Introduction to Apache Camel
This tutorial introduces Apache Camel's architecture and shows you how to implement some simple Camel integrations and tests.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free1.0 Overview
Apache Camel is a versatile Java-based open source enterprise service bus and supports most of the Enterprise Integration Patterns (EIP). Camel is also known as a routing and mediation engine as it effectively routes data between endpoints, while taking heavy loads like transformation of data formats, endpoint connectivity, and much more. Apache Camel provides support for bean binding and seamless integration with popular frameworks such as CDI, Spring, Blueprint, and Guice. Camel empowers you to write rules and meditation in a variety of domain-specific languages (DSL) including Java-based Fluent API, Spring or Blueprint XML Configuration files, and a Scala DSL. Apache Camel uses URIs to work directly with any kind of Transport or messaging model such as HTTP, ActiveMQ, JMS, JBI, SCA, MINA, or CXF, as well as pluggable components and data format options.
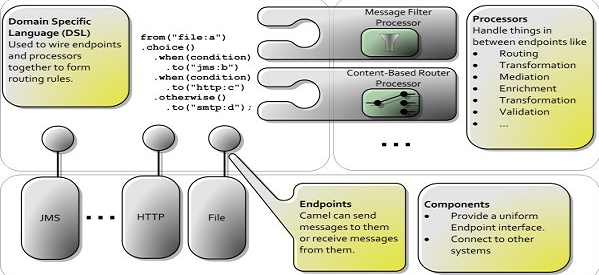
2.0 Architecture
Camel Context provides the runtime system. Processors handles things in between endpoints like routing, transformation, validation, enrichment, etc. Endpoints connects several systems to be integrated and it acts as URI or URL in a web application or destination JMS queue. Apache Camel offers different DSLs to realize the integration problems.
3.0 Download and Extract Apache Camel
Download the Apache Camel (Camel 2.19.1) from this link.
Unzip the apache-camel-x.xx.x and it will unzip all the jar files required for implementing integration solutions with Apache Camel.
4.0 Create Java Project and Add Camel Dependencies
Make sure you have Eclipse installed in your system for implementing Camel integrations.
Create a new Java project by selecting File < New < Java Project.
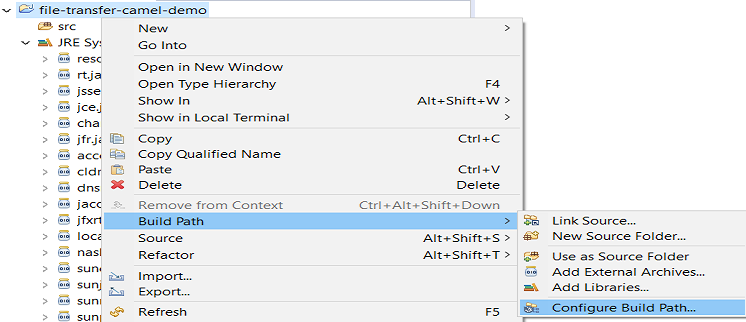
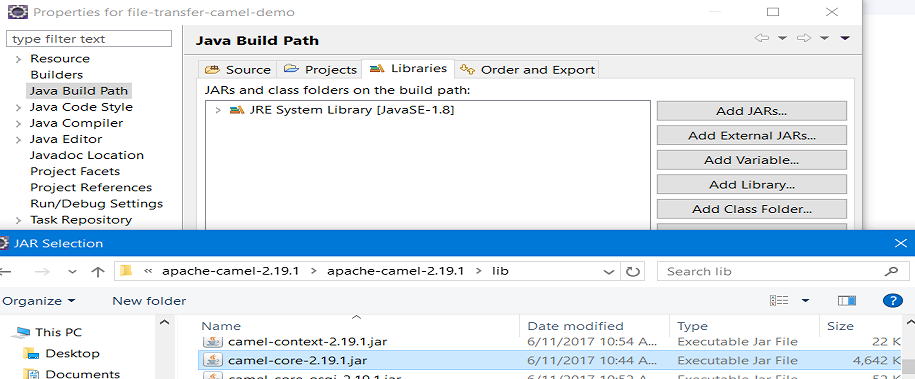
Now you need to add a jar dependency to build the path the application requires to implement Camel projects. Right click on "application" and select Build Path < Configure Build Path.
This will open a new dialog window. Now select Libraries < Add External Jars. You need to add camel-core-2.19.1.jar from the path \apache-camel-2.19.1\lib. Click OK.
5.0 Implementing Simple Apache Camel Integrations
Here we will implement a simple Apache Camel integration which transfers a file from one location to another.
Create Java class in your project and name it SimpleFileRouter.
Import the Apache Camel dependency into your Java class.
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
import org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultCamelContext;5.1 Camel Context
The CamelContext is the runtime system of Apache Camel and connects its different concepts, such as routes, components, or endpoints. Below is the Java code for initializing the Camel Context.
package com.file.demo;
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
import org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultCamelContext;
public class SimpleFileRouter {
public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception
{
CamelContext camelContext=new DefaultCamelContext();
camelContext.addRoutes(new RouteBuilder(){
});
camelContext.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
camelContext.stop();
}
}5.2 Domain Specific Language (DSLs)
Apache Camel offers various DSLs, such as Java-based Fluent API, Spring, or Blueprint XML Configuration files, and a Scala DSL. Spring XML DSL is based on the Spring framework and uses XML configuration. Java DSL has the best IDE support. Groovy and Scala DSLs are similar to the Java DSL; in addition, they offer the typical features of modern JVM languages, such as concise code or closures.
5.3 Routes
Routes are important when you're defining the Camel integration; it is defined as shown below.
package com.file.demo;
import org.apache.camel.CamelContext;
import org.apache.camel.builder.RouteBuilder;
import org.apache.camel.impl.DefaultCamelContext;
public class SimpleFileRouter {
public static void main(String [] args) throws Exception
{
CamelContext camelContext=new DefaultCamelContext();
System.out.println("Apache Camel Context Intialize....");
try
{
camelContext.addRoutes(new RouteBuilder(){
@Override
public void configure() throws Exception
{
from("file:F:\\Apache_Camel_Test\\IN?noop=true")
.to("file:F:\\Apache_Camel_Test\\OUT");
}
});
System.out.println("File Moved To Output Directory....");
camelContext.start();
Thread.sleep(5000);
camelContext.stop();
}catch (Exception Ex) {
System.out.println(Ex.toString());
}
}
}
The DSLs are very easy to use. A file will be dropped to the input directory and it will be processed and sent to out directory. Routes have extends "RouteBuilder" and override "configure" method. The route itself begins with "from" endpoints and ends at one or more "to" endpoints.
6.0 Testing
For testing, drop the file to input directory, and run your application as a Java application. Once you run the application, the file will be moved to the output directory.
7.0 Conclusion
Apache Camel is a very powerful open source ESB and it supports most of Enterprise Integration Patterns. It is very easy to implement Camel integrations.
Now you know the basic components of Apache Camel and how to implement the integration application.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments