How to Initialize Database With Default Values in SQLAlchemy Once After Database Creation
Recently, while working on a Python app, I needed an SQLAlchemy functionality to insert default values into SQLite database. In particular, I simply needed to execute some DDL only once after the database was created. How does SQLAlchemy handle this? Let’s investigate it on a simple database model for a prototype of a todo app created in the online database designer Vertabelo.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Recently, while working on a Python app, I needed an SQLAlchemy functionality to insert default values into SQLite database. In particular, I simply needed to execute some DDL only once after the database was created.
How does SQLAlchemy handle this? Let’s investigate it on a simple database model for a prototype of a todo app created in the online database designer Vertabelo.
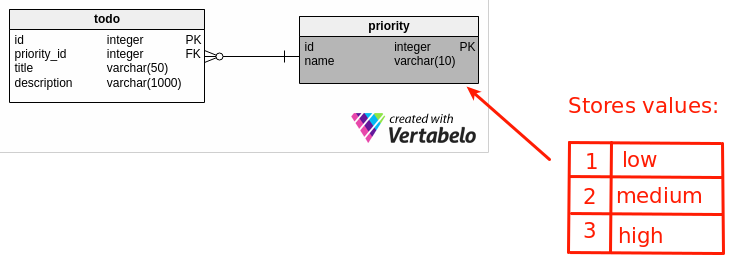
The todo table stores basic information about task (title, description) and references priority table. This one stores three provided priorities (low, medium, high).
Solution
Use after_create event from the event API
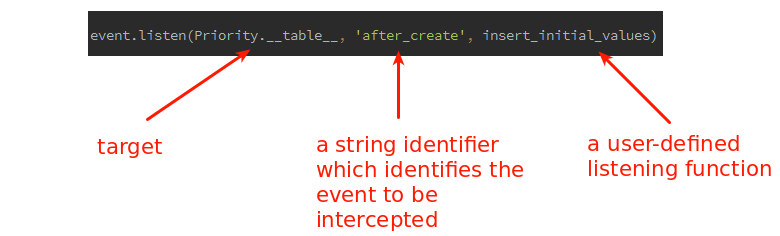
Subscribing to an event is possible through listen() function.
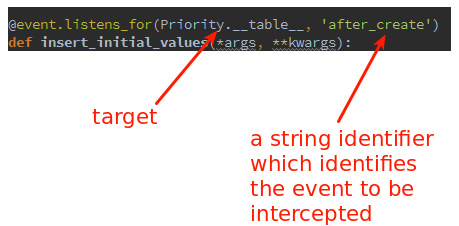
Or alternatively, the listens_for() decorator.
For my case, I can do it in two equivalent ways.
- Register a listener function for the table
piority. - Decorate the function as a listener with
listens_fordecorator.
def insert_initial_values(*args, **kwargs):
db.session.add(Priority(name='low'))
db.session.add(Priority(name='medium'))
db.session.add(Priority(name='high'))
db.session.commit()
event.listen(Priority.__table__, 'after_create', insert_initial_values)
DDL construct event.listen(Priority.__table__, 'after_create',
DDL(""" INSERT INTO priority (id, name) VALUES (1, 'low'), (2, 'medium'), (3, 'high') """))
@event.listens_for(Priority.__table__, 'after_create')
def insert_initial_values(*args, **kwargs):
db.session.add(Priority(name='low'))
db.session.add(Priority(name='medium'))
db.session.add(Priority(name='high'))
db.session.commit()
Testing
For testing, I created a prototype application in Flask framework that uses plain SQLAlchemy models with the Flask-SQLAlchemy session.
The SQLAlchemy models were generated directly from the model designed in Vertabelo using script hosted on Github.
Here's the demo app (the code is also available on Github):
# models.py
from sqlalchemy.ext.declarative import declarative_base
from sqlalchemy import Column, Integer, ForeignKey, Unicode
from sqlalchemy.orm import relationship
Base = declarative_base()
class Todo (Base):
__tablename__ = "todo"
id = Column('id', Integer, primary_key = True)
priority_id = Column('priority_id', Integer, ForeignKey('priority.id'))
title = Column('title', Unicode)
description = Column('description', Unicode)
priority = relationship('Priority', foreign_keys=priority_id)
class Priority (Base):
__tablename__ = "priority"
id = Column('id', Integer, primary_key = True)
name = Column('name', Unicode)
# app.py
from flask import Flask
from sqlalchemy.event import listen
from models import Todo, Priority, Base
from sqlalchemy import event, DDL
from flask_sqlalchemy import SQLAlchemy
app = Flask(__name__)
app.config['SQLALCHEMY_DATABASE_URI'] = 'sqlite:///db.test'
db = SQLAlchemy(app)
# first solution
# @event.listens_for(Priority.__table__, 'after_create')
# def insert_initial_values(*args, **kwargs):
# db.session.add(Priority(name='low'))
# db.session.add(Priority(name='medium'))
# db.session.add(Priority(name='high'))
# db.session.commit()
# second solution
# def insert_initial_values(*args, **kwargs):
# db.session.add(Priority(name='low'))
# db.session.add(Priority(name='medium'))
# db.session.add(Priority(name='high'))
# db.session.commit()
#
#
# event.listen(Priority.__table__, 'after_create', insert_initial_values)
# third solution
event.listen(Priority.__table__, 'after_create',
DDL(""" INSERT INTO priority (id, name) VALUES (1, 'low'), (2, 'medium'), (3, 'high') """))
@app.before_first_request
def setup():
# Recreate database each time for demo
Base.metadata.drop_all(bind=db.engine)
Base.metadata.create_all(bind=db.engine)
low_priority = db.session.query(Priority).filter_by(name=u'low').first()
medium_priority = db.session.query(Priority).filter_by(name=u'medium').first()
high_priority = db.session.query(Priority).filter_by(name=u'high').first()
db.session.add(Todo(title=u'title1', description=u'description1', priority_id=low_priority.id))
db.session.add(Todo(title=u'title2', description=u'description2', priority_id=medium_priority.id))
db.session.add(Todo(title=u'title3', description=u'description3', priority_id=high_priority.id))
db.session.commit()
@app.route('/')
def index():
todos = db.session.query(Todo).join(Priority).all()
return u"".join([u"{0}: {1}: {2}".format(todo.title, todo.description, todo.priority.name) for todo in todos])
if __name__ == '__main__':
Base.metadata.create_all(bind=db.engine)
app.run(debug=True)
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments