Microservice Integration — SAGA Pattern
Read on to find out more about how to integrate your microservices using the SAGA pattern — including choreography-based SAGA.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free

There are some issues to consider while designing these integration patterns:
- Partial error handling: MicroServices are single responsibility units but business transactions require more than one of these units. If one unit(it is called a local transaction) fails, the system must be designed to do its rollback actions(it is called compensation transaction) accordingly.
- Manage the situations where we need to collect data from multiple services: Microservices only have their entity data; when we need enriched data from multiple entities, we need to have proper integration principles.
- Testing requirements of the system design: Some patterns are more appropriate for testing purposes while some others are not.
- The organization (the company) structure is a key point: The Agile/Waterfall working principles of the organization is also a key point for architectural design.
You may also like: Principles for Microservices Integration
Microservice Architecture depends on the Database per Service principle. On top of that principle, there is a SAGA pattern that can be applied to ensure the integrity of distributed transactions because the Database per Service principle results in a context that we need to synchronize these databases.
SAGA Pattern depends on consecutive local transactions. It can be applied in two ways:
Choreography Based SAGA Pattern
In this method, each local transaction publishes an event when its job is done. The other local transaction that receives this event performs the appropriate behavior. The work is finished when all the local transactions are done.
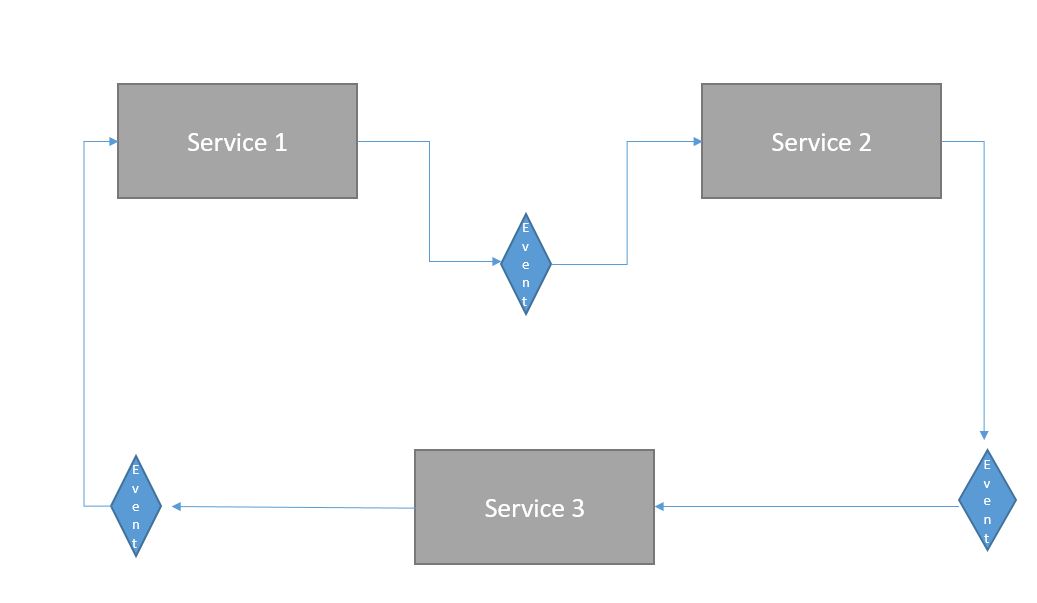
In choreography based SAGA, the process is managed by local transactions itself. This confirms the principle of intelligent endpoints and dummy communication channels.
The benefits of this method are as follows:
- Easy to implement.
- Appropriate if the number of local transactions is small.
- Loosely coupled endpoints.
- Suitable for agile organizations.
There are some drawbacks of the method:
- It gets very complicated when the number of local transactions increases.
- Cyclic dependency may occur between services.
Orchestration Based SAGA Pattern
In this method, there is an intelligent endpoint (a separate service that performs orchestration) that coordinates the whole process. It manages which service will perform when. If one of the local transactions fails for some reason, the Orchestrator is also responsible for a rollback of the previously performed transactions.
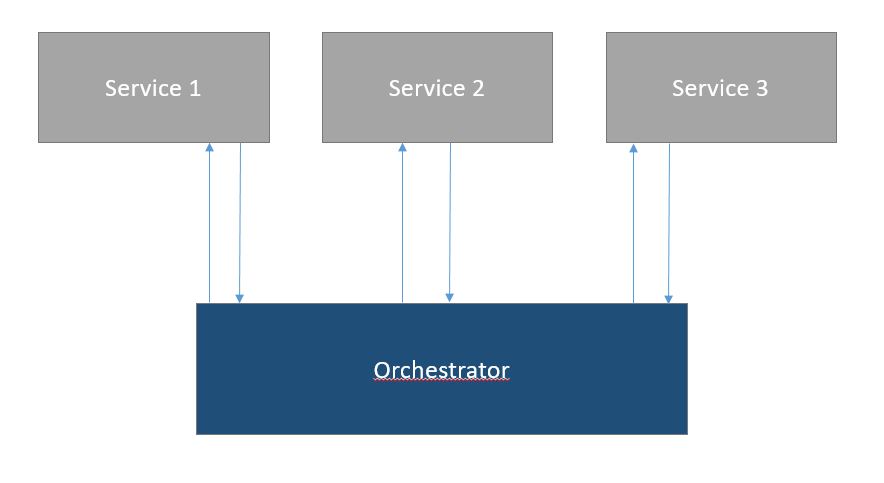
The benefits of this method are:
- Easy to implement.
- Easy to understand and maintain.
- Complexity is not an issue when local transactions’ count dramatically increases.
The drawbacks are:
- This method creates a situation that the communication channel becomes intelligent and the endpoints become a dummy.
- All the business logic is implemented inside the orchestrator. So the orchestrator becomes the monolith.
Which method to consider is determined by the needs of the system and the organization.
Further Reading
Microservice Architecture and Design Patterns for Microservices
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments