Introduction to Spring Data JPA - Part 5 Unidirectional One to One Relations
In the next article in this series, we take a look at unidirectional one-to-one relations with CRUD operations.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeUnidirectional One to One Relations
We will discuss the following:
- Unidirectional One to One Relations
- All CRUD Operations - CREATE, READ, UPDATE, DELETE
Let us model the entities. I have chosen different entities this time. Let us talk about the organization and address. Every organization will be associated with an address. So you can call it a one-to-one relation. Let us model the model entities as a unidirectional relation.
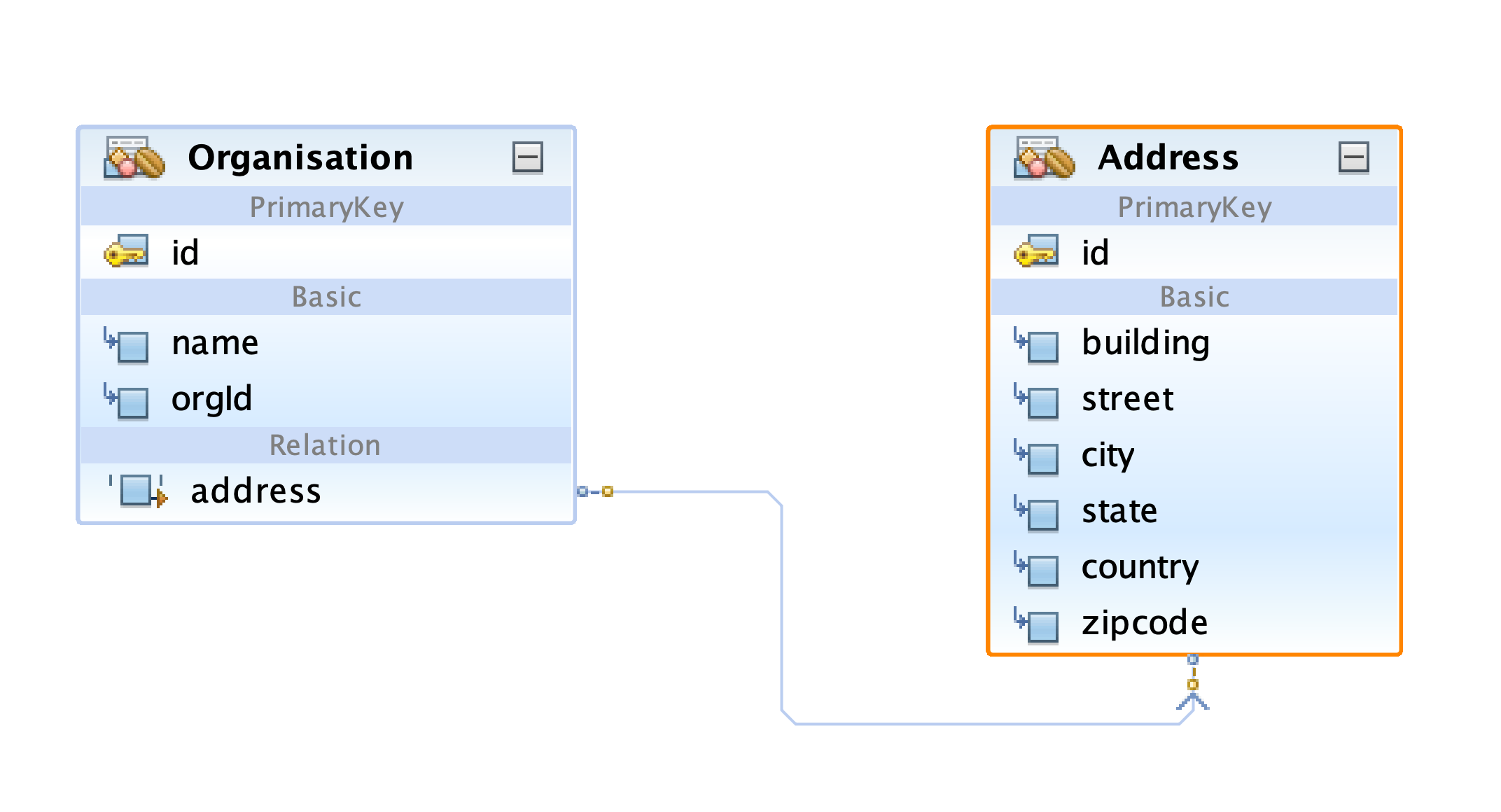
You can find a reference to address entity in the organization entity but no reference to the organization entity in the address entity, so we call it a unidirectional relation.
Now let us look at the default tables created by Hibernate.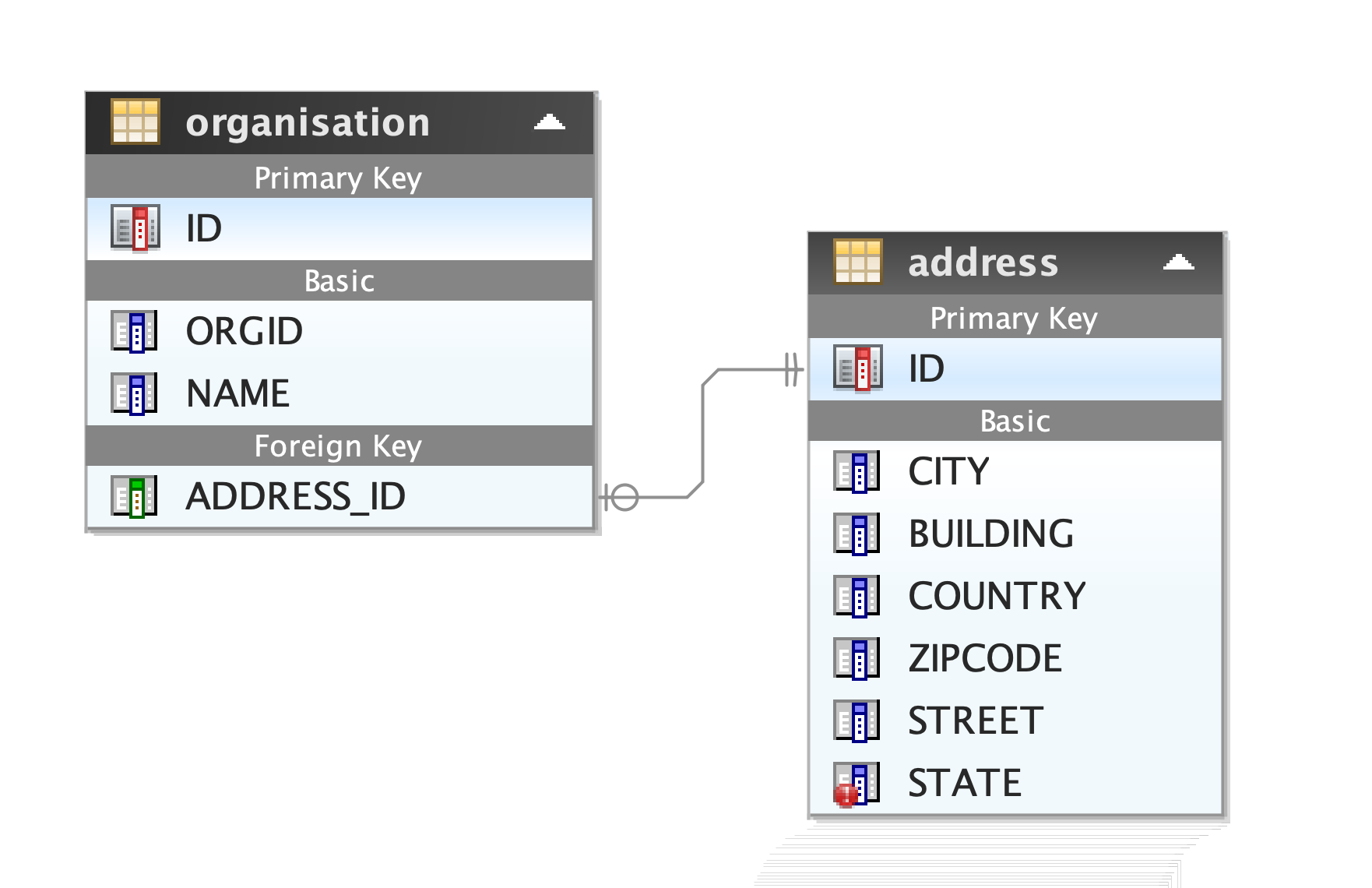 You can see the foreign key reference
You can see the foreign key reference (address_id) in the organization table.
Now let us write the code.
Organization Entity
package com.notyfyd.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
(name = "t_organization")
public class Organization {
(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String name;
private String orgId;
(targetEntity = Address.class, cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private Address address;
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getName() {
return this.name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getOrgId() {
return this.orgId;
}
public void setOrgId(String orgId) {
this.orgId = orgId;
}
public Address getAddress() {
return this.address;
}
public void setAddress(Address address) {
this.address = address;
}
}
@OneToOne(targetEntity = Address.class, cascade = CascadeType.ALL)
private Address address; are how you define a one-to-one mapping.
Address Entity
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.notyfyd.entity;
import javax.persistence.*;
(name = "t_address")
public class Address {
(strategy = GenerationType.IDENTITY)
private Long id;
private String building;
private String street;
private String city;
private String state;
private String country;
private String zipcode;
public Long getId() {
return this.id;
}
public void setId(Long id) {
this.id = id;
}
public String getBuilding() {
return this.building;
}
public void setBuilding(String building) {
this.building = building;
}
public String getStreet() {
return this.street;
}
public void setStreet(String street) {
this.street = street;
}
public String getCity() {
return this.city;
}
public void setCity(String city) {
this.city = city;
}
public String getState() {
return this.state;
}
public void setState(String state) {
this.state = state;
}
public String getCountry() {
return this.country;
}
public void setCountry(String country) {
this.country = country;
}
public String getZipcode() {
return this.zipcode;
}
public void setZipcode(String zipcode) {
this.zipcode = zipcode;
}
}
Address Repository
package com.notyfyd.repository;
import com.notyfyd.entity.Address;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
public interface AddressRepository extends JpaRepository<Address,Long> {
}
Organization Repository
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.notyfyd.repository;
import com.notyfyd.entity.Organization;
import org.springframework.data.jpa.repository.JpaRepository;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;
public interface OrganizationRepository extends JpaRepository<Organization, Long> {
}
Organization Service
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.notyfyd.service;
import com.notyfyd.entity.Organization;
import com.notyfyd.repository.AddressRepository;
import com.notyfyd.repository.OrganizationRepository;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;
import org.springframework.transaction.annotation.Transactional;
public class OrganizationService {
private OrganizationRepository organizationRepository;
private AddressRepository addressRepository;
public OrganizationService(OrganizationRepository organizationRepository, AddressRepository addressRepository) {
this.organizationRepository = organizationRepository;
this.addressRepository = addressRepository;
}
public ResponseEntity<Object> createOrganization(Organization organization) {
Organization org = new Organization();
org.setName(organization.getName());
org.setOrgId(organization.getOrgId());
org.setAddress(organization.getAddress());
Organization savedOrg = organizationRepository.save(org);
if(organizationRepository.findById(savedOrg.getId()).isPresent())
return ResponseEntity.ok().body("Organization created successfully.");
else return ResponseEntity.unprocessableEntity().body("Failed to create the organization specified.");
}
public ResponseEntity<Object> updateOrganization(Long id, Organization org) {
if(organizationRepository.findById(id).isPresent()) {
Organization organization = organizationRepository.findById(id).get();
organization.setName(org.getName());
organization.setOrgId(org.getName());
addressRepository.deleteById(organization.getAddress().getId());
organization.setAddress(org.getAddress());
Organization savedOrganization = organizationRepository.save(organization);
if(organizationRepository.findById(savedOrganization.getId()).isPresent())
return ResponseEntity.ok().body("Successfully Updated Organization");
else return ResponseEntity.unprocessableEntity().body("Failed to update the specified Organization");
} else return ResponseEntity.unprocessableEntity().body("The specified Organization is not found");
}
}
UPDATE Operation ( updateOrganization method)
Here, you find the organization by its Id, and you will use setters to set the name and organisation Id. We use the findById method again to get the address. I am using the delete method to delete the address, and then I am setting the new address with the setter method. Finally, the organization is saved. Since we are setting the cascade type to "ALL," the address is saved automatically. This way of updating brings up an issue. The primary key of the address will be changed. This might work for some cases but not a good practice. Let us correct this by modifying the update method.
Organization Controller
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.notyfyd.controller;
import com.notyfyd.entity.Organization;
import com.notyfyd.repository.OrganizationRepository;
import com.notyfyd.service.OrganizationService;
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.*;
import java.util.List;
public class OrganizationController {
private OrganizationService organizationService;
private OrganizationRepository organizationRepository;
public OrganizationController(OrganizationService organizationService, OrganizationRepository organizationRepository) {
this.organizationService = organizationService;
this.organizationRepository = organizationRepository;
}
("/organization/create")
public ResponseEntity<Object> createOrganization( Organization organization) {
return organizationService.createOrganization(organization);
}
("/organization/delete/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Object> deleteOrganization( Long id) {
if(organizationRepository.findById(id).isPresent()) {
organizationRepository.deleteById(id);
if (organizationRepository.findById(id).isPresent())
return ResponseEntity.unprocessableEntity().body("Failed to delete the specified organization");
else return ResponseEntity.ok("Successfully deleted the specified organization");
} else return ResponseEntity.unprocessableEntity().body("Specified organization not present");
}
("/organization/get/{id}")
public Organization getOrganization( Long id) {
if(organizationRepository.findById(id).isPresent())
return organizationRepository.findById(id).get();
else return null;
}
("/organization/get")
public List<Organization> getOrganizations() {
return organizationRepository.findAll();
}
("/organization/update/{id}")
public ResponseEntity<Object> updateOrganization( Long id, Organization org) {
return organizationService.updateOrganization(id, org);
}
}
We are using @PutMapping for the UPDATE operation.
Run the application. Open Postman and send in the requests.
CREATE - JSON Object
xxxxxxxxxx
{
"name": "Nooble Academy",
"orgId": "NAL",
"address": {
"building": "XII/706-A",
"street": "Andheri",
"city": "Mumbai",
"state": "Maharashtra",
"zipcode": "400703",
"country": "India"
}
}
When we send the request we will get that the organization is created successfully. You can use the GET requests to verify the same. We have the API'S which gives all the the organization and also methods that gives you the organization given the ID.
UPDATE - JSON Object
xxxxxxxxxx
{
"name": "Nooble Academy Pvt Ltd",
"orgId": "NAL",
"address": {
"building": "XII/706-A",
"street": "Andheri West",
"city": "Mumbai",
"state": "Maharashtra",
"zipcode": "400703"
}
}
Use PUT to send the request and a success message is returned.
Please find the source code here.
Modified UPDATE method
xxxxxxxxxx
public ResponseEntity<Object> updateOrganization(Long id, Organization org) {
if(organizationRepository.findById(id).isPresent()) {
Organization organization = organizationRepository.findById(id).get();
organization.setName(org.getName());
organization.setOrgId(org.getName());
Address address = addressRepository.findById(organization.getAddress().getId()).get();
address.setBuilding(organization.getAddress().getBuilding());
address.setStreet(organization.getAddress().getStreet());
address.setCity(organization.getAddress().getCity());
address.setState(organization.getAddress().getState());
address.setCountry(organization.getAddress().getCountry());
address.setZipcode(organization.getAddress().getZipcode());
Address savedAddress = addressRepository.save(address);
organization.setAddress(savedAddress);
Organization savedOrganization = organizationRepository.save(organization);
if(organizationRepository.findById(savedOrganization.getId()).isPresent())
return ResponseEntity.ok().body("Successfully Updated Organization");
else return ResponseEntity.unprocessableEntity().body("Failed to update the specified Organization");
} else return ResponseEntity.unprocessableEntity().body("The specified Organization is not found");
}
When we use this method the Id of the address will not get altered. You should try both and see the difference.
Please find source code at here.
Please find the video tutorials here:
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments