Microservice Architecture Best Practices: Messaging Queues
In this article, we discuss why queues are needed, and how they form the cornerstone of asynchronous communication in microservices architectures.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn this article, we discuss why queues are needed, and how they form the cornerstone of asynchronous communication in microservices architectures.
What You Will Learn
- What is a Queue?
- What is asynchronous communication or asynchronous messaging?
- What are the advantages of using Queues in microservices architectures?
Best Practices With Cloud and Microservices
This is the fourth article in a series of six articles on best practices with cloud and microservices. The first three parts can be found here:
The 12 Factor App: Best Practices in Cloud Native Applications and Microservices
Microservices Best Practices: Why Do You Build a Vertical Slice?
Why Asynchronous Messaging?
Why is asynchronous messaging important?
Consider the simple example of an ordering service:
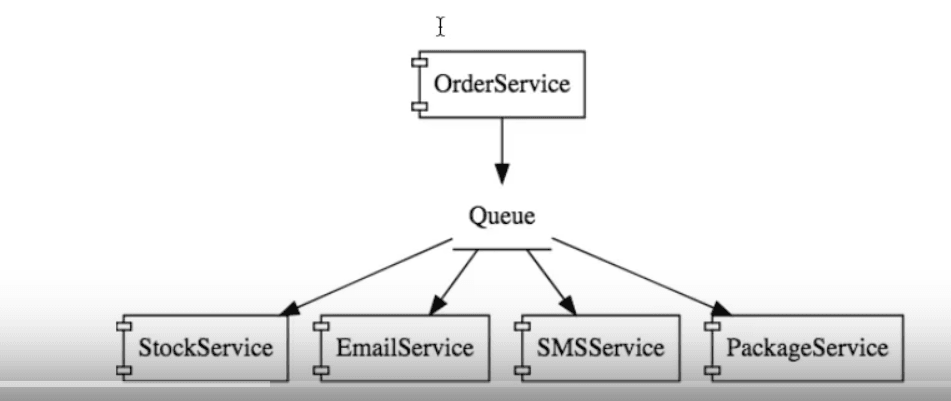
A customer places an order through the OrderService. Let's say following steps are involved:
- It needs to send a request to the StockService.
- Send communication to the user through the EmailService and SMSService.
- Call the PackageService to start delivery.
Option 1: Single Component for All Processing
One way to design this application would be to have a single component that accomplishes all this functionality. For example, write a Java class which accepts the order, and does all of the processing itself.
Option 2: Introducing Asynchronous Messaging Using Queues
The other option is to have a queue in-between the receiving OrderService component, and the rest of the components. When the OrderService receives an order, it places the request on the Queue. The rest of the components are independent services, listening on the Queue.
As soon as an order is placed on the queue:
- The StockService processes the order and updates the database.
- The EmailService sends out an email to the customer.
- The SMSService sends out an SMS to the user.
- The PackageService does the required package processing on the item.
Single Components vs. Queues
If your business goal is to support a few hundreds or thousands of users, then a simple architecture would be a good choice. The first architecture might be all you need.
However, when we talk of a large scale e-commerce web applications, such as Amazon.com, that receive millions of orders in a short time, you need a lot of flexibility. That's when you go for the second approach, of bringing a queue in.
Advantages of Using a Messaging Queue
Let's look at the advantages of using asynchronous communication based on a messaging queue.
A Queue Improves Reliability
Let's say the SMSService is down for a short time.
In Option 1, since the OrderService directly invokes the SMSService on receiving an order, an SMS cannot be sent out. That might mean canceling the order, as all steps are part of a single transaction. Failure of one of the components would lead to cancellation of the customer request, with a need for him to re-initiate the order — at a later point in time.
However, in the second approach, called asynchronous communication, the order request is placed on the queue. When the SMSService comes back up, it will find the order event and process it. It can then send out the SMS messages for all its pending requests.
A Queue Provides Scalability
Suppose, on any given day, that there is a need to send out 100,000 SMS messages. An option with having asynchronous communication is that you can increase the number of instances of the SMSService. This flexibility in the instances of the components improves system scalability.
A Queue Improves Testability
Each of the components/services are loosely tied, and have independent requirements. It is thus much easier to test each one of them, preferably in isolation.
A Queue Improves Maintainability
A queue also improves system maintainability, as the application is divided into smaller services.
A Queue Improves Flexibility
Not only does a queue increase the instances of existing services, it makes the system flexible and able to add more services in the future. All you need to do is add a new service listener to events on the queue and consum them. The new service could be plugged in, with minimum down time.
Popular Message Queues
An extremely popular message queue framework is RabbitMQ.
Different frameworks use different communication protocols, but the concept underlying all of them is the same. At its core, a queue separates the component that generates the event from the services that consume the event.
In general, if you need a system that addresses a very large user base, whose users submit a large number of requests to be processed, go for queue-based systems.
Summary
In this article, we looked at the fact that there are two types of architectures — synchronous and asynchronous. Synchronous systems have the disadvantage that one component being down, causes loss of service to the entire system. Asynchronous systems solve this problem by introducing an intermediary queue to hold events. An architecture based on asynchronous communication using a queue improves testability, scalability, maintainability, and flexibility.
Published at DZone with permission of Ranga Karanam, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments