JMeter Tutorial for Beginners
Get started with load testing in this JMeter tutorial.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIt is important to ensure effective performance for software applications, and software testing is often required to ensure that the application runs without any failures. This blog on JMeter will provide in-depth knowledge about this load testing tool for analyzing and measuring the performance in the following sequence. Let's get started.
What Is Performance Testing?
It is very important to verify whether the product meets expected or required performance. Unfortunately, we figure out this pitfall post delivery of the product. But performance has become an inevitable factor nowadays, especially for web and mobile applications as the user strength is very huge for each application.
Performance testing is defined as a type of software testing to ensure that software applications will perform well under their expected workload. It focuses on certain factors of a software program such as:
- Speed — It checks whether the response of the application is fast.
- Scalability — It determines the maximum user load.
- Stability — It checks if the application is stable under varying loads.
Now, let's move ahead with our JMeter tutorial and find out some of the best tools used for performance testing.
Tools Used for Performance Testing
Performance testing is significant in real time, particularly from the point of view when it comes to customer satisfaction. There are several performance testing tools available, such as:
- Apache JMeter
- LoadRunner
- WebLOAD
- LoadUI
- LoadView
- NeoLoad
JMeter is one of the most preferred tools for performance testing. So, let's move ahead with our tutorial to learn more about the particular testing tool.
What Is JMeter?
Apache JMeter is a testing tool used for analyzing and measuring the performance of different software services and products. It is a pure Java open-source software used for testing web applications or FTP applications.
It is used to execute performance testing, load testing, and functional testing of web applications. JMeter can also simulate a heavy load on a server by creating tons of virtual concurrent users to web server.
How Does JMeter Perform Testing?
Let's have a look at the different steps performed by JMeter during testing:
- It creates a request and sends it to the server.
- It receives the response from server, collects them, and visualizes those details in a chart or graph.
- It processes the response from the server.
- It generates the test result in several formats such as text, XML, and JSON so that the tester can analyze data.
Now, let's move ahead with our JMeter tutorial and find out what makes JMeter one of the most preferred tools for testing.
Advantages of JMeter
Apache JMeter is open-source software that fills a big void by making the testing process easy. Some of the advantages of JMeter include:
Open-source — JMeter is an open-source software. This means that it can be downloaded free of cost. It is also a 100 percent pure Java application. The developer can use its source code and can modify and customize it as per their requirement.
User-friendly — JMeter has a comprehensive GUI, which helps to create a test plan and configure the elements. Adding elements is also easy. You just have to right-click on the tree scenario and add what you need to do.
Support — Basically, it is designed for performance testing but also supports other non-functional tests such as stress testing, distributed testing, web service testing, etc. by creating test plans.
Comprehensive Documentation — This is one of the most important things to be highlighted. Because of its robust documentation, a user can have a clear idea on each and every step starting from scratch, including installation and configuration of the test settings and generating final report.
Recording — JMeter allows users to record HTTP/HTTPS to create a test plan using the recording facility. We use the Proxy Server that allows JMeter to watch and record your actions while browsing your web application with your normal browser.
Reporting — JMeter supports dashboard report generation. A host of reports are generated through JMeter, which helps the user to understand performance test execution results.
JMeter Tutorial
Now that you know what JMeter is and why we prefer this testing tool over other tools, let's move ahead and focus on the following:
JMeter Installation Process
Let's have a look at the steps involved in the installation process of JMeter:
Step 1 — Install Java
JMeter is a pure Java desktop application and it requires a fully compliant JVM 6 or higher. You can download and install the latest version of Java SE Development Kit.
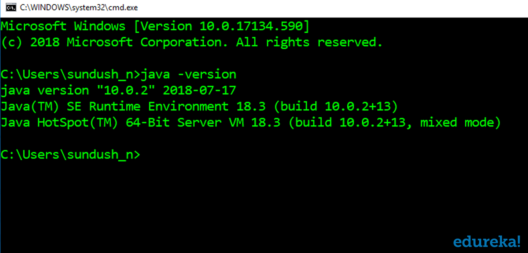
You can check in the command prompt if the installation is successful. It will give you the following output:
 Step 2 — Download JMeter
Step 2 — Download JMeter
The latest version of JMeter available is 5.1. You can download any of the binaries.
Step 3 — Install JMeter
Installation of JMeter is extremely easy and simple. You simply unzip the zip/tar file into the directory where you want JMeter to be installed. There is no tedious installation screen to deal with.
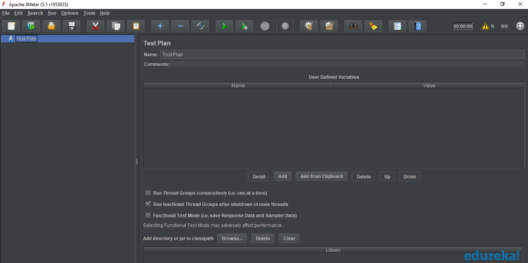
If you are using Window, just run the file /bin/jmeter.bat to start JMeter in GUI mode:
Now that you have learned about the installation process of JMeter, let's move ahead with the next part of our JMeter tutorial — the different elements of JMeter.
Elements of JMeter
The different components of JMeter are called elements. Each element is designed for a specific purpose. Some of the main elements are:
- Thread Group
- Samplers
- Listeners
- Configuration
Thread Group
Thread Groups is a collection of Threads. Each thread represents one user using the application under test. It simulates one real user request to the server. The controls for a thread group also allow you to set the number of threads for each group.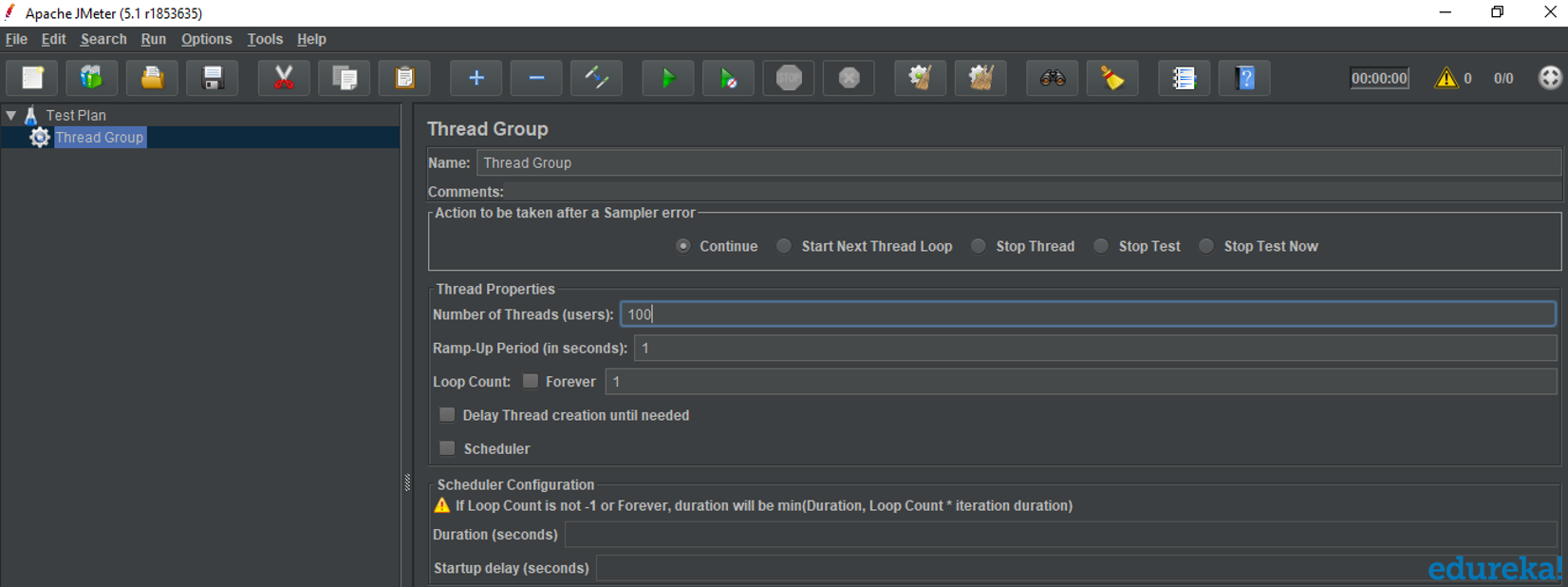
For example, if you set the number of threads as 100, JMeter will create and simulate 100 user requests to the server under test.
Samplers
JMeter supports testing HTTP, FTP, JDBC, and many more protocols. Thread Groups simulate the user request to the server. Samplers help the Thread Group know which type of requests (HTTP, FTP, etc.) it needs to make.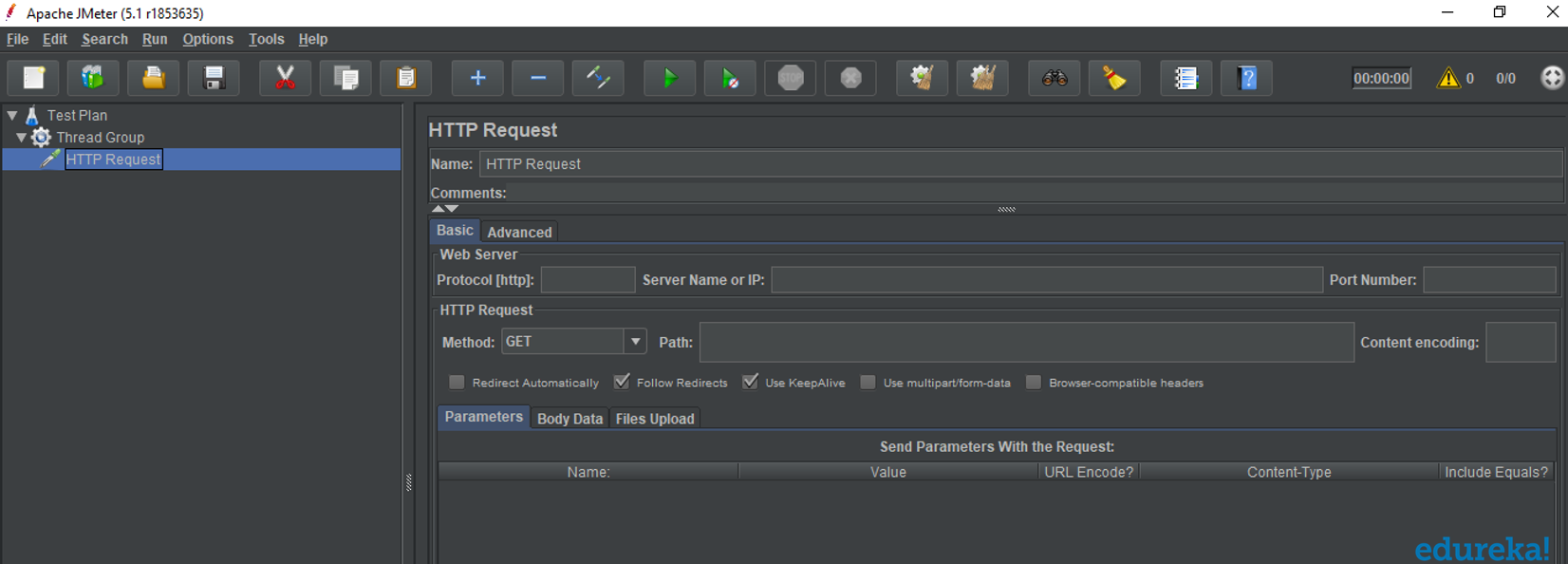
- FTP request: You can use an FTP request sampler in JMeter to do a performance test on an FTP server. This controller lets you send an FTP "download file" or "upload file" request to an FTP server.
- HTTP request: This sampler lets you send an HTTP/HTTPS request to a web server.
- JDBC request: This sampler lets you execute database performance testing. It sends a JDBC Request to a database.
- BSF Sampler: This sampler allows you to write a sampler using a BSF scripting language.
- Access Log Sampler: This sampler allows you to read access logs and generate HTTP requests.
- SMTP Sampler: This sampler is used to send email messages using the SMTP protocol.
Listeners
Listeners show the results of the test execution. They can show results in a different format such as a tree, table, graph, or log file.
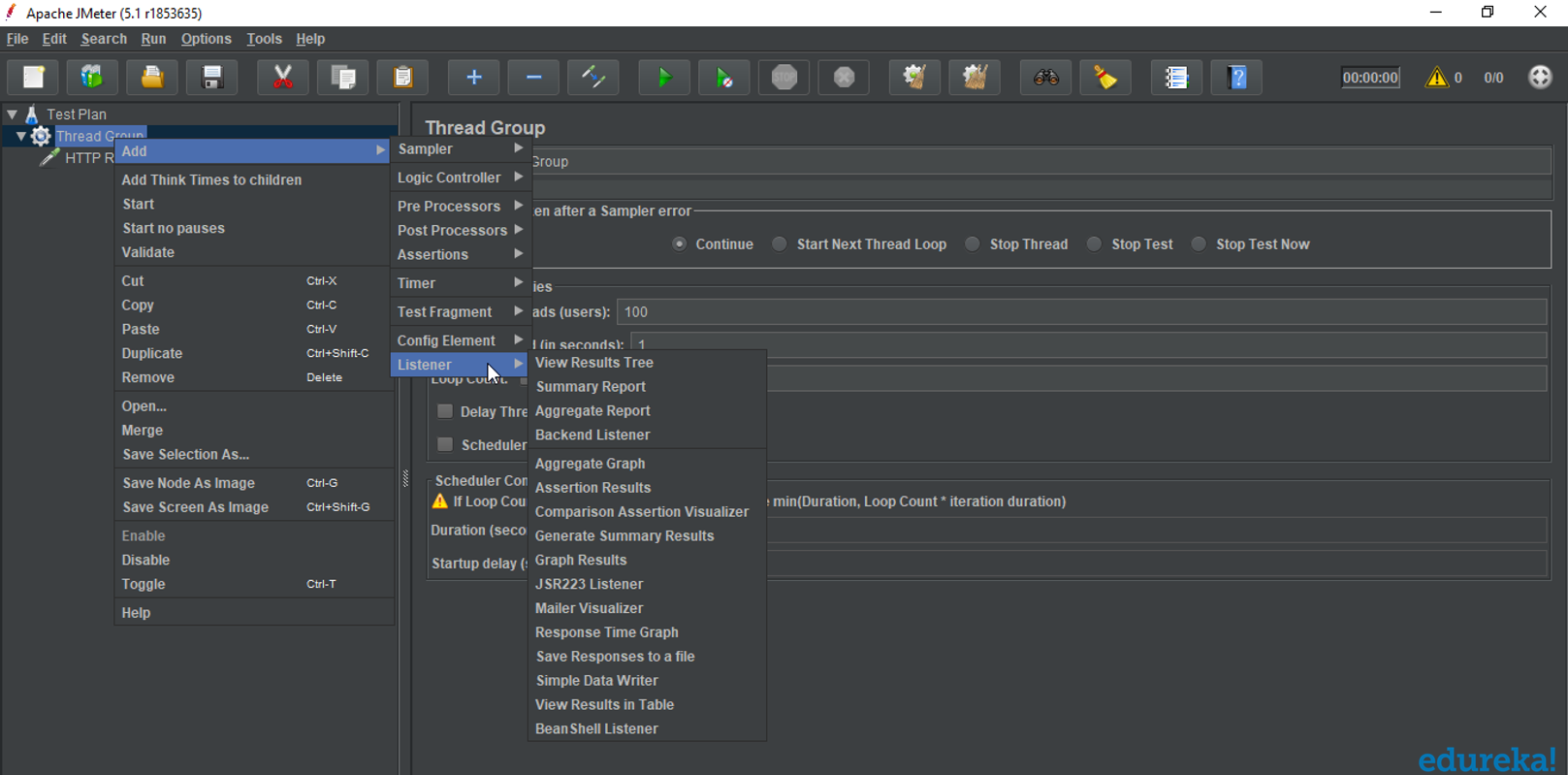
- Graph result listeners display the server response times on a graph
- View Result Tree show results of the user request in basic HTML format
- Table Result show summary of a test result in table format
- Log show summary of a test results in the text file
Configuration Elements
Configuration Elements are used to set up defaults and variables for later use by samplers.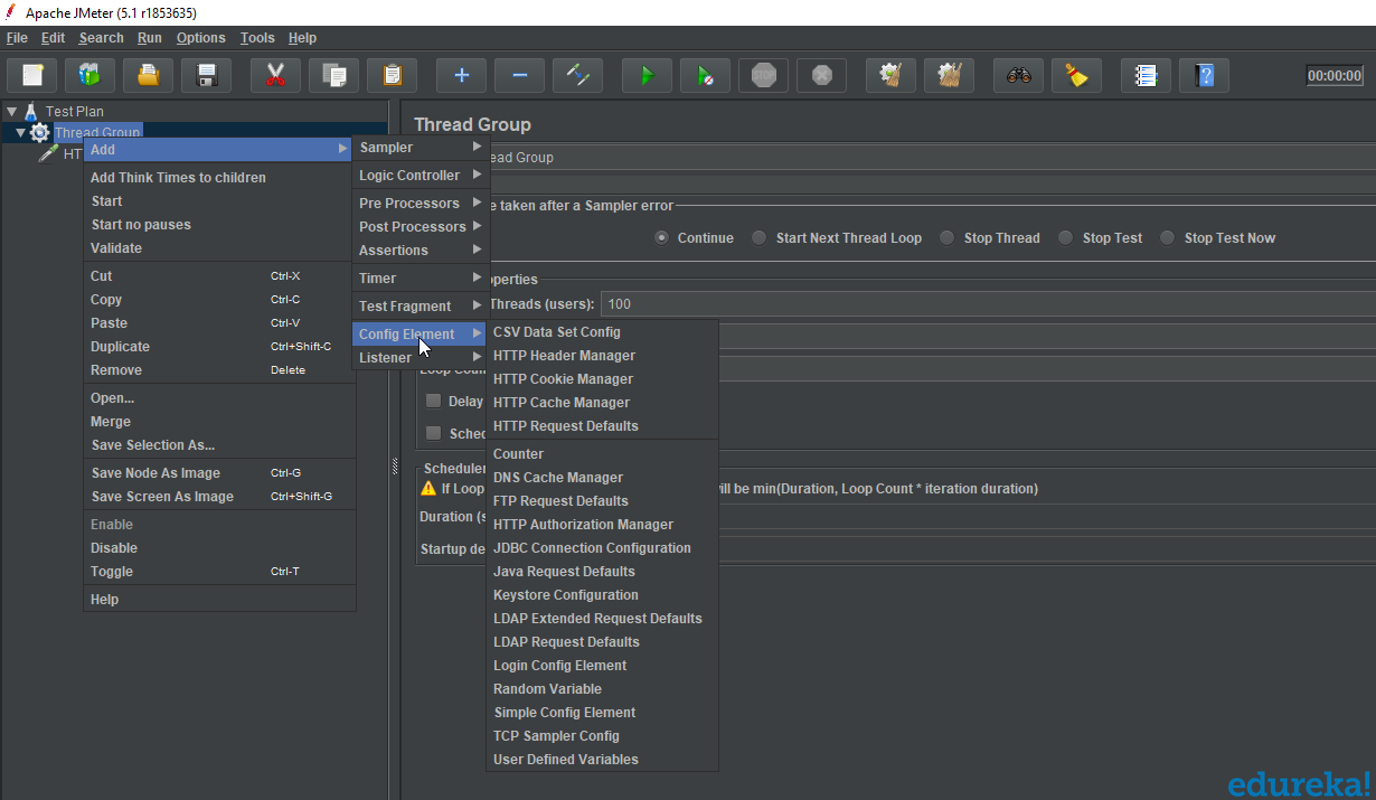
- CSV Data Set Config: TheCSV Data Set Config allows you to read different parameters from text file. It is used to read lines from a file, and split them into variables.
- HTTP Cookie Manager: HTTP Cookie Manager has the same feature as a web browser. If you have an HTTP Request and the response contains a cookie, the Cookie Manager automatically stores that cookie to use it for all future requests.
- HTTP request default: This element lets you set default values that your HTTP Request controllers use.
- Login Config Element: The Login Config Element lets you add or override username and password settings in samplers.
That's all for this JMeter tutorial. I hope you enjoyed this article and better understand what performance testing is and how JMeter works.
If you have any questions or feedback, please feel free to leave a comment below!
Happy testing!
Published at DZone with permission of Sayantini Deb, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments