Microservices Tutorial: Ribbon as a Load Balancer
Learn how to set up Ribbon as a load balancer for microservices with a little background on the different types of load balancing.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the previous microservices tutorial, we learned how to communicate with other microservices using Feign as a REST client and Eureka server as a service discovery.
In all cases, we consider only one instance of a microservice, which calls another instance of a dependent microservice (EmployeeDasBoard service call to EmployeeSearch service).
This is good for demo purposes, or when you are practicing how to develop microservices.
In production, it is certainly not the case- we break monolithic applications into microservice applications because we can scale each service based on the payload. A single instance of a service is unimaginable in production- so what we generally do is use a load balancer, which balances the payload among multiple instances of a service.
Before digging into Ribbon, the client side load balancer for microservice architecture, let's discuss how our old fashioned Java EE services, AKA monolith, maintain load balancing.
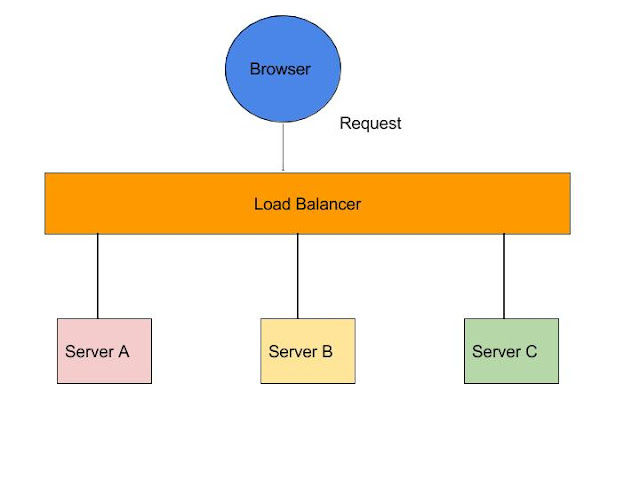
Server Side Load Balancing
In Java EE architecture, we deploy our war/ear files into multiple application servers, then we create a pool of server and put a load balancer (Netscaler) in front of it, which has a public IP. The client makes a request using that public IP, and Netscaler decides in which internal application server it forwards the request by round robin or sticky session algorithm. We call it server side load balancing.
Problem: The problem of server side load balancing is if one or more servers stop responding, we have to manually remove those servers from the load balancer by updating the IP table of the load balancer.
Another problem is that we have to implement a failover policy to provide the client with a seamless experience.
But microservices don't use server side load balancing. They use client side load balancing.
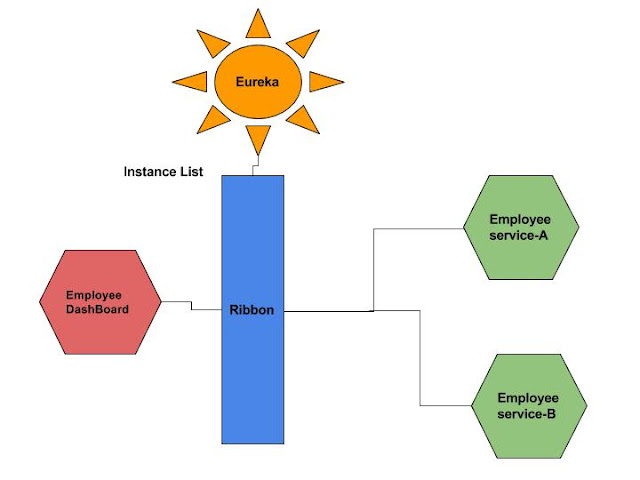
Client Side Load Balancing
To understand client side load balancing, let's recap microservices architecture. We generally create a service discovery like Eureka or Consul, where each service instance registers when bootstrapped. Eureka server maintains a service registry; it maintains all the instances of the service as a key/value map, where the {service id} of your microservice serves as the key and instances serve as the value. Now, if one microservice wants to communicate with another microservice, it generally looks up the service registry using DiscoveryClient and Eureka server returns all the instances of the calling microservice to the caller service. Then it was a caller service headache which instance it calls. Here, client side load balancing stepped in. Client side load balancing maintains an algorithm like round robin or zone specific, by which it can invoke instances of calling services. The advantage is s service registry always updates itself; if one instance goes down, it removes it from its registry, so when the client side load balancer talks to the Eureka server, it always updates itself, so there is no manual intervention- unlike server side load balancing- to remove an instance.
Another advantage is, as the load balancer is in the client side, you can control its load balancing algorithm programmatically. Ribbon provides this facility, so we will use Ribbon for client side load balancing.
Coding Time
We will configure Ribbon in our EmployeeDashBoardService, which will communicate with Eureka to fetch EmployeeSearchservice instances.
Step 1: To enable Ribbon in EmployeeDashBoard, we have to add the following dependency in pom.xml:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-ribbon</artifactId>
</dependency>Step 2: Now we have to Enable Ribbon so it can load balance the EmployeeSearch application. For that, we need to put @RibbonClient(name="EmployeeSearch") on top of the EmployeeServiceProxy interface. By doing this, we instruct Spring Boot to communicate with Eureka server and get the list of instances for service id EmployeeSearch. Please note that this is the {service-id} for the EmployeeSearch application.
package com.example.EmployeeDashBoardService.controller;
import java.util.Collection;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.feign.FeignClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.RibbonClient;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.PathVariable;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import com.example.EmployeeDashBoardService.domain.model.EmployeeInfo;@FeignClient(name="EmployeeSearch" )
@RibbonClient(name="EmployeeSearch")
public interface EmployeeServiceProxy {
@RequestMapping("/employee/find/{id}")
public EmployeeInfo findById(@PathVariable(value="id") Long id);
@RequestMapping("/employee/findall")
public Collection<EmployeeInfo> findAll();
}Our Ribbon Client is ready now.
Testing Time
Start Configserver and Eureka server first.
Then start EmployeeService; it will be on port 8080, as we mentioned in bootstrap.preoperties.
Now run another instance, but this time, starting with -Dserver.port=8082 so another instance comes up on 8082 port.
After that, run the EmployeeDashBoard service.
Now check the Eureka server GUI; it will look like the following:
Now, if you hit the URL http://localhost:8081/dashboard/feign/1 you can see the following response:
{
"employeeId": 1,
"name": "Shamik Mitra",
"practiceArea": "Java",
"designation": "Architect",
"companyInfo": "Cognizant"
}Now open the EmployeeDashBoard Console. You can see the following lines printed in the console:
DynamicServerListLoadBalancer
for client EmployeeSearch initialized: DynamicServerListLoadBalancer: {
NFLoadBalancer: name = EmployeeSearch,
current list of Servers = [192.168 .0 .103: 8080, localhost: 8082],
Load balancer stats = Zone stats: {
defaultzone = [Zone: defaultzone;Instance count: 2;Active connections count: 0;Circuit breaker tripped count: 0;Active connections per server: 0.0;]
},
Server stats: [
[Server: localhost: 8082;Zone: defaultZone;Total Requests: 0;Successive connection failure: 0;Total blackout seconds: 0;Last connection made: Thu Jan 01 05: 30: 00 IST 1970;First connection made: Thu Jan 01 05: 30: 00 IST 1970;Active Connections: 0;total failure count in last(1000) msecs: 0;average resp time: 0.0;90 percentile resp time: 0.0;95 percentile resp time: 0.0;min resp time: 0.0;max resp time: 0.0;stddev resp time: 0.0]
,
[Server: 192.168 .0 .103: 8080;Zone: defaultZone;Total Requests: 0;Successive connection failure: 0;Total blackout seconds: 0;Last connection made: Thu Jan 01 05: 30: 00 IST 1970;First connection made: Thu Jan 01 05: 30: 00 IST 1970;Active Connections: 0;total failure count in last(1000) msecs: 0;average resp time: 0.0;90 percentile resp time: 0.0;95 percentile resp time: 0.0;min resp time: 0.0;max resp time: 0.0;stddev resp time: 0.0]
]
}
ServerList: org.springframework.cloud.netflix.ribbon.eureka.DomainExtractingServerList @a1df28c
2017 - 08 - 04 22: 56: 47.180 INFO 3293-- - [erListUpdater - 0] c.netflix.config.ChainedDynamicProperty: Flipping property: EmployeeSearch.ribbon.ActiveConnectionsLimit to use NEXT property: niws.loadbalancer.availabilityFilteringRule.activeConnectionsLimit = 2147483647Published at DZone with permission of Shamik Mitra, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments