Memcached - A Distributed Memory Object Caching System
Here's an overview of memcached: what it is, why it's valuable, and more!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this article, we will learn about Memcached. Let us see what it is? How can we use it?
What is “Memcached”?
Memcached is an in-memory key-value store for small chunks of arbitrary data (strings, objects) from results of database calls, API calls, or page rendering HTML . Memcached uses LRU caching algorithm(Least Recently Used (LRU) – discards the least recently used items first).
Why “Memcached”?
It's free and source
To achieve high performance
It's Simple to set up
Ease of development
- Client APIs are available for most of the popular languages
Who is Using “Memcached”?
Youtube.com
- Digg.com
- Twitter.com
- Wikipedia.com
Flickr
Craiglist.com
and the list goes on ...........
Why Do We Need to Use “Memcached”?
To achieve high performance
- To achieve high scalability
The architecture of the traditional system is given below.
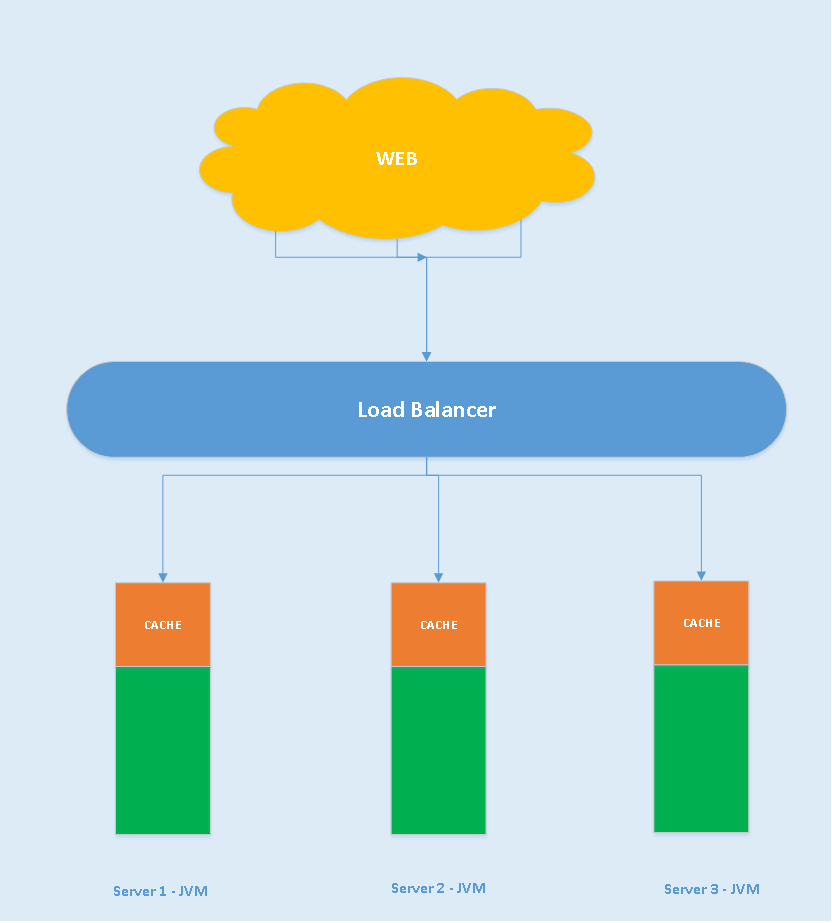
In the above design, the cache is part of the application server's JVM. In this case, some of the memory is allocated for the cache from the heap size allotted to the JVM. If the cache size increases, then the heap size need to increase. There is no better control over the cache because the cache is tightly associated with the app server's JVM. To have better control, we need to separate the cache from the app server's JVM.
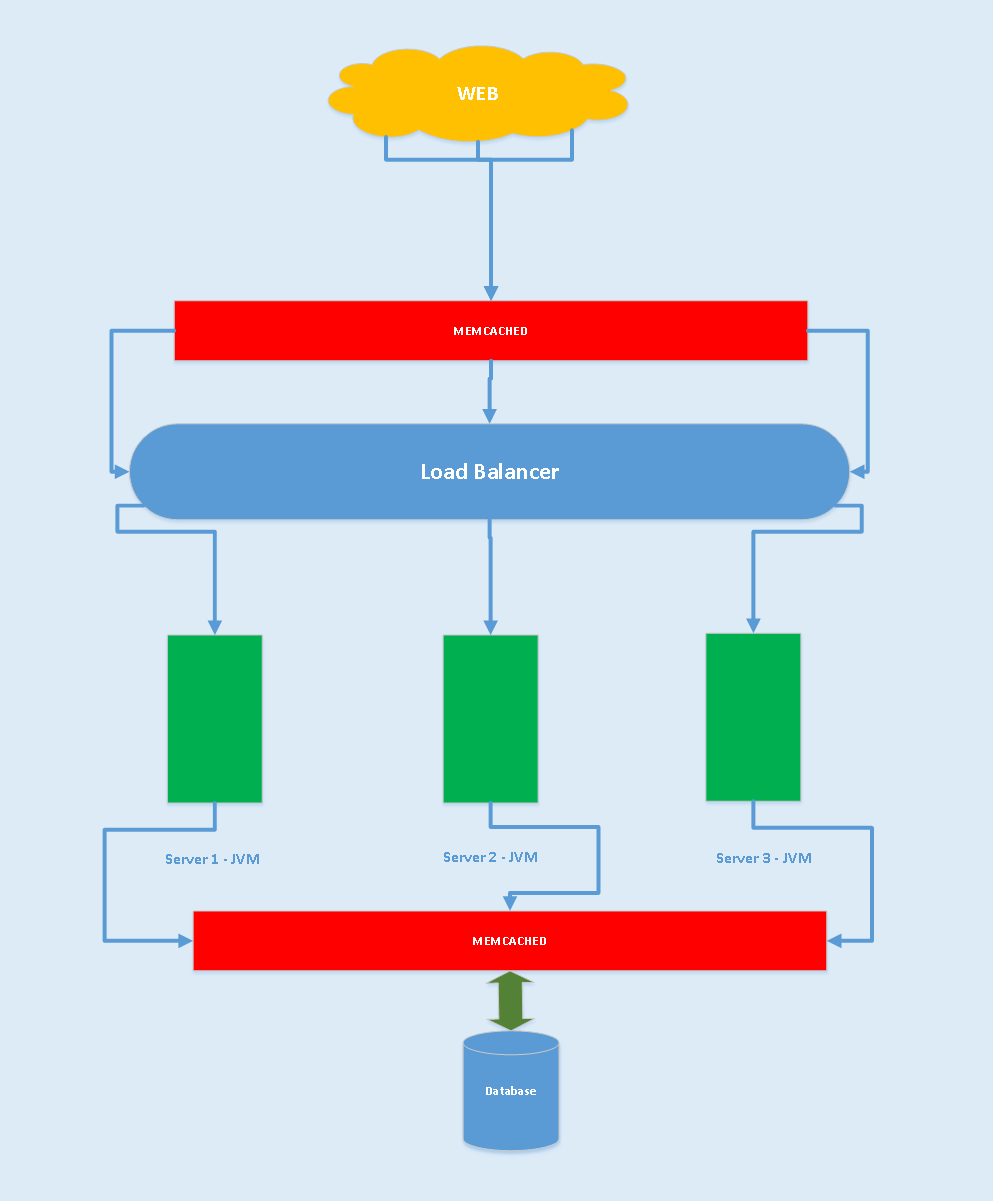
In the above design, we have separated the cache from the application's JVM. This gives better control to manage the cache in a separate server. Based on the data size to cache, we can increase the cache server capacity without affecting the application.
How to Install and Set Up “Memcached”?
I have used Ubuntu operating system to install and set up the memcacahed. Follow the below steps to install and run the memcahed.
- Download the source code from https://memcached.org/files/memcached-1.4.25.tar.gz
- Extract the downloaded file and get into the extracted folder.
- Run the below commands
- ./configure
- Make & make install
- After successful installation, start the memcached using memcached -u <user name>
- The Memcached server will run by default on 11211 port
- Now, open a new command prompt and try to connect to the Memcached through telnet . For example telnet <host> 11211. If you are able to connect successfully to the Memcached server then the you are done with the installation and the setup.
What Operations Can We Perform With “Memcached”?
After establishing the connection to the memcached through telnet, we can perform the below operations.
Operation | Format | Parameters | Return Value |
| Set (Store key/value pair in Memcached) | set <key> <flags> <exptime> <bytes> |
|
|
Get (Get value for key) | get <key> | <key> : the key of the data stored. To retrieve client can request value of multiple keys separated by white space |
|
Add (Store key/value pair in Memcached, but only if the server doesn’t already hold data for this key) | add <key> <flags> <exptime> <bytes> |
|
|
| Replace (Store key/value pair in Memcached, but only if the server already hold data for this key) | replace <key> <flags> <exptime><bytes> | ||
Delete (Deletes key/value pair in Memcached) | delete <key> | ||
Flush_all (Flush the server key/value pair (invalidating them) ) | flush_all | ||
stats (Return general-purpose statistics like up time, version, memory occupation, …) | stats | ||
Item stats (Return items statistics, will display items statistics (count, age, eviction, …)) | stats items |
How to Use JAVA Client API?
Follow the below steps to use the JAVA client API.
- To contact Memcached from Java, download the java client from http://code.google.com/p/spymemcached/
- Get Memcached client
MemcachedClient client = new MemcachedClient(new InetSocketAddress(“localhost”, 11211));Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments