Low-Code Approach to Application Development: Exploring Low Code vs. No Code, Tools, Benefits, Challenges, and Design Patterns
Take a look into the details of low-code and no-code application development methodologies, business use cases, challenges, and future predictions.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis is an article from DZone's 2023 Development at Scale Trend Report.
For more:
Read the Report
Traditional software development involves a lot of manual coding, which requires technical experts who can design and develop applications from scratch. Although it is more flexible, those methods are time-consuming, costly, and complex. Today, enterprises are seeking to expedite their application development procedures whilst catering to customer demands. It's for this reason that the low-code approach has become an efficient solution.
Low-code platforms have a relatively short history that started around early 2000 and stemmed from rapid application development tools. With the increasing popularity and advantages, low-code platforms and tools are continuously evolving to cater to a wide variety of domains and personas.
This article will look into the details of various low-code and no-code application development methodologies, business use cases, challenges, and future predictions, with a primary focus of low code.
Low-Code Development
Low code is an approach to software development that uses visual tools and pre-built components to build software applications with minimal manual coding. No code is a step further, allowing even citizen developers to develop applications without writing any code.
Tools and Programming Languages: Examples
No-code platforms provide solutions for wide variations of domains, including mobile and web applications, workflow automations, data management, e-commerce, marketing, etc. Each platform has its strengths and weaknesses for a given use case, and selecting the right platform based on the business needs is vital. Some popular open-source no-code development tools are as follows:
- Budibase – allows building apps, forms, and workflows
- Convertigo – mobile app development platform to integrate mobile applications with back-end applications or data sources
Low-code platforms provide more flexibility and customizations than no-code platforms via coding or scripting. The programming languages supported by low-code platforms can vary depending on the specific platform. Popular open-source low-code platforms include:
- Joget – web-based workflow software to develop workflow and business process management applications
- StackStorm – event-driven platform for runbook automation
- Microsoft PowerApps – allows developers to create mobile and web applications
Low-code programming languages are designed to simplify the application development processes by providing high-level abstractions, diagram support, constructs, and libraries. There are a number of programming languages that offer both pro-code and low-code support, including JavaScript, Python, and Ballerina.
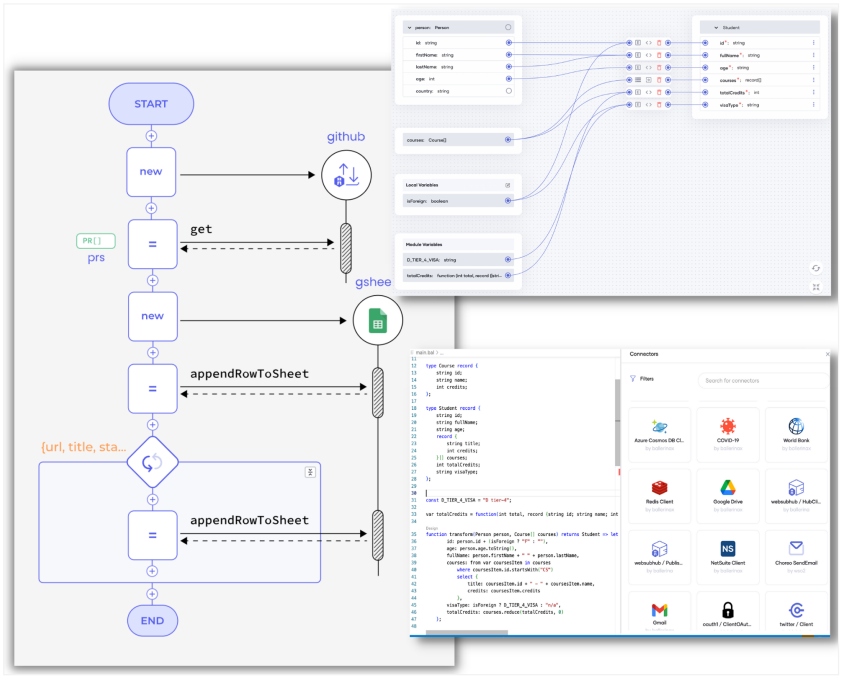
Figure 1: Low-code development using Ballerina programming language
Benefits of Using Low Code and No Code
Low-code and no-code application development methods are becoming increasingly popular among developers as well as citizen developers due to promising advantages. Some key benefits of using no-code and low-code development methodologies are as follows.
Increased agility is one of the main advantages, as new applications can be developed faster and with minimal learning curves, even without in-depth knowledge of technologies. This makes it easier for businesses to respond to growing demands and stay competitive in a rapidly changing market.
Low-code application development can significantly reduce costs in several ways. It reduces the need for skilled developers, who are costly to hire and retain. It also decreases the time required to develop applications and offers a high level of automation, which eventually reduces the associated costs.
Since low- and no-code platforms allow citizen and experienced developers to experiment and build new applications quickly, it saves time and effort. This can help businesses to stay ahead of the competition by increasing innovation. Creating rapid prototypes of applications is easy. These development methodologies facilitate collaboration by allowing stakeholders to test and refine them quickly using available prototypes, visual models, and auto-generated code segments.
Challenges of Low Code
While low-code application development methods have several benefits, there are also several challenges that organizations and users must be aware of. Limited customization flexibility, compared to traditional coding environments, can make it difficult to build highly customized applications. If the application needs to handle large amounts of data or high levels of traffic, traditional development methods would be ideal. Vendor lock-in is another challenge where the code generated by the platforms is usually specific to the platform. Switching to a different low-code platform may result in a complete rewrite of the application, as it can limit flexibility, make it difficult to adopt new technologies, and may result in higher costs in the long run.
The pre-built components and visual interfaces which are used to create applications can raise security concerns and may not be as secure as traditional development methods. Security concerns in low-code development can arise due to the lack of control over the underlying code, potential vulnerabilities in pre-built components, and limited options for security testing and customization.
If the requirements are complex and not straightforward, implementing them via low-code platforms can be challenging. Also, if the applications are quickly built to cater to market needs, the technical debt can increase if the code is not properly structured and maintained.
Design Patterns for Low-Code Development
To overcome these challenges and limitations of low-code platforms, developers follow various design patterns to improve the quality, consistency, and maintainability of the applications.
Model-Driven
The model of the application — which represents the structure of the application, user interface, business requirements, and data schema — is created using a visual interface or a domain-specific language (DSL). Then the code for this model is generated automatically by the platforms, and developers can extend or customize it as needed.
For example, the low-code platform can generate the DB schema, custom types, business logic, and user interface based on the visual model defined by the user.
Event-Driven
Event-driven development relies on building applications that initiate actions based on events or triggers such as user interactions, system notifications, changes in the system data, etc. The visual tools allow users to define triggers, event handlers, and workflows based on the requirements. For example, users can define an event that triggers a notification email to be sent when a status is changed in the system.
Form-Based
Using the visual tools, non-technical application developers can create forms, and then the platform can generate the code for the application automatically based on the form's specifications. The forms can be used to handle data validations, conditional logic, input handling, and business rule enforcement.
Data-Driven
This is widely used in applications that provide data analysis, data visualization, and reporting capabilities. Users can create data models using visual tools, and the generated code can be customized further to include additional data validations, transformations, and integrations.
Real-World Use Cases
Real-world use cases of low-code applications span a wide variety of domains. Some common usages are process automation, supply chain management, customer relationship management, enterprise resource planning, data analysis and visualization, and mobile and web application development. The ability to quickly and easily create custom applications for these common use cases has led to the emergence of self-building apps.
How Low Code Enables Self-Building Apps
Self-building apps are applications that are built and deployed by non-technical users with little or no coding knowledge. With the low-code platforms, users can build and deploy applications without depending on skilled development teams or dedicated IT departments with little or no coding knowledge.
To support self-building apps, low-code platforms have pre-built components, templates, forms, workflows, data models, etc., which allow visualization of the applications while building without having complex deployments.
Low-code platforms provide additional tools that support testing and documentation of the applications. The application developers can quickly release the applications and iteratively improve them based on feedback from the stakeholders.
Trends in Low Code and AI
AI has enabled low-code development platforms to provide new capabilities and enhancements that weren't previously possible, including intelligent automations, cognitive services, and AI-powered auto-generations and suggestions. Using machine learning algorithms is one example of how AI has impacted low-code platforms.
With that, low-code platforms can automatically generate code based on input and suggest more improvements, too. Also, AI can provide cognitive services that can make predictions by analyzing data. That will provide better insights and decision-making capabilities to the low-code applications.
Conclusion
Low-code development has transformed how applications are built and deployed, providing a more efficient and cost-effective approach for organizations. In fact, Gartner predicts that 65% of new applications will be developed using low-code platforms by 2024. This reflects the growing popularity of low-code development platforms and the increasing demand for fast and efficient application development. Low-code application development has revolutionized the software industry by allowing new dimensions in application building.
This is an article from DZone's 2023 Development at Scale Trend Report.
For more:
Read the Report
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments