How to Make an Ajax Call in Laravel
An introduction to making an Ajax call in the Laravel framework using code snippets from search-suggested use cases to demonstrate its implementation.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIntroduction
In this article, we will go through the main steps of making an Ajax call in the Laravel framework. To understand this article, the reader must have a basic understanding of HTTP, HTML, JavaScript, PHP, Laravel framework, and MySQL database.
What Is Ajax
Ajax (Asynchronous JavaScript and XML) is a technique for making asynchronous calls to the server. It is a particular way of using JavaScript language for downloading data from the server in the background. Ajax allows us to dynamically update part of a web page without making the user wait, thus improving the overall user experience. It is now an integral part of modern web development and helps in creating rich, user-friendly websites.
XMLHTTPRequest API
XMLHttpRequest API is responsible for making Ajax calls in JavaScript. All modern browsers (Chrome, Firefox, IE7+, Edge, Safari, and Opera) have a built-in XMLHttpRequest API. To initiate an Ajax call, first we have create an object of the XMLHttpRequest API.
var request = new XMLHttpRequest();XMLHttpRequest API provides a set of properties and methods. We will use these properties and methods for implementing Ajax in the subsequent sections.
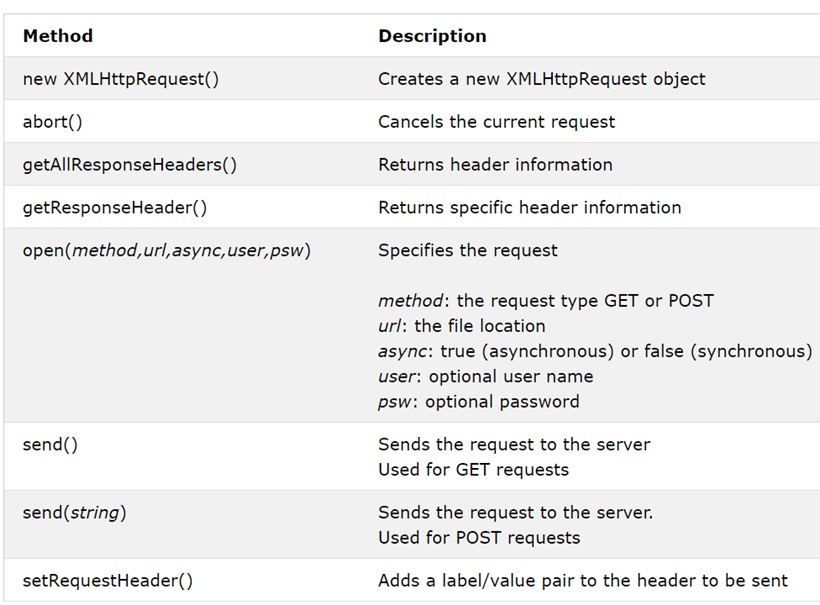

Ajax Implementation Steps in Laravel
Assume that we have to implement a search suggest functionality in Laravel using Ajax. For that, we need to understand the following set of steps.
- We need an HTML form that takes input search terms from the user and a back-end MySQL database table for searching the term.
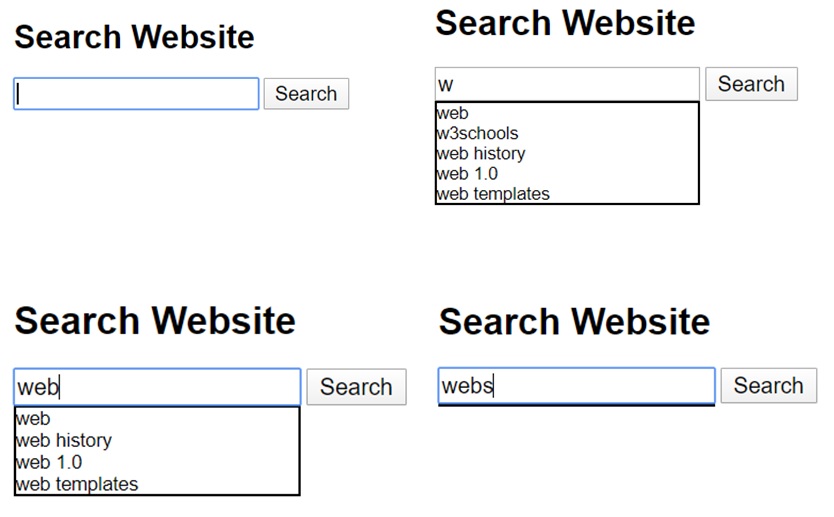
![Sample search form]()
A sample HTML form for search suggests functionality. Multiple screenshots depict different stages of the search procedure.
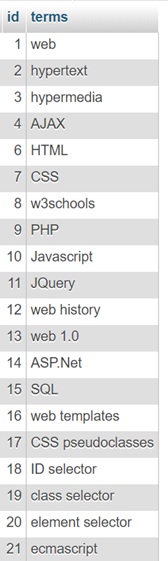
![Sample MySQL database table]() A sample MySQL database table having search terms
A sample MySQL database table having search terms - Laravel framework is based on MVC(model-view-controller) architecture. We have to write the route, controller, and view parts of the code for implementing Ajax.
- In the view part, we will be having an HTML markup for the search form along with the JavaScript function for initiating the Ajax request.
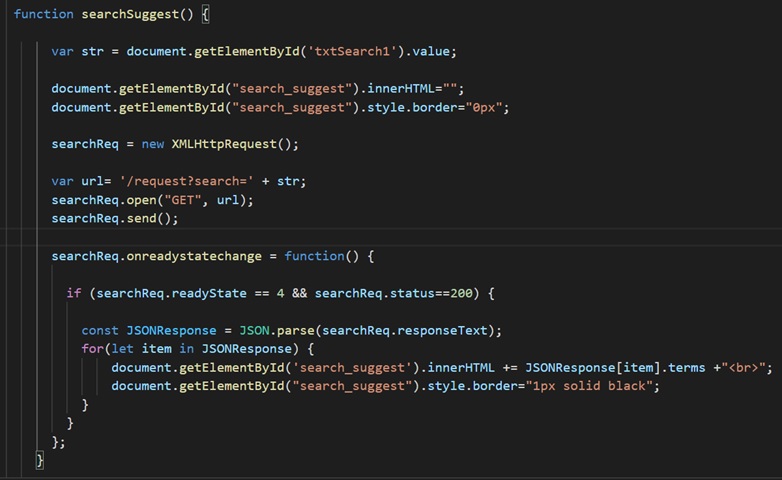
- When users start typing the search term,
onkeyupevent is triggered, which in turn calls thesearchSuggest()JavaScript function. This JavaScript function reads the value from the search field using the statement "document.getElementById("txtSearch1").value."![]()
- The value read from the search field is then appended with the URL and passed into the
open()method of the XMLHttpRequest API along with the HTTP GET method.![]()
- The Ajax call is sent to the server using the
send()method. - The client-side is now waiting for the server response.
readyStateproperty tracks the status of the request on the server. Whenever the value ofreadyStateproperty changes,onreadystatechangeproperty calls the anonymous callback function. When the response is ready from the server, the value ofreadyStateproperty becomes four. - The callback function reads the response data when the value of
readyStateproperty becomes four and the status of the response is the HTTP status code 200. - It then displays the response on the screen by giving it an HTML line break tag <br/> and situating it inside the HTML <div> tag.
- When users start typing the search term,
- In the Route part, we will call the controller function which will handle the request corresponding to the route URL activated from the view.
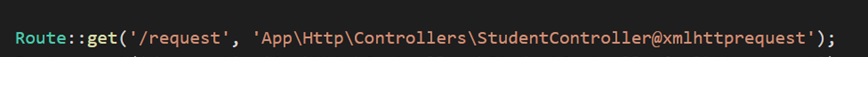
- This route is activated whenever the Ajax request is received on
'/request'URL. - The server then calls the
xmlhttpreuestmethod defined in the controller file.![Laravel route definition.]()
- This route is activated whenever the Ajax request is received on
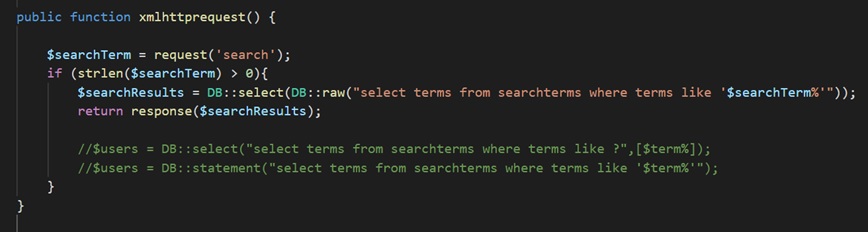
- In the controller part, we will define the function responsible for executing a SQL query to the database. It will fetch relevant search terms from the database based on the search term entered by the user in the search field.
- The search term sent by the client-side as a query parameter is retrieved and stored in the PHP variable
$searchTerm. SQL SELECTquery is executed with theLIKEclause to partially match and return all those search terms from the MySQL database table which have received the user search term at their start.![]()
- The search term sent by the client-side as a query parameter is retrieved and stored in the PHP variable
- In the view part, we will be having an HTML markup for the search form along with the JavaScript function for initiating the Ajax request.
Conclusion
This article has given a beginner-level overview of making an Ajax call in the Laravel framework. It uses code snippets from search-suggested use cases to demonstrate its implementation. The target audience of this article comprises web developers who are actively involved in web development using the Laravel framework but need ready-made solutions to accelerate the pace of their learning.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.


Comments