How To Optimize AG Grid Performance With React
React is the market leader of JavaScript libraries. In this article, we will set up a React web application and use AG Grid to build a performant data table.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAG Grid is a feature-rich JavaScript library primarily used to build robust data tables in web applications. It’s used by almost 90% of Fortune 500 companies and it’s especially useful in Business Intelligence (BI) applications and FinTech applications.
React is the market leader of JavaScript libraries to build enterprise web and mobile applications. It is widely adopted by major companies and boasts a large community.
In this article, we will set up a React web application and use AG Grid to build a performant data table. All the code in this article is available at this GitHub link.
Prerequisites
- Node.js and npm are installed on your system.
- Knowledge of JavaScript and React.
Set up a New React Application
- Verify that NodeJS and NPM are installed. Commands to check:
node -vandnpm -v![command prompt]()
- We will use "create react app" to initiate a new React application, let's install it globally on the machine using
npm install -g create-react-app - Create a new React application using
npx create-react-app AGGridReact - Wait for the app to be fully created and then go to the newly created app’s folder using
cd AGGridReact - Start the application using
npm start. Soon you will be able to access this react app on localhost port 3000 using the URL - Now we are ready to make modifications to our React app. You can use the code editor of your choice, I have used Visual Studio Code.
Integrating AG Grid Into Our React App
AG Grid comes in two flavors, community version and enterprise version. We will use the community version to not incur any licensing fee. The enterprise version is preferred in large corporations due to the set of additional features it provides.
- Install the AG Grid community version with React support using
npm install ag-grid-react - Let’s create two folders under the src folder in our project: components and services.
- Let's create a service under the services folder. This service will have the job of communicating to the backend and fetching data. For simplicity purposes we will not be doing actual API calls, instead, we will have a JSON file with all sample data.
- Let's create
movie-data.jsonfile and add content to it from here. - Add
movie-service.jsto the services folder. Our service will have two methods and one exported constant. Soon, all of these will make sense. Below is the reference code for this file.
import movies from './movie-data.json';
const DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE = 5;
const countOfMovies = async() => {
return movies.movies.length;
};
const fetchMovies = async() => {
return movies.movies;
};
export { DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE, countOfMovies, fetchMovies };At this point let’s create our React component which will hold AG Grid Table. Add AGGridTable.js file under the components folder under the src directory.
Let's import React and AG Grid in our component and lay down basic component export
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { AgGridReact } from 'ag-grid-react';
import 'ag-grid-community/styles/ag-grid.css';
import 'ag-grid-community/styles/ag-theme-quartz.css';
export const AgGridTable = () => {}We are going to use the AGGridReactcomponent to render our table, this component needs two main things:
- Columns we want to display in our table.
- Rows we want to display in our table.
We have to pass a parameter named columnDefs to our AGGridReact to tell it how we want our columns to be set up. If you look at our movie data in movie-data.json file we have columns movieID, movieName and releaseYear. Let’s map these to our column definitions parameters. We can achieve it using the below lines of code.
const columnDefs = [
{ field: 'movieId', headerName: "Movie ID", minWidth: 100 },
{ field: 'movieName', headerName: "Movie Name", flex: 1 },
{ field: 'releaseYear', headerName: "Release Year", flex: 1 }
];We need to fetch actual movie data, and we are going to leverage the fetchMovies function from our movie service. Also, we would want to load it on page load. This can be achieved using the useEffect hook of React by passing an empty dependency array.
useEffect(() => {
const fetchCount = async () => {
const totalCount = await countOfMovies();
setTotalRecords(totalCount);
}
fetchCount();
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
fetchData();
}, []);
const fetchData = async () => {
setIsLoading(true);
try {
const response = await fetchMovies();
setMovieData(response);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
};Let’s add some nice loading indicator variables to indicate to our users something is getting processed.
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);Putting everything together we get our component as below.
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import { AgGridReact } from 'ag-grid-react';
import 'ag-grid-community/styles/ag-grid.css';
import 'ag-grid-community/styles/ag-theme-quartz.css';
import { countOfMovies, fetchMovies } from '../services/movie-service';
export const AgGridTable = () => {
const [movieData, setMovieData] = useState([]);
const [totalRecords, setTotalRecords] = useState(0);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const columnDefs = [
{ field: 'movieId', headerName: "Movie ID", minWidth: 100 },
{ field: 'movieName', headerName: "Movie Name", flex: 1 },
{ field: 'releaseYear', headerName: "Release Year", flex: 1 }
];
useEffect(() => {
const fetchCount = async () => {
const totalCount = await countOfMovies();
setTotalRecords(totalCount);
}
fetchCount();
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
fetchData();
}, []);
const fetchData = async () => {
setIsLoading(true);
try {
const response = await fetchMovies();
setMovieData(response);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
};
return (
<>
{isLoading && <div>Loading...</div>}
<div
className="ag-theme-quartz"
style={{ height: 300, minHeight: 300 }}
>
{
totalRecords > 0 &&
<AgGridReact
rowData={movieData}
columnDefs={columnDefs}
/>
}
</div>
</>
)
}Let's update our app.js to include our newly built component and perform cleanup to remove basic create React app-generated code. Below is the updated code for app.js:
import './App.css';
import { AgGridTable } from './components/AgGridTable';
function App() {
return (
<div className="App">
<header className="App-header">
<h1>Welcome logged in user.</h1>
</header>
<AgGridTable></AgGridTable>
</div>
);
}
export default App;
Our table should load on the UI now.
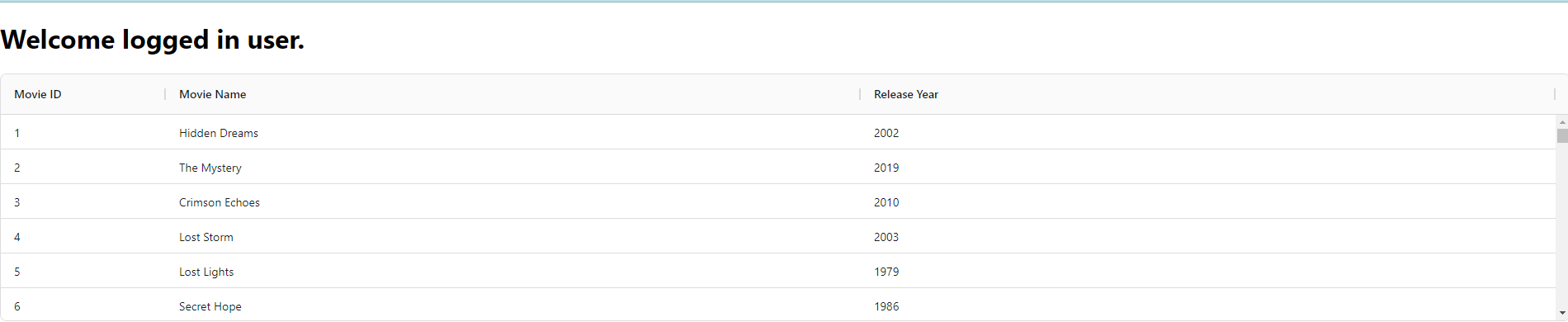
Enhancing Performance With Pagination
We have been rendering all the rows in the table in one go till now. This approach doesn’t scale in the real world. Imagine we had 10000 rows instead of just 100, our page would be very slow and UI performance would take a huge hit.
We can easily enhance this by paginating through our data. In simpler terms, pagination means breaking our data into a set of x items and displaying one set item at a time.
Some key benefits of adding paginations are:
- Reduced DOM Size resulting in Optimized Memory Usage
- Improved Rendering Speed
- Enhanced Scrolling Performance
- Faster Updates
Let's add additional parameters to the AGGridReact setup to enable pagination.
pagination = trueto tells AG Grid we want to paginatepaginationPageSizetells AG Grid what is the default number of items to be displayed on the page initially.- We would be passing an array to the
paginationPageSizeSelectorparameter. It will define different page sizes we allow our users to choose from. totalRowstells AG Grid how many records in total there are, which, in turn, helps count the number of pages in our table.- To have the right value for all of the above parameters we need to update our code to fetch the total row count and define the page size selector array.
import React, { useState, useEffect, useMemo } from 'react';
import { AgGridReact } from 'ag-grid-react';
import 'ag-grid-community/styles/ag-grid.css';
import 'ag-grid-community/styles/ag-theme-quartz.css';
import { DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE, countOfMovies, fetchMovies } from '../services/movie-service';
export const AgGridTable = () => {
const [movieData, setMovieData] = useState([]);
const [totalRecords, setTotalRecords] = useState(0);
const [isLoading, setIsLoading] = useState(false);
const columnDefs = [
{ field: 'movieId', headerName: "Movie ID", minWidth: 100 },
{ field: 'movieName', headerName: "Movie Name", flex: 1 },
{ field: 'releaseYear', headerName: "Release Year", flex: 1 }
];
useEffect(() => {
const fetchCount = async () => {
const totalCount = await countOfMovies();
setTotalRecords(totalCount);
}
fetchCount();
}, []);
useEffect(() => {
fetchData();
}, []);
const fetchData = async () => {
setIsLoading(true);
try {
const response = await fetchMovies();
setMovieData(response);
} catch (error) {
console.error(error);
} finally {
setIsLoading(false);
}
};
const paginationPageSizeSelector = useMemo(() => {
return [5, 10, 20];
}, []);
return (
<>
{isLoading && <div>Loading...</div>}
<div
className="ag-theme-quartz"
style={{ height: 300, minHeight: 300 }}
>
{
totalRecords > 0 &&
<AgGridReact
rowData={movieData}
columnDefs={columnDefs}
pagination={true}
paginationPageSize={DEFAULT_PAGE_SIZE}
paginationPageSizeSelector={paginationPageSizeSelector}
totalRows={totalRecords}
/>
}
</div>
</>
)
}With this code, we will have nice pagination built into it with default page size.
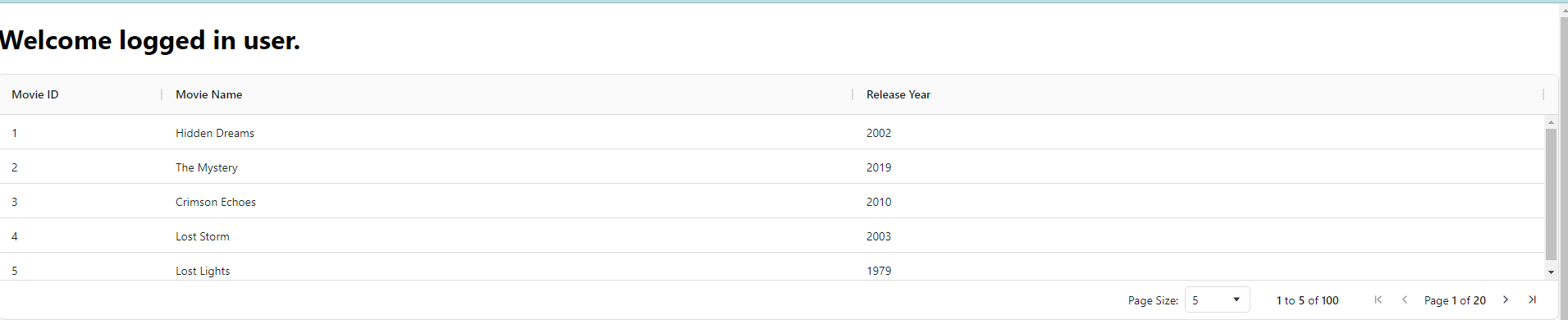
Conclusion
AG Grid integration with React is easy to set up, and we can boost the performance with techniques such as paginations. There are other ways to lazy load rows in AG Grid beyond pagination. Going through the AG Grid documentation should help you get familiar with other methods. Happy coding!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments