/stats.
cd haproxy-1.8-dev1/
make TARGET=linux2628The Statistics of HAProxy
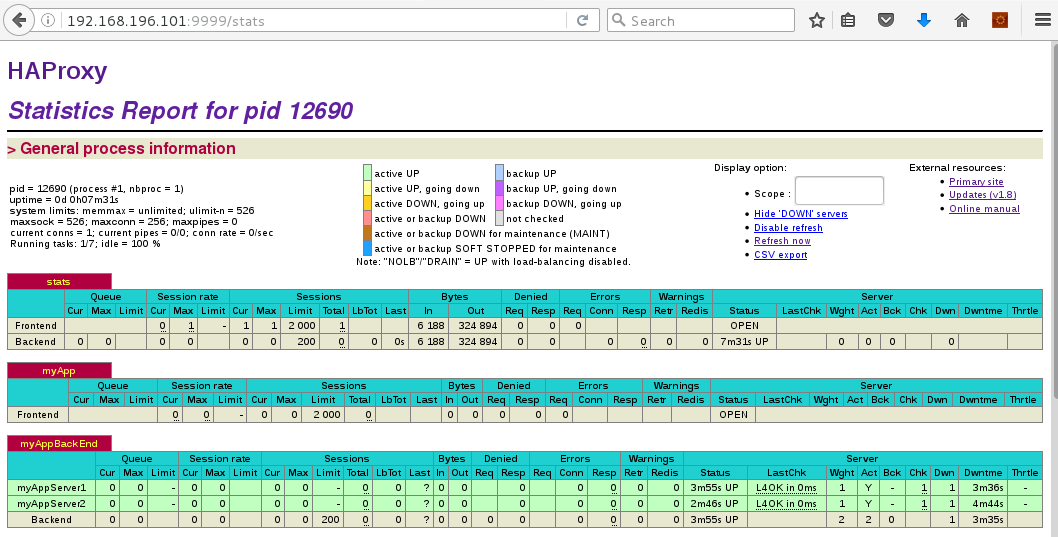
For more details, please refer to the official HAProxy site.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments