Implementing RBAC Configuration for Kubernetes Applications
A robust role-based access control (RBAC) system is one of the most important things any business can have since over-privileged users can be a threat to security.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSecurity is challenging to implement, and when your infrastructure is made up of many dynamic, scalable, distributed microservices running in containers, the task becomes even more complex.
Kubernetes is an open-source container orchestration technology that may be used to automate software applications' deployment, scaling, and administration. We commonly refer to these levels as the 4Cs because they are formed of distinct layers (cloud, clusters, containers, and code).
There are numerous layers in the Kubernetes stack, each of which has its own set of security issues; it is important to understand how they interact. We can't just secure the first tier of the stack and neglect the rest of the levels because each of those layers is critical to the operation of Kubernetes and must be protected as thoroughly as possible.
To secure the layers, we must design various types of mitigations, which can be difficult at times because of the complexity of the technology. Additionally, many users do not have a thorough understanding of security when it comes to Kubernetes security, which can be frustrating.
Why Implementing RBAC Is Necessary
A robust role-based access control (RBAC) system is one of the most important things any business can have since over-privileged users are a threat to an organization. Restricting privileges for users to the bare minimum required to complete job obligations, ensuring systems are set to "deny all" by default, and establishing suitable documentation describing roles and responsibilities should all be considered essential measures.
An API is used to access resources in Kubernetes. When the API makes a request to the API server, all validation performed on the request, such as accept, deny, or RBAC permissions, is performed only at that point on the API server. The Kubernetes' RBAC allows businesses to group resources, such as pods, services, nodes, clusters, and their namespaces. Consequently, after integrating resources and applying roles to them, there is a clear delineation between the duties and responsibilities of the various users.
However, suppose companies require stringent access control in addition to RBAC. In that case, they can use RBAC and node together, and combinations of both are accessible in a plugin known as NodeRestriction admission, which is available in the NodeRestriction plugin.
Kubernetes makes use of the rbac.authorization.k8s.io API to create RBAC, which dynamically configures policies and allows users to log in. For API changes to take effect, the server must be restarted after each modification is made to allow the changes to be implemented.
Scanning for RBAC Issues and Enforcing Them
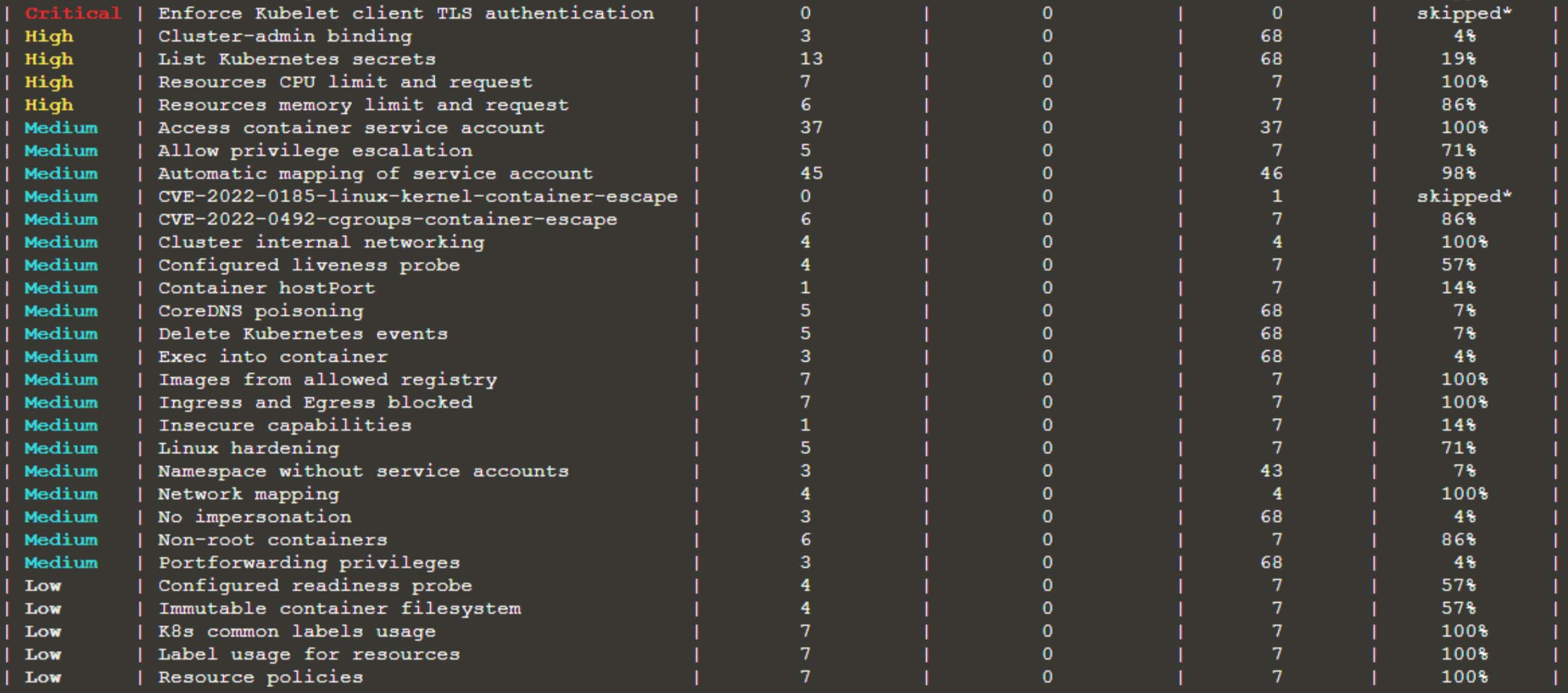
As Kubernetes is a complicated technology, it is difficult to scan and control items on the Kubernetes cluster, and managing permissions is difficult when it comes to RBAC. There are many open-source tools available on the market that can scan for RBAC concerns, but they are generally confined to advising that RBAC be enforced on a resource.
Kubescape is an open-source tool that does several types of scanning, including risk assessment, security compliance, RBAC visualization, scanning for vulnerable pictures, and completing assessments on the YAML file. In addition, it displays issues clearly and understandably, allowing you to identify and resolve them quickly.
To run the analysis on your Kubernetes cluster, you must first install it, which is a simple process that takes only a few minutes. Simply open a terminal window and enter the following command:
curl -s https://raw.githubusercontent.com/armosec/kubescape/master/install.sh | /bin/bash
Start by registering on their portal, which you can do by using your Google or GitHub account. Following your successful login, you will be presented with a number of commands to execute.
Because we have already installed Kubescape, we can skip through the first sequence of commands. Notice that I have redacted the account ID from the second command. You will be provided with your own account ID, which is extremely crucial because it informs Kuberscape as to which dashboard should be displayed.
To execute the vulnerability scan, reopen the terminal and paste the following command into it:
Kubescape scan –submit –account=<your account id>
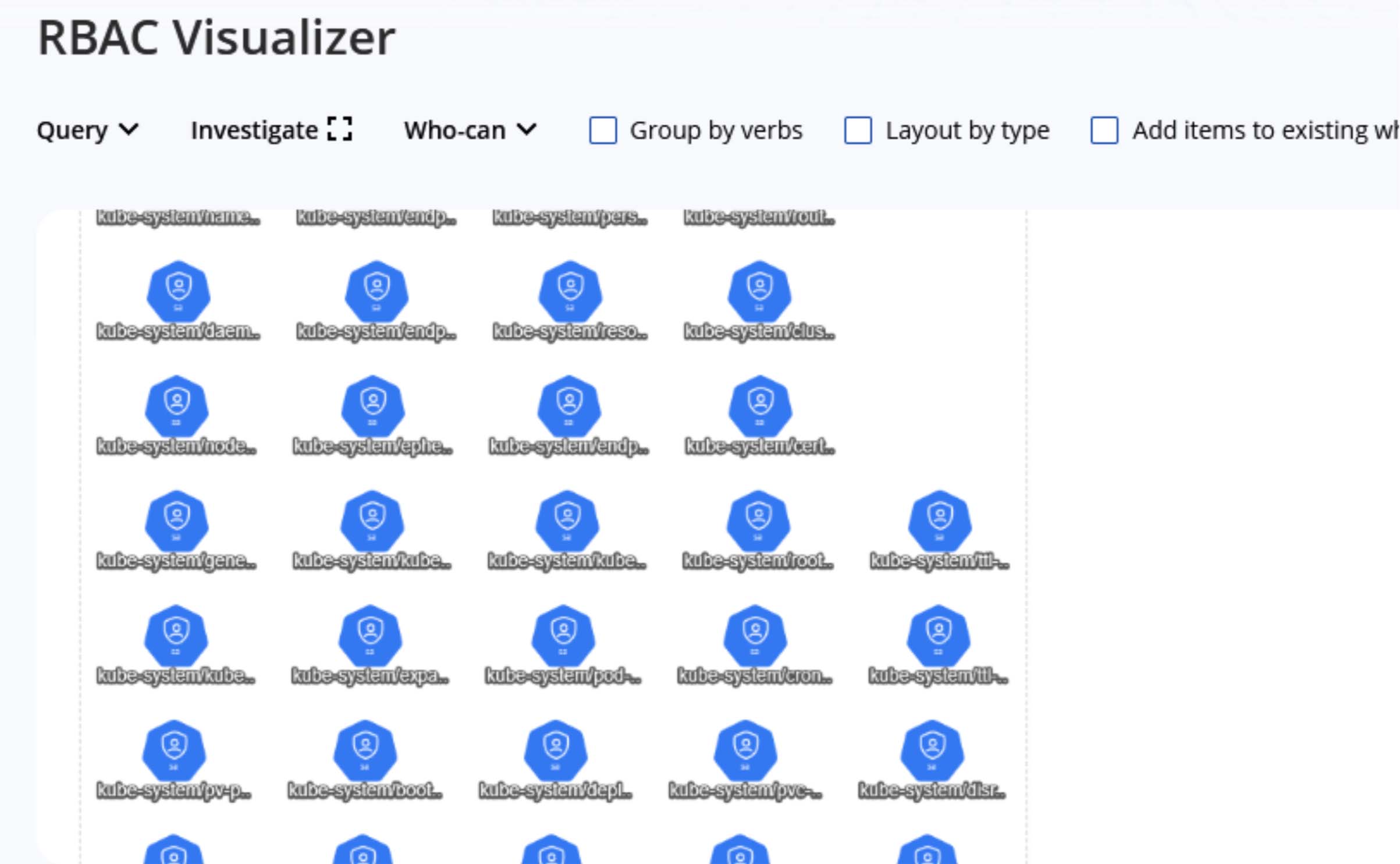
When testing for the RBAC system, there are a handful of commands that you can run. Let's execute one to visualize the RBAC system while testing for it.
kubescape submit rbac --account <your account ID>
As you can see, the command has been successfully executed and now I can see the visualization in my dashboard.
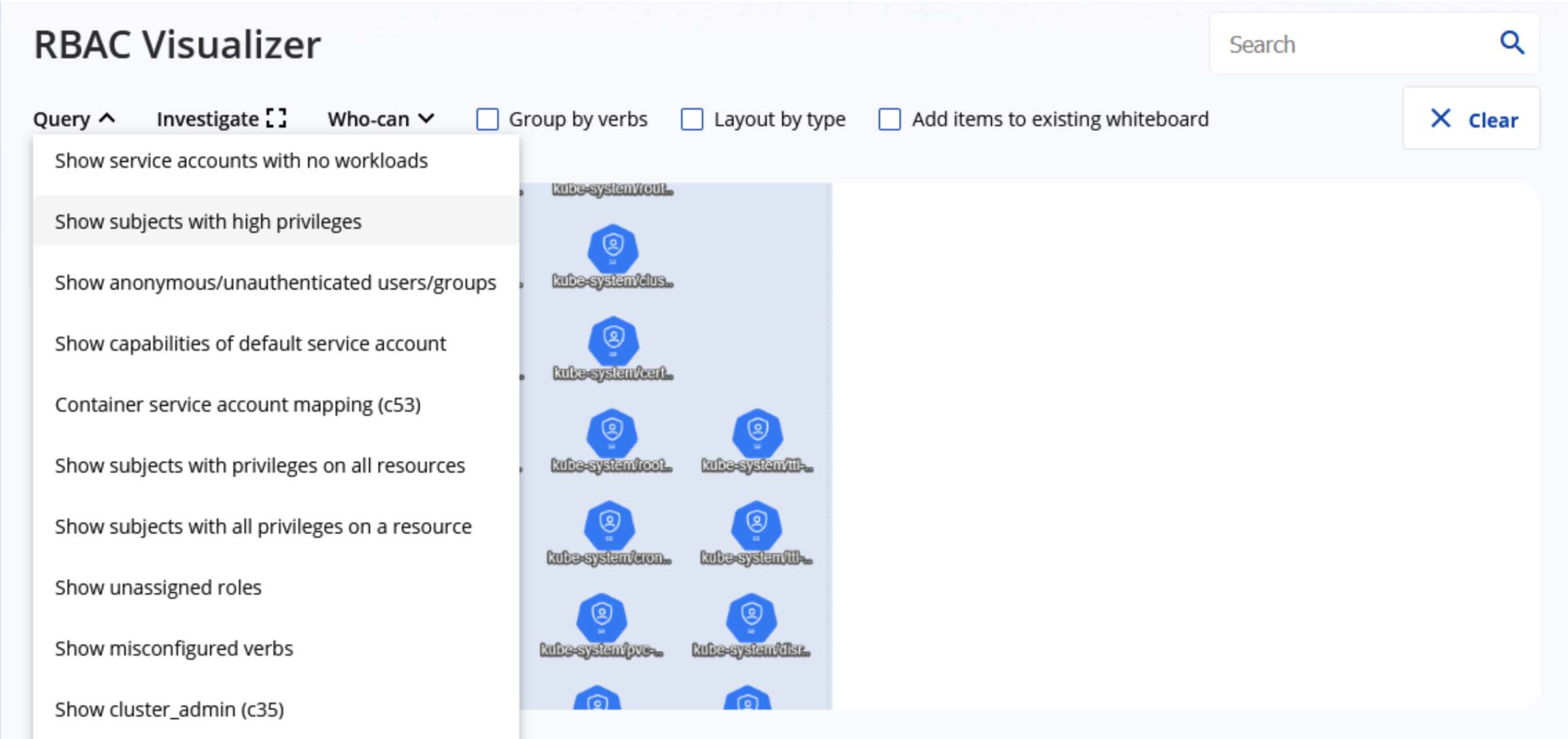
It has a lot of different queries that can be run:
To enforce RBAC, we can simply run a couple of commands. Let’s first understand how validations will be performed.
An API server in Kubernetes called Kube-apiserver is responsible for performing API object validations. RBAC must be enabled in this cluster, which means the value of the —authorization-mode argument must be set to authorization. If you want to specify other choices, use the –other-option flag. This command below can enforce the RBAC on the cluster:
kube-apiserver --authorization-mode=Cluster,RBAC --other-options
Adding permissions to a certain role, a specific user, or a group of users is a simple process. It contains a list of subjects (such as individuals, groups, or service accounts), as well as a reference to the role that is being provided to each of those topic lists. Unlike RoleBinding, which allows access to a certain namespace alone, a ClusterRoleBinding grants access to all namespaces inside the cluster.
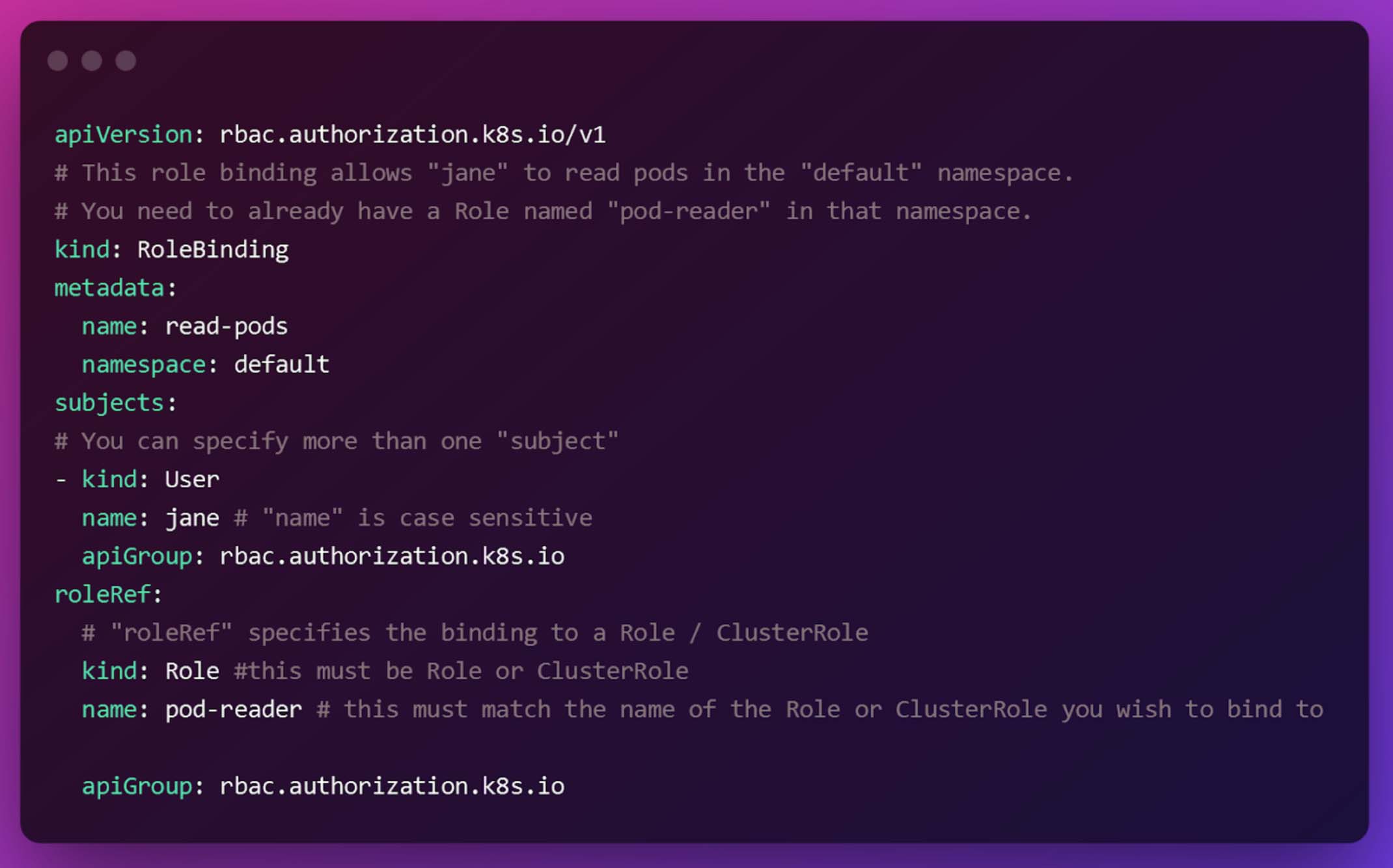
Conclusion
The Kubernetes RBAC framework enables you to implement role-based authorization on a user through the usage of the RBAC framework. For example, it can be used to ensure that developers can only access specific nodes and clusters within a given namespace, or that your infrastructure management teams have view-only access to perform monitoring activities on your infrastructure.
Unfortunately, managing RBAC in Kubernetes requires a significant amount of human labor and is not without its challenges. Few issues have been presented regarding how we may view the RBAC and enforce authorization in the most effective way possible.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments