Implement PHP Zmanim in WordPress Using Zmanim-WP
The Zmanim-WP plugin for WordPress helps you implement the PHP-Zmanim library, letting you choose the time calculation you need and display it with simple shortcodes.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIf you’ve been following this blog, you know I’ve had a running series on implementing PHP Zmanim, the library based on Kosher Java that simplifies the work needed to calculate times related to Jewish religious observance. (If you need a full explanation of what that is, check out the first blog in the series.)
While the work of understanding and implementing PHP Zmanim has been fun for it’s own sake, I was working on a larger goal behind the scenes: A WordPress plugin that implemented the library in a way that non-programmers could use on their (WordPress-based) websites.
Today, I’m thrilled to announce that the plugin is available for download. My wife is equally excited because it means I’ll (hopefully) go back to more consistently remembering to eat, bathe, and come to bed.
Zmanim WP is free* and can be downloaded from within your WordPress environment (go to Plugins, Add a New Plugin, and search for “Zmanim WP” or even just “zmanim”).
Like the upcoming movie The Thunderbolts*, the splat (or “asterisk” for youngsters and pedantic linguists) is doing a bit of heavy lifting. Zmanim WP is actually “freemium,” meaning that some features are available and free to you forever, and other capabilities are only open if you buy a license.
Before you fire up the torches, grab anti-capitalist pitchforks, and head to my luxurious mansion in Cleveland with arson in your heart, note that all the proceeds are going to charity. The initial charity will be my synagogue because:
- The Rabbi is my cousin, and he’s an amazing guy…but more importantly,
- They’ve been alpha-testing this for over two years, and they've had to suffer all my false starts, mistakes, bad time calculations, and questions. They did so with patience, equanimity, and good humor.
With all that said, I’d like to talk about how the plugin works overall, and then I’ll explain what’s in the free version versus what I’ve held back in exchange for some filthy lucre.
How Zmanim WP Works
In its simplest form, the day-to-day use (I’ll get to the initial setup in a minute) of this plugin involves shortcodes that might look like this:
[zman_sunset]or
[zman_shema]or
[zman_misheyakir]Basically, it’s a set of brackets ([...]) with the word “zman_” followed by a specific type of time. When a visitor comes to your live (WordPress-based) website and views a page, post, or widget with that shortcode, it will display the corresponding time.
For example, I have it running on THIS website, with the location set to Disneyland in California (Lat: 33.8120918, Long: -117.9215545). By using the shortcode [ zman_sunset ], you will see TODAY’S sunset for that location, no matter which day you view this page: 5:46 pm.
If you don’t include any other options, it will show the time for the current day, in a standard _hh:mm am/pm_ format.
But the fact is that you CAN include options – a lot of them. For example (and this is just a sample. For the full list of options you should check out the Zmanim WP documentation on AdatoSystems.com) you can include a date option
- “tomorrow” will show the day after the one when the page is viewed.
[ zman_alot date="tomorrow" ](which, again, is set for “the happiest place on earth” would be 4:22 am)
- “sunday” (or monday, tuesday, etc) will show the next upcoming day of that name. So if it’s currently Monday, the following code will show sunset for the upcoming Wednesday:
[ zman_sunset date="Wednesday" ](which results in 5:46 pm)
- (an actual date) will show the time for the specified date.
[ zman_alot date="2025-01-10" ](that gives you 4:57 am)
You can also include a time offset. Let’s say that Mincha starts 20 minutes before sunset every day. You could automatically display that time using the code:
[ zman_sunset offset=-20 ] (resulting in 5:26 pm)
You can also change the time formatting. This gets a little more into the weeds, as it leverages PHP’s built-in datetime formatting (Here’s a nice tutorial on how those formatting codes work.). Thus, if I wanted to get the date information along with the time (including seconds) for sunset, I could use this:[ zman_sunset dateformat="m-d-Y h:i:s a" ] (that would be: 02-26-2025 05:46:02 pm)
And just to be super clear about things, you can use all of those codes together if you want.
There are also some options that don’t work across the board. For example “lang” will let you specify hebrew or english for some output like the Torah Portion or the Date. But it wouldn’t work for sunset.
Fall Back: Setting Up Zmanim WP
I said I would get to this part. To be honest, the setup isn’t all THAT involved. Once you install the plugin, you’ll get a new menu in the WordPress Admin portal. Clicking on the top level menu takes you to the Main Options page:
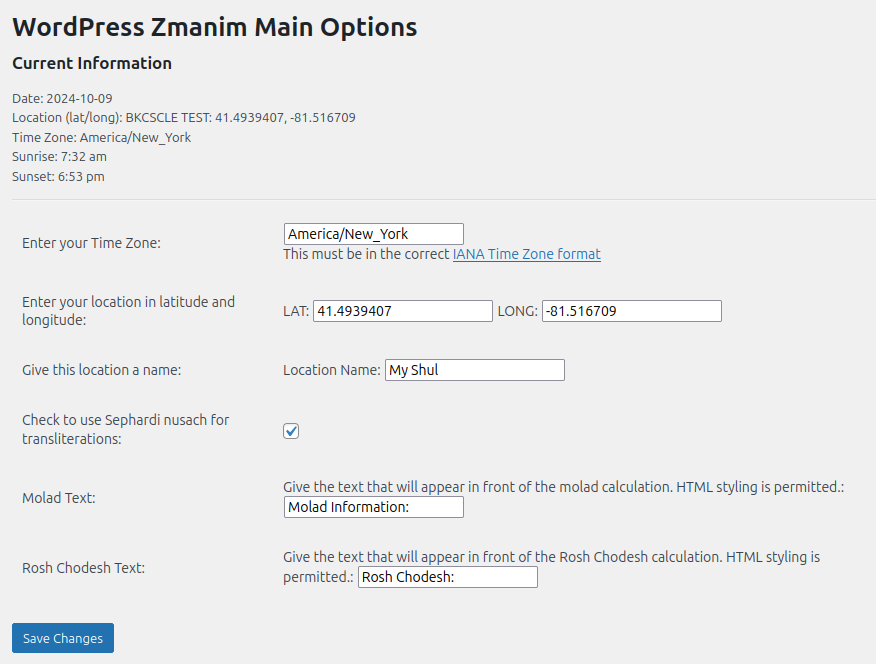
Here, you set the location (using latitude and longitude), the time zone, and a few other cosmetic elements.
However, the main work of configuration happens on the Standard Zmanim Settings page.
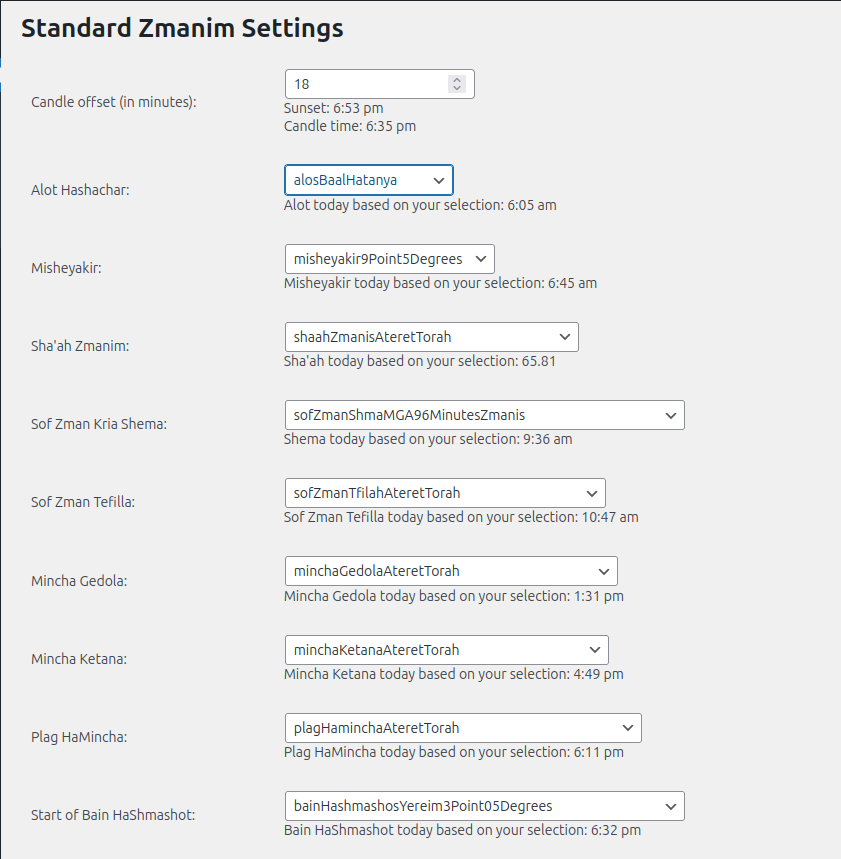
This is where you select the method of calculating each zman from dropdowns populated with a wide range of halachic opinions.
Free Features
The shortcodes that are available to all users are:
Location and Reference
- zman_location – Displays the location, as defined on the admin page.
- zman_lat – Shows the latitude, as defined on the admin page.
- zman_long – Shows the longitude, as defined on the admin page.
- zman_tzone – Shows the Time Zone, as defined on the admin page.
- Special Dates and Days
- zman_shaah – A halachic hour, or 1/12 of the available daylight, as calculated based on the shita selected in the drop-down on the admin page.
- zman_parsha – Provides the Torah reading for that week
- zman_zmandate – Provides the date
- zman_chodesh – The day(s) for the indicated Rosh Chodesh. If the date indicated is “today” or “next”, text ONLY be visible if this week/next week is Rosh Chodesh.
- zman_molad – The day/time for the indicated Molad. If the date indicated is “today” or “next”, text ONLY be visible if this week/next week is the Molad.
Standard Zmanim
- zman_sunrise – Netz haChachma (nautical sunrise, without elevation).
- zman_sunset – Shkia (nautical sunset, without elevation).
- zman_candles – The time for Shabbat candles, which is sunset/shkia minus the number of minutes indicated on the admin page.
- zman_alot – Alot haShachar (earliest time for tallit & tefillin).
- zman_misheyakir – Misheyakir (earliest time for tefillot).
- zman_shema – Sof Zman Kriat Shema (latest time to say Shema)
- zman_tefilla – Sof Zman Tefilla (latest time to say Shacharit)
- zman_gedola – Mincha Gedola
- zman_ketana – Mincha Ketana
- zman_plag – Plag haMincha
- zman_bain – B’ain haShmashot (time between sunset/shkia and tzeit haKochavim).
- zman_tzait – Tzait haKochavim (the time 3 stars are visible in the night sky).
Paid Features
The following shortcodes are only available in the paid version of the Zmanim WP plugin. Along with the shortcodes you see below, there are additional configuration screens to set up key options and elements of the codes.
- zman_earlyshkia -Displays the earliest shkia time for the week (Sunday – Thursday) in which the provided date occurs.
- Example 1: show earliest shkia for this week:
- 5:43 pm
- Example 2: show earliest shkia for next week:
- 5:49 pm
- Example 1: show earliest shkia for this week:
- zman_lateshkia – Displays the latest shkia time for the week (Sunday – Thursday) in which the provided date given
- zman_fullyear* – as described in the “Full Year Display” section above, this displays a grid of times for a complete year.
- zman_early_shabbat_1* through zman_early_shabbat_4* – As described in the “Early Shabbat Options” section above, each of these will display one of two shortcode outputs for early/regular Shabbat.
- zman_misheyakirweekly – provide an array of times for misheyakir, either for this week or next week. Specific times are accessed by using the “daynum” option.
The Last Word (for now)
Going all the way back to my first “Time Data Series” post:
“What time will afternoon prayers (Mincha) be this week?” is a deceptively complex question. It’s deceptive because “afternoon prayers” seems to be self-explanatory, but (as with so many things related to Jewish religious rules (halacha) there’s a vast amount of background, commentary, and specificity required.
If answering this question has stymied you, the Zmanim WP plugin might just be able to help. For more details, including how to download, install, and upgrade to the paid version of the plugin, check out the Zmanim WP documentation on .
Published at DZone with permission of Leon Adato. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments