Introduction To Git
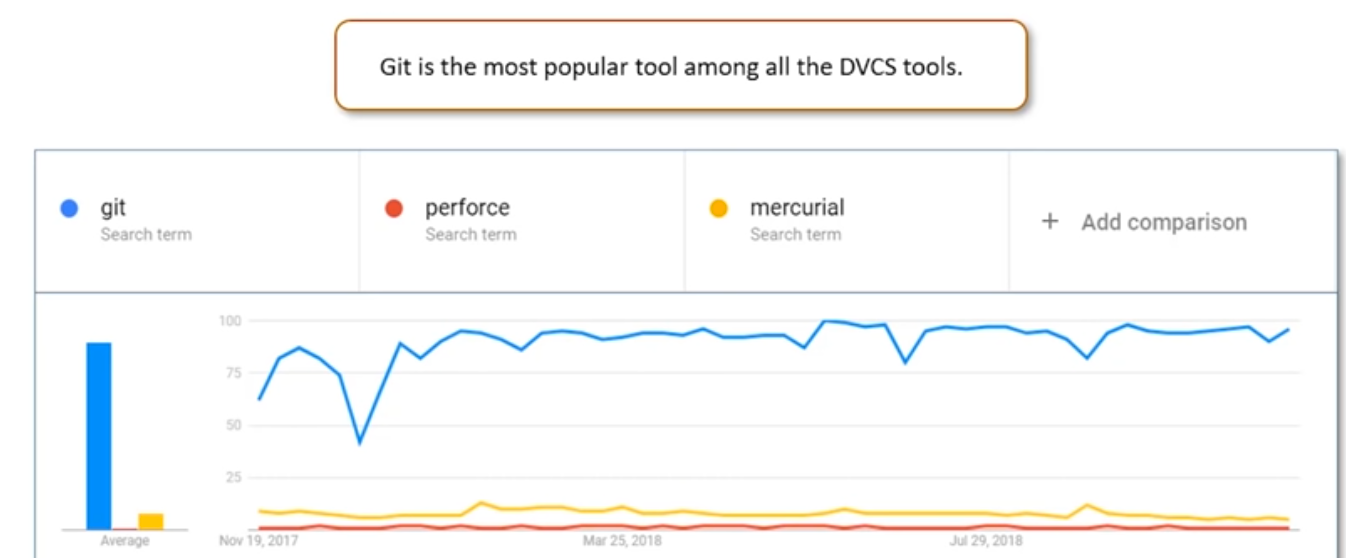
Git is a powerful version control system for tracking and managing changes to code and files collaboratively and efficiently.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeImagine you're working on a critical project, pouring hours of effort into writing code, only to accidentally delete a crucial file. Panic sets in as you realize there's no way to retrieve the previous version. But wait! Introducing Git, the superhero of version control systems. With Git, you can effortlessly track changes, revert to previous versions, collaborate seamlessly with teammates, and even branch out to experiment without fear of irreversible consequences. Git saves the day by empowering developers to confidently navigate the complex world of software development, ensuring smooth workflows and protecting precious code from the clutches of accidental deletions.
Git is a version-control system for tracking changes in computer files and coordinating work on those files among multiple people. It is primarily used for source-code management in software development, but it can be used to keep track of changes in any set of files.
How It Works
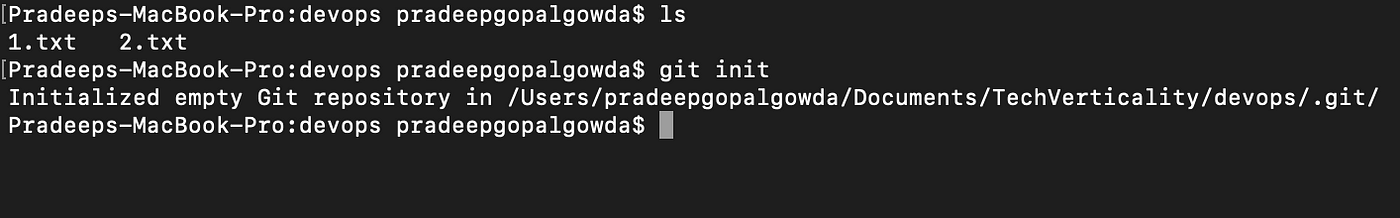
- Creating Repository: You can create a repository using the command git init. Navigate to your project folder and enter the command git init to initialize a git repository for your project on the local system.
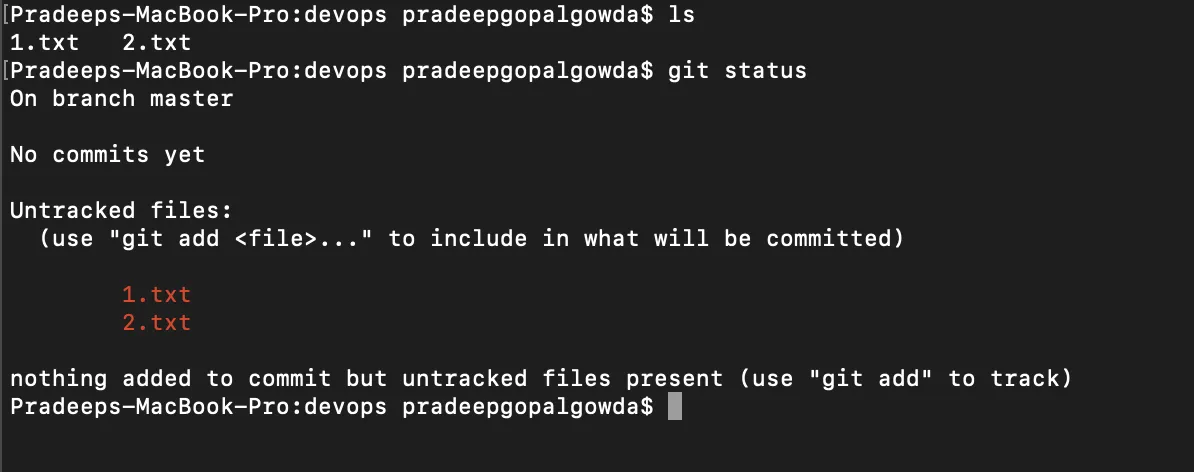
- Making Changes: Once the directory has been initialized, you can check the status of the files, whether they are being tracked by a git or not, using the command git status.
Since no files are being tracked right now, let us stage these files. For that, use the command git add, which will track all the files in the project folder.
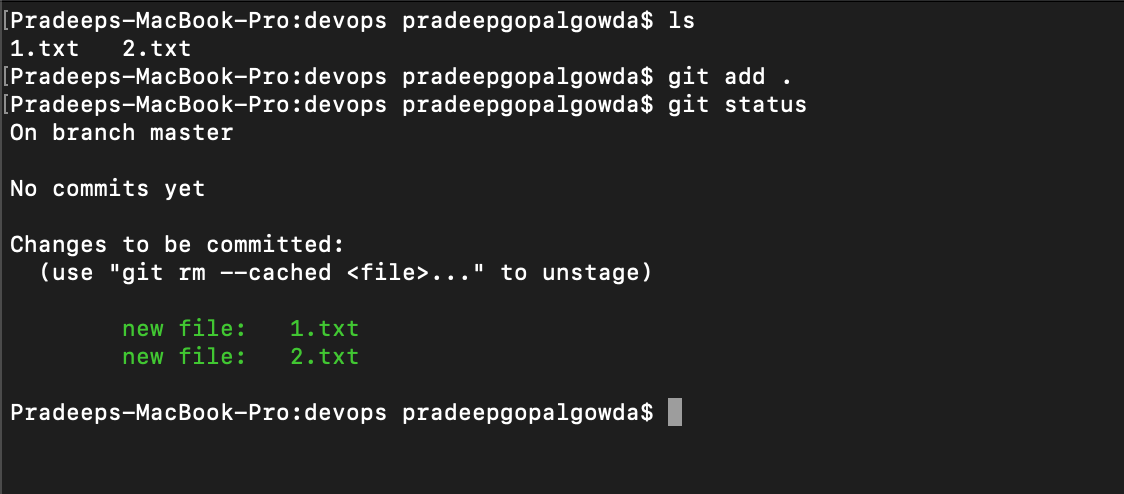 Git add
Git add
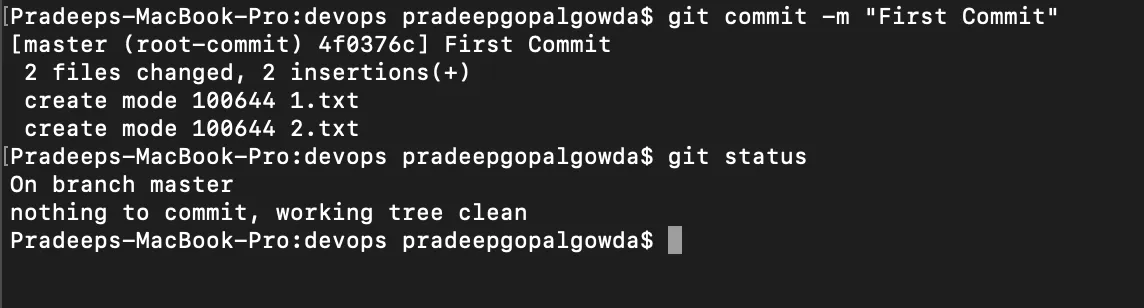
Once the files or changes have been staged, we are ready to commit them to our repository. We can commit the files using the command git commit -m "custom message."
- Syncing Repositories: Once everything is ready on our locally, we can start pushing our changes to the remote repository. Copy your repository link and paste it in the command git remote add origin "<URL to repository>." To push the changes to your repository, enter the command git push origin <branch-name>. In our case branch is master, hence git push origin master. This command will then prompt for username and password, enter the values, and hit enter.
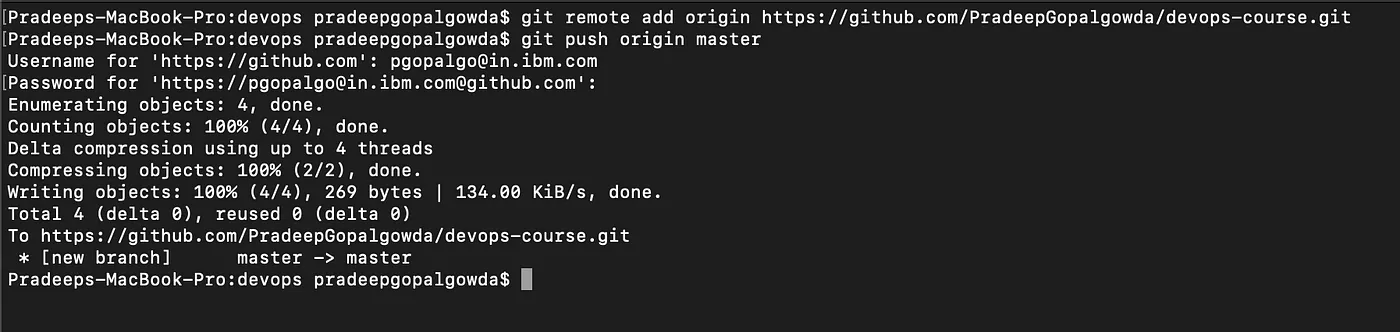
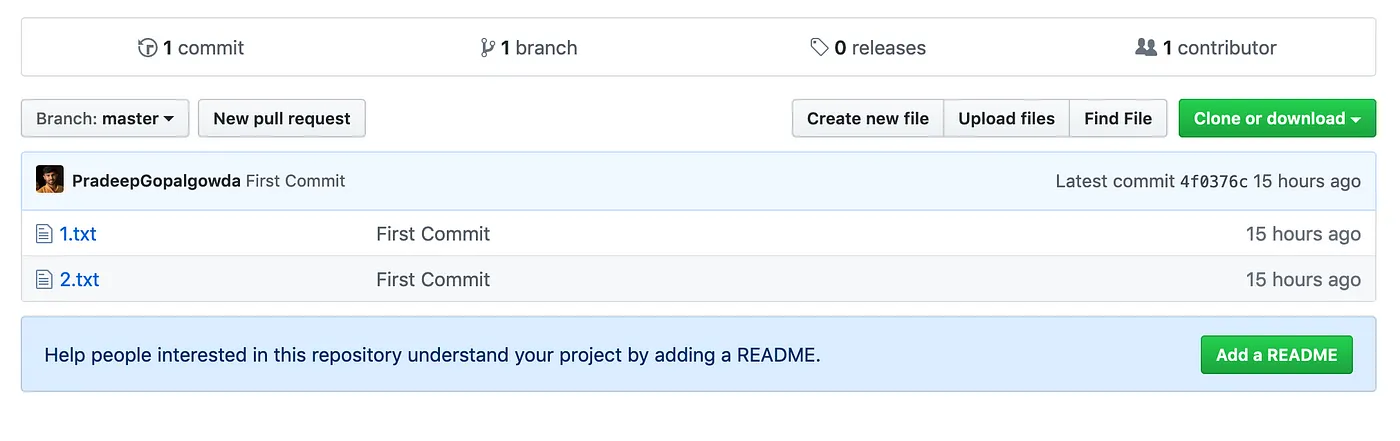
Your local repository is now synced with the remote repository on GitHub.
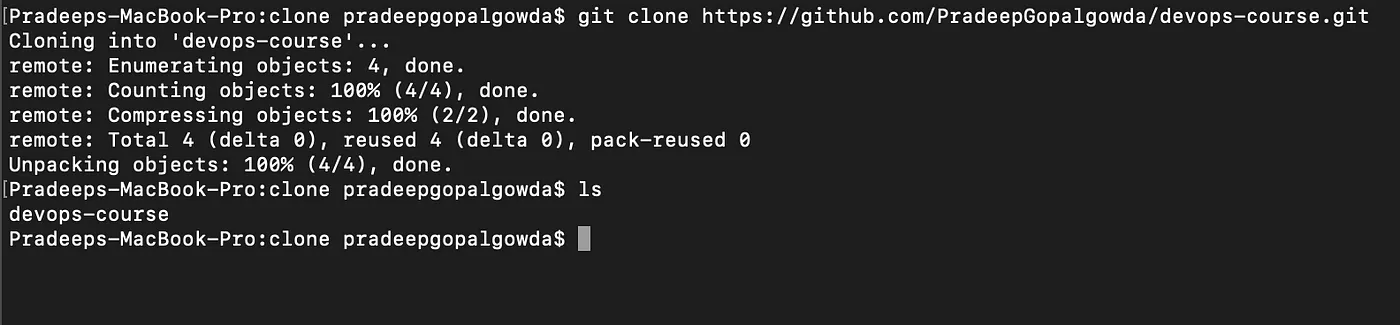
Similarly, if we want to download the remote repository to our local system, we can use the command git clone <URL>. This folder will create a folder with the repository name and download all the contents of the repository inside this folder.
The git pull command is also used for pulling the latest changes from the repository; unlike git clone, this command can only work inside an initialized git repository. This command is used when you are already working in the cloned repository, and want to pull the latest changes, that others might have pushed to the remote repository git pull <URL>.
Until now, you have seen how we can work on Git. But now, imagine multiple developers working on the same repository or project. To handle the workspace of multiple developers, we use branches. To create a branch from an existing branch, we use the command git branch <new-branch-name>. Similarly, to delete the branch git branch -D <branch-name>. To switch to the new branch, use the command git checkout <branch-name>.
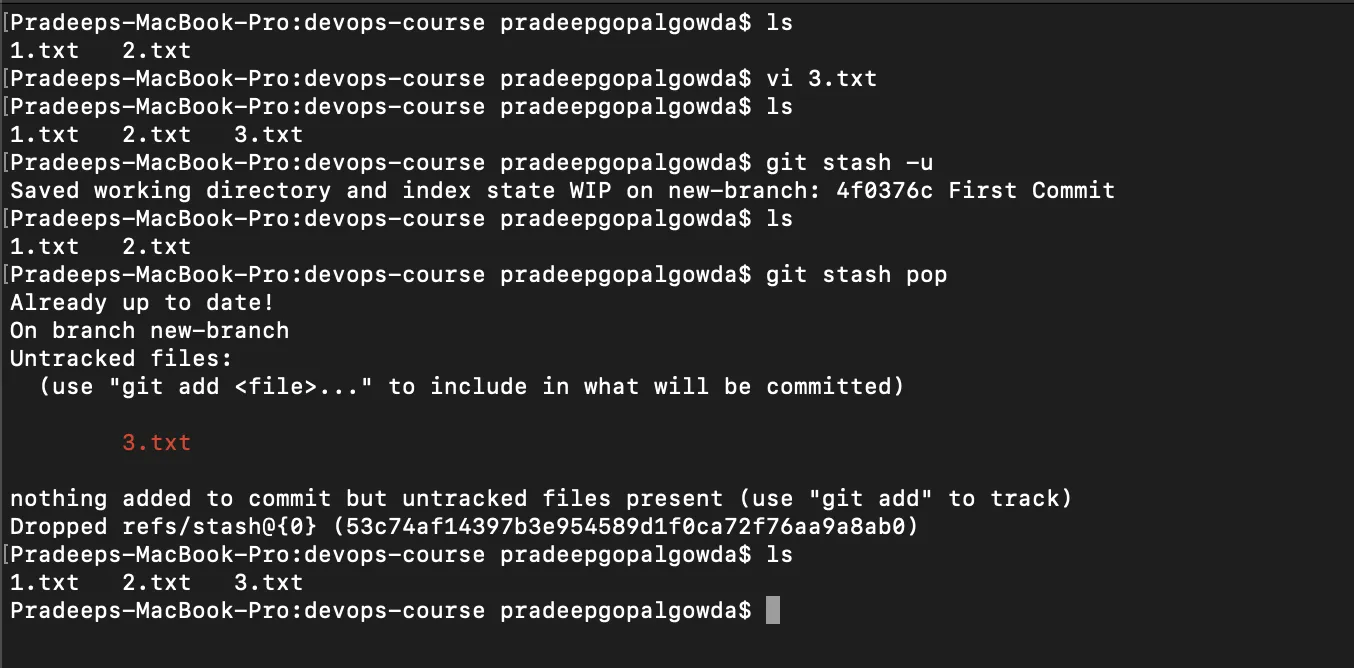
Want to save your work without committing the code? Git has got you covered. This can be helpful when you want to switch branches but do not want to save your changes to the git repository. To stash your staged files without committing, just type in git stash. If you want to stash your untracked files as well, type git stash -u. Once you are back and want to retrieve working, type in git stash pop.
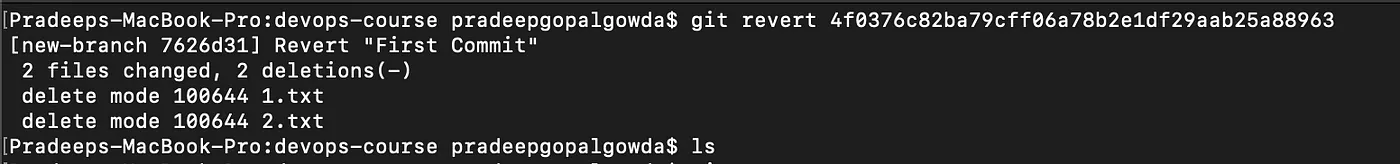
git revert command helps you in reverting a commit to a previous version git revert <commit-id>. <commit-id> can be obtained from the output of git log.
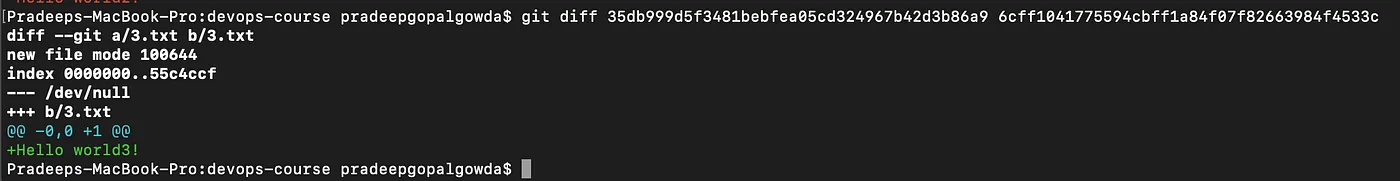
git diff command helps us in checking the differences between 2 versions of a file. git diff <commit-id of version x> <commit-id of version y>
In conclusion, Git is an essential tool for developers and teams, providing efficient and reliable version control capabilities that facilitate collaboration, track changes, and simplify the management of code and files throughout a project's lifecycle. It's versatility and robust features make it a valuable asset in software development and other industries where version control is crucial.
Published at DZone with permission of Pradeep Gopalgowda. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments