A Look at Java Collections
In a kickoff to a series on the Java Collections framework, we look at the hierarchy and an overview of uses. It's more than just generic lists, maps, and sets!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThe Java Collections framework is an architecture for storing, managing, and manipulating collections of objects. It provides many data structures and algorithms commonly used for dealing with collections — searching and sorting, for instance. Many details about storing objects are abstracted away (meaning you do not have to deal with it in code). A unified interface is provided to manipulate them, for example for adding and removing entries.
The Collections Hierarchy
The Collections Framework is organized into a class hierarchy, which can be understood at a glance from the picture below.
Note: The hierarchy shown below includes only the most common and useful classes and interfaces. Some have been skipped to facilitate easier understanding.
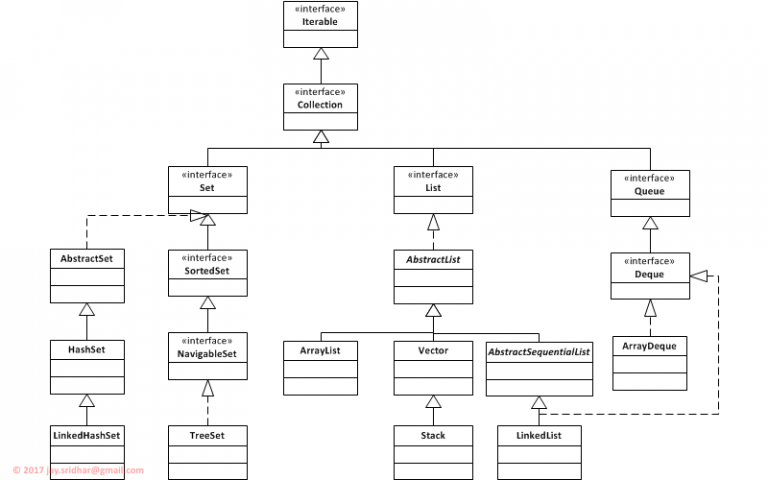
Java Collections Framework
A Brief Introduction to Collections
- At the root of the hierarchy is Iterable which, as the name indicates, provides for iterating over the collection.
- The next is the Collection interface, which provides most of the methods representing a collection. These methods include providing for adding and removing elements, checking if the collection includes an element, and obtaining the number of elements in the collection.
- A Set contains no duplicate elements. Common implementations are:
- HashSet does not provide any ordering of the elements in the Set.
- LinkedHashSet maintains a double-linked list of the elements and thus provides a predictable iteration order.
- TreeSet which uses a comparator function to maintain element ordering.
- A List is an ordered sequential collection. Concrete implementations include:
- ArrayList is a re-sizable list backed by an array.
- Vector is also a re-sizable array similar to an ArrayList. Use it only when you need thread-safety and synchronization.
- Stack is a LIFO(Last-In-First-Out) array. A subclass of Vector and is also thread-safe.
- LinkedList is a doubly linked list of elements. Offers fast adds and removes from intermediate positions. Note that this class also implements the Deque interface.
- A Queue orders elements in a FIFO (First-In-First-Out) order. The add() method adds elements at the tail and remove() removes elements from the head. Typical usage is storage to hold elements before processing in the order of receipt.
- On the other hand, a Deque (Double-Ended-Queue) can add and remove elements at both ends.
- ArrayDeque is an implementation of Deque using an array for storage.
- A LinkedList is also a Deque.
Summary
This article presented a brief overview of the Java Collections hierarchy. In further articles, we explore the various collection classes and their usage.
If you enjoyed this article and want to learn more about Java Collections, check out this collection of tutorials and articles on all things Java Collections.
Published at DZone with permission of Jay Sridhar, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments