Microservice Architectures With Spring Cloud and Docker
How to set up a microservice architecture using Spring Boot, Spring Cloud, Docker, and some of Netflix's open source tools.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article provides a starting point for understanding common Microservice architecture patterns by example of a proof-of-concept application built with Spring Boot, Spring Cloud, and Docker.
The code is available on Github, and images are available on Docker Hub. You can start the whole system with just one command.
As a basis for this system I chose an old project, whose backend used to be a monolith. The application provides a way to deal with personal finances, organize incomes and expenses, manage savings, analyze statistics, and create simple forecasts.
Functional Services
The monolith application was decomposed into three core microservices. All of them are independently deployable applications, organized around certain business capabilities.
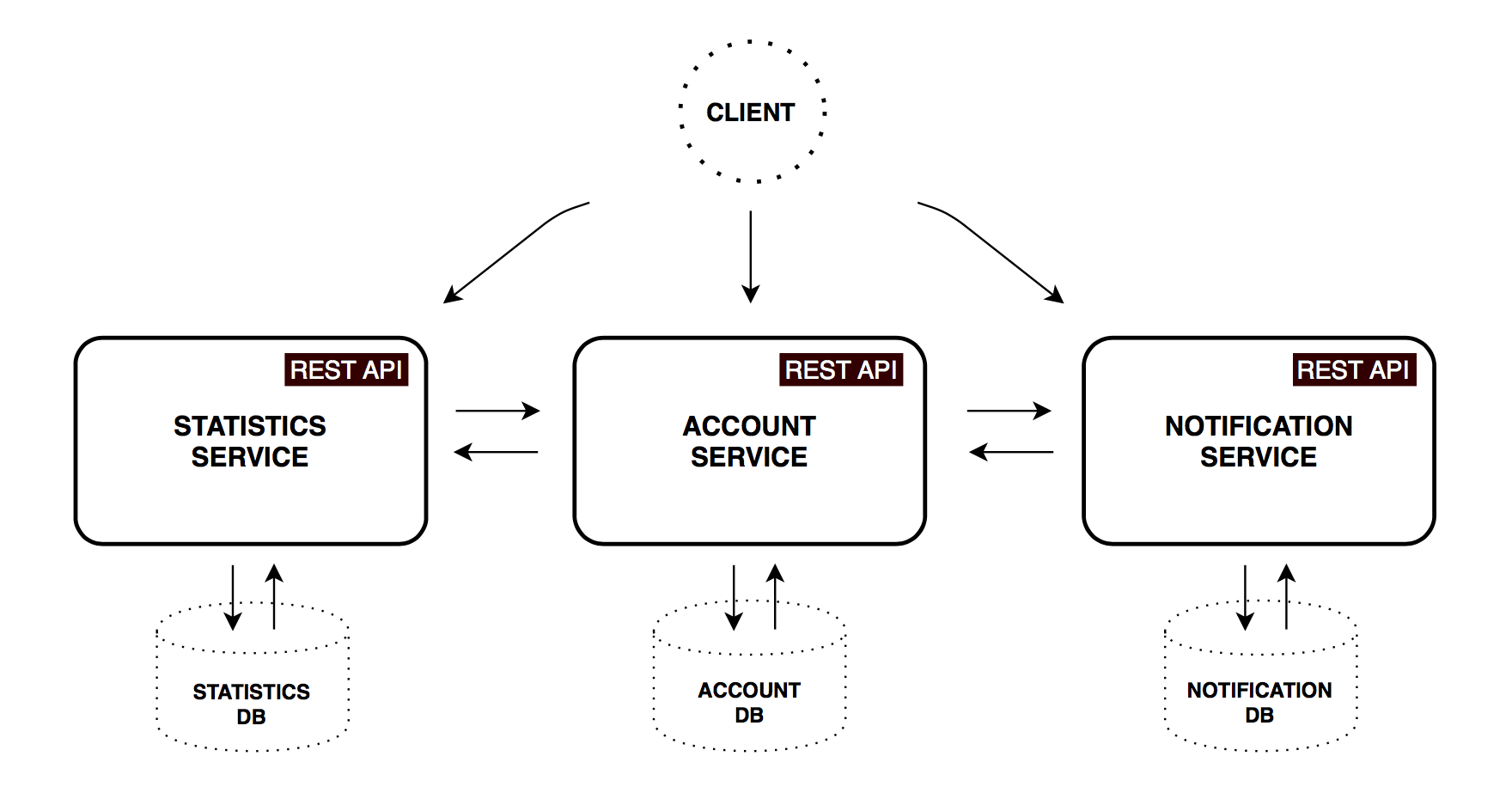
Account Service
Contains general user input logic and validation: incomes/expenses items, savings, and account settings.
| Method | Path | Description | User authenticated | Available from UI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /accounts/{account} | Get specified account data | ||
| GET | /accounts/current | Get current account data | × | × |
| GET | /accounts/demo | Get demo account data (pre-filled incomes/expenses items, etc) | × | |
| PUT | /accounts/current | Save current account data | × | × |
| POST | /accounts/ | Register new account | × |
Statistics Service
Performs calculations on major statistics parameters and captures time series for each account. A datapoint contains values normalized to base currency and time period. This data might be used to track cash flow dynamics in an account's lifetime.
| Method | Path | Description | User authenticated | Available from UI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /statistics/{account} | Get specified account statistics | ||
| GET | /statistics/current | Get current account statistics | × | × |
| GET | /statistics/demo | Get demo account statistics | × | |
| PUT | /statistics/{account} | Create or update time series datapoint for specified account |
Notification Service
Stores a user's contact information and notification settings (like remind and backup frequency). Scheduled worker collects required information from other services and sends e-mail messages to subscribed customers.
| Method | Path | Description | User authenticated | Available from UI |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GET | /notifications/settings/current | Get current account notification settings | × | × |
| PUT | /notifications/settings/current | Save current account notification settings | × | × |
Notes
- Each microservice has it's own database, so there is no way to bypass the API and access persistance data directly.
- For this project, I used MongoDB as the primary database for each service. It also might make sense to have a polyglot persistence architecture (to сhoose the type of database that is best suited to the service requirements).
- Service-to-service communication is quite simplified: microservices talking using only synchronous REST API. Common practice in a real-world systems is to use combination of interaction styles. For example, perform synchronous GET request to retrieve data and use asynchronous approach via Message broker for create/update operations in order to decouple services and buffer messages. However, this brings us in eventual consistency world.
Infrastructure Services
There's a bunch of common patterns in distributed systems, which could help us to make described core services work. Spring cloud provides powerful tools that enhance Spring Boot applications behaviour to implement those patterns. I'll cover them briefly.
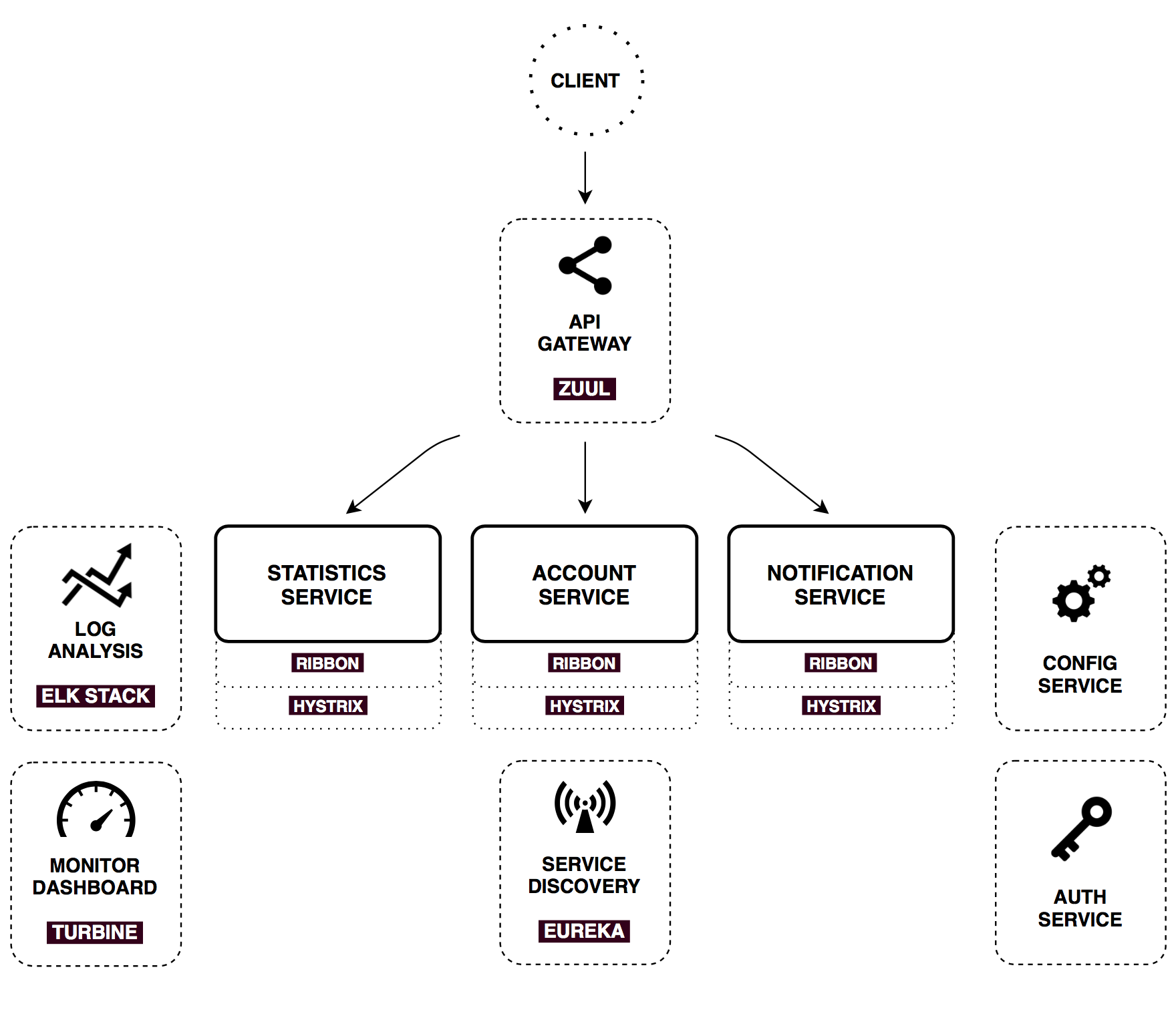
Config Service
Spring Cloud Config is horizontally scalable centralized configuration service for distributed systems. It uses a pluggable repository layer that currently supports local storage, Git, and Subversion.
In this project, I use native profile, which simply loads config files from the local classpath. You can see shareddirectory in Config service resources. Now, when Notification-service requests it's configuration, Config service responses with shared/notification-service.yml and shared/application.yml (which is shared between all client applications).
Client-side Usage
Just build Spring Boot application with spring-cloud-starter-config dependency, autoconfiguration will do the rest.
Now you don't need any embedded properties in your application. Just provide bootstrap.yml with the application name and Config service url:
spring:
application:
name: notification-service
cloud:
config:
uri: http://config:8888
fail-fast: trueWith Spring Cloud Config, You Can Change App Configuration Dynamically
For example, the EmailService bean was annotated with @RefreshScope. That means you can change e-mail text and subject lines without rebuilding and restarting the Notification service application.
First, change the required properties in the Config server. Then, perform the refresh request to the Notification service: curl -H "Authorization: Bearer #token#" -XPOST http://127.0.0.1:8000/notifications/refresh
You could also use webhooks to automate this process.
Notes
- There are some limitations for dynamic refreshes though.
@RefreshScopedoesn't work with@Configurationclasses and can't affect@Scheduledmethods. fail-fastproperty means that the Spring Boot application will fail startup immediately if it cannot connect to the Config Service. That's very useful when you're starting all applications together.- There are significant security notes below.
Auth Service
Authorization responsibilities are completely extracted to separate server, which grants OAuth2 tokens for backend resource services. Auth Server is used for user authorization as well as for secure machine-to-machine communication inside a perimeter.
In this project, I use Password credentials as a grant type for user authorization (since it's only used by the native application UI) and Client Credentials as a grant type for microservices authorization.
Spring Cloud Security provides convenient annotations and autoconfigurations to make this really easy to implement from both the server and client side. You can learn more about it in the documentation and check configuration details in Auth Server code.
From the client side, everything works exactly the same as with traditional session-based authorization. You can retrieve Principal objects from request, check user roles and other stuff with expression-based access control and @PreAuthorize annotation.
Each client in PiggyMetrics (account-service, statistics-service, notification-service and browser) has a scope: serverfor backend services, and ui - for the browser. So we can also protect controllers from external access, for example:
@PreAuthorize("#oauth2.hasScope('server')")
@RequestMapping(value = "accounts/{name}", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public List<DataPoint> getStatisticsByAccountName(@PathVariable String name) {
return statisticsService.findByAccountName(name);
}API Gateway
As you can see, there are three core services, which expose external APIs to the client. In a real-world system, this number can grow very quickly as well as whole system complexity. Actuallyy, hundreds of services might be involved in rendering one complex webpage.
In theory, a client could make requests to each of the microservices directly. But obviously there are challenges and limitations with this option, like necessity to know all endpoints addresses, perform http request for each peace of information separately, merge the result on a client side. Another problem is non-web-friendly protocols, which might be used on the backend.
Usually a much better approach is to use an API Gateway. It is a single entry point into the system, used to handle requests by routing them to the appropriate backend service or by invoking multiple backend services and aggregating the results. Also, it can be used for authentication, insights, stress and canary testing, service migration, static response handling, active traffic management.
Netflix open sourced such an edge service, and now with Spring Cloud we can enable it with one @EnableZuulProxyannotation. In this project, I use Zuul to store static content (UI application) and to route requests to the appropriate microservices. Here's a simple prefix-based routing configuration for the Notification service:
zuul:
routes:
notification-service:
path: /notifications/**
serviceId: notification-service
stripPrefix: false
That means all requests starting with /notifications will be routed to Notification service. There is no hardcoded address, as you can see. Zuul uses Service discovery mechanism to locate Notification service instances and also Circuit Breaker and Load Balancer, described below.
Service Discovery
Another commonly known architecture pattern is service discovery. It allows automatic detection of network locations for service instances, which could have dynamically assigned addresses because of auto-scaling, failures, and upgrades.
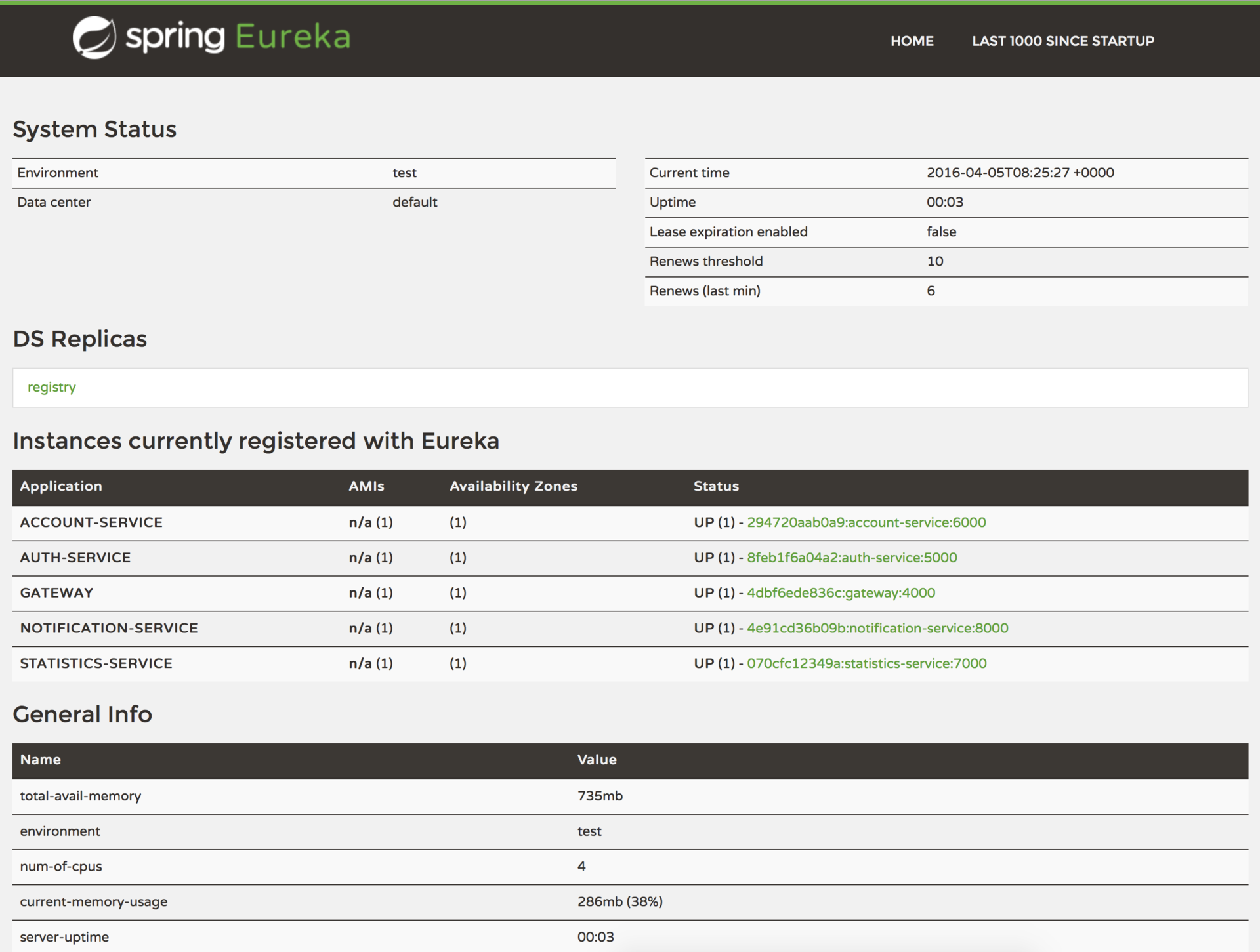
The key part of service discovery is the registry. I used Netflix Eureka for this project. Eureka is a good example of the client-side discovery pattern, when the client is responsible for determining the locations of available service instances (using a registry server) and load balancing requests across them.
With Spring Boot, you can easily build Eureka Registry with a spring-cloud-starter-eureka-server dependency, @EnableEurekaServer annotation, and simple configuration properties.
Client support is enabled with @EnableDiscoveryClient annotation and bootstrap.yml with application name:
spring:
application:
name: notification-serviceNow, on application startup, it will register with Eureka Server and provide meta-data, such as host and port, health indicator URL, home page, etc. Eureka receives heartbeat messages from each instance belonging to a service. If the heartbeat fails over a configurable timetable, the instance will be removed from the registry.
Also, Eureka provides a simple interface, where you can track running services and the number of available instances: http://localhost:8761
Load Balancer, Circuit Breaker, and Http Client
Netflix OSS provides another great set of tools.
Ribbon
Ribbon is a client side load balancer which gives you a lot of control over the behavior of HTTP and TCP clients. Compared to a traditional load balancer, there is no need of an additional hop for every over-the-wire invocation — you can contact the desired service directly.
Out of the box, it natively integrates with Spring Cloud and Service Discovery. Eureka Client provides a dynamic list of available servers so Ribbon could balance between them.
Hystrix
Hystrix is the implementation of a Circuit Breaker pattern, which gives a control over latency and failure from dependencies accessed over the network. The main idea is to stop cascading failures in a distributed environment with a large number of microservices. That helps to fail fast and recover as soon as possible — important aspects of fault-tolerant systems that self-heal.
Besides circuit breaker control, with Hystrix you can add a fallback method that will be called to obtain a default value in case the main command fails.
Moreover, Hystrix generates metrics on execution outcomes and latency for each command, that we can use to monitor system behavior.
Feign
Feign is a declarative HTTP client, which seamlessly integrates with Ribbon and Hystrix. Actually, with one spring-cloud-starter-feign dependency and @EnableFeignClients annotation you have a full suite of a load balancer, circuit breaker, and HTTP client with a sensible ready-to-go default configuration.
Here is an example from Account Service:
@FeignClient(name = "statistics-service")
public interface StatisticsServiceClient {
@RequestMapping(method = RequestMethod.PUT, value = "/statistics/{accountName}", consumes = MediaType.APPLICATION_JSON_UTF8_VALUE)
void updateStatistics(@PathVariable("accountName") String accountName, Account account);
}- Everything you need is just an interface
- You can share
@RequestMappingpart between Spring MVC controller and Feign methods - Above example specifies just desired service id -
statistics-service, thanks to autodiscovery through Eureka (but obviously you can access any resource with a specific url)
Monitor Dashboard
In this project configuration, each microservice with Hystrix on board pushes metrics to Turbine via Spring Cloud Bus (with AMQP broker). The Monitoring project is just a small Spring boot application with Turbine and Hystrix Dashboard.
Let's see our system behavior under load: Account service calls Statistics service and it responses with a vary imitation delay. Response timeout threshold is set to 1 second.
Log Analysis
Centralized logging can be very useful when attempting to identify problems in a distributed environment. Elasticsearch, Logstash, and Kibana stack lets you search and analyze your logs, utilization and network activity data with ease. Ready-to-go Docker configuration is described in my other project.
Security
An advanced security configuration is beyond the scope of this proof-of-concept project. For a more realistic simulation of a real system, consider using https and JCE keystore to encrypt microservices passwords and Config server properties content (see documentation for details).
Infrastructure Automation
Deploying microservices, with their interdependence, is a much more complex process than deploying a monolith application. It is important to have a fully automated infrastructure. We can achieve following benefits with a Continuous Delivery approach:
- The ability to release software anytime.
- Any build could end up being a release.
- Build artifacts once, deploy as needed.
Here is a simple Continuous Delivery workflow, implemented in this project:
In this configuration, Travis CI builds tagged images for each successful Git push. So there is always a latest image for each microservice on Docker Hub and older images are tagged with Git commit hash. It's easy to deploy any of them and quickly roll back, if needed.
How to Run All the Things?
It's really easy and I suggest you to try. Keep in mind, that you are going to start 8 Spring Boot applications, 4 MongoDB instances, and RabbitMq. Make sure you have 4 Gb RAM available on your machine. You can always run just vital services though Gateway, Registry, Config, Auth Service, and Account Service.
Before You Start
- Install Docker and Docker Compose.
- Export environment variables:
CONFIG_SERVICE_PASSWORD,NOTIFICATION_SERVICE_PASSWORD,STATISTICS_SERVICE_PASSWORD,ACCOUNT_SERVICE_PASSWORD,MONGODB_PASSWORD
Production Mode
In this mode, all of the latest images will be pulled from Docker Hub. Just copy docker-compose.yml and hit docker-compose up -d.
Development Mode
If you'd like to build images yourself (with some changes in the code, for example), you have to clone all repository and build artifacts with Maven. Then, run docker-compose -f docker-compose.yml -f docker-compose.dev.yml up -d
docker-compose.dev.yml inherits docker-compose.yml with additional possibility to build images locally and expose all containers ports for convenient development.
Important Endpoints
- localhost:80 - Gateway
- localhost:8761 - Eureka Dashboard
- localhost:9000 - Hystrix Dashboard
- localhost:8989 - Turbine stream (source for Hystrix Dashboard)
- localhost:15672 - RabbitMq management
Notes
All Spring Boot applications require already running Config Server for startup. But we can start all containers simultaneously because of fail-fast Spring Boot property and restart: always docker-compose option. That means all dependent containers will try to restart until Config Server will be up and running.
Also, Service Discovery mechanism needs some time after all applications startup. Any service is not available for discovery by clients until the instance, the Eureka server and the client all have the same metadata in their local cache, so it could take 3 hearbeats. Default hearbeat period is 30 seconds.
Published at DZone with permission of Alexander Lukyanchikov. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.







Comments