Mule Scatter-Gather Shallow Diving: Part I
The Mule Scatter-Gather component can be used to solve typical message multicasting scenarios. The flow is pretty simple.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeLet's assume that we have a common integration scenario. You are querying the price of an iPhone. The system should return you all possible prices of the iPhone, consulting various sites. This turns out to be a typical message multicasting scenario.
Mule Solution
To solve this kind of integration scenario, Mule provides an awesome component called Scatter-Gather. The most important points of this component are as follows.
Parallel Processing
The Scatter-Gather component can send messages to all the routes concurrently. It maintains a thread pool to concurrently execute the provided routes. Thus, the time needed to execute all routes is less, in contrast to its previous version, which executes the routes in a parallel fashion. This means that when a route is being processed the remaining routes must have to wait for its completion.
Error Handling
Each route executes in its own thread and thus, if an exception occurs, it does not prevent the execution of other routes that execute in their own threads. So, the final result may contain responses from the successful routes as well as from the failed ones.
Configuration
By default, Scatter-Gather uses the default Mule implementation for aggregating messages. However, this behavior can be overridden by using the custom Java implementation.
Getting Your Hands Dirty
In this post, I will try to explain the use of the Scatter-Gather component with a simple example.
The scenario is as follows: "Let's suppose we have two websites called "Wallmarty" and "Amazona" selling iPhones. Now, I want a list of the iPhones available in both sites in descending order of price."
Mock Services
I have created a mock service exposing the following two REST URLs:
http://localhost:9090/amazona?type=iphone.
http://localhost:9090/wallmarty?type=iphone.
Please download the JAR named market-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar and execute it. Make sure that port 9090 is not being used on your machine. After running the service, you can verify the above-quoted links.
Creating the Flow
Please find the complete source code here. I have created a simple flow named scatter-gather-example.xml .Here is a screenshot.
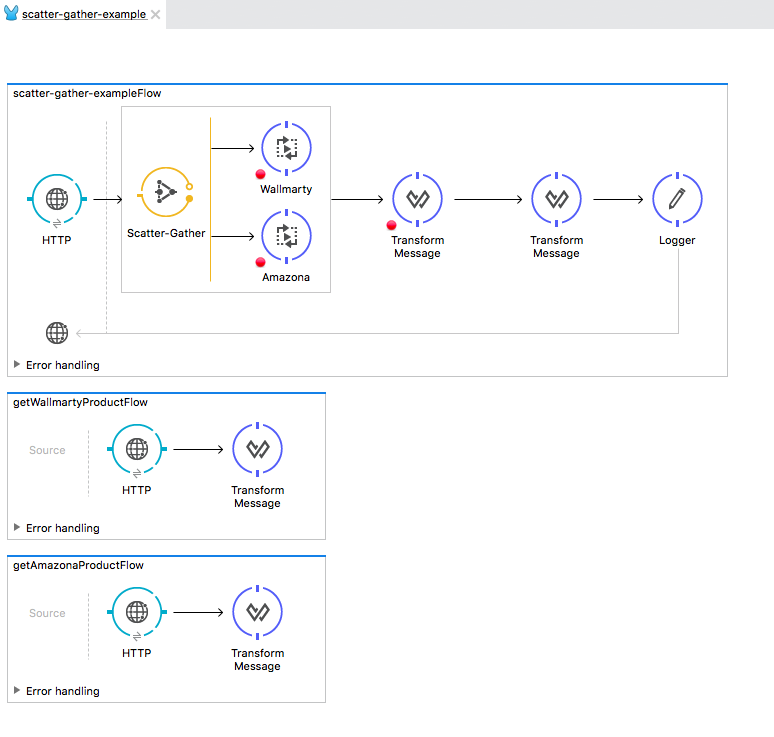
The flow is simple. The Scatter-Gather component simply gathers information from the sub-flows getWallmartyProductFlow and getAmazonaProductFlow and merges the information. The transformers simply transform the response based on some JSON schema and orders the output in descending order of price.
Simple Output
Here is the screenshot of a simple output.
[
{
"price": 185.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 186.5,
"product_name": "IPhone5",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 187.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 188.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 188.5,
"product_name": "IPhone5",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 188.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 189.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 189.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 189.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 190.5,
"product_name": "IPhone5",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 190.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 190.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 191.5,
"product_name": "IPhone5",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 191.5,
"product_name": "IPhone5",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 194.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 194.5,
"product_name": "IPhone5",
"vendor": "www.wallmarty.com"
},
{
"price": 194.5,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 194.5,
"product_name": "IPhone5",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 450,
"product_name": "Mac Pro",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 451,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 453,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 453,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 453,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 455,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 457,
"product_name": "IPhone6",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 458,
"product_name": "Mac Pro",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
},
{
"price": 458,
"product_name": "Mac Pro",
"vendor": "www.amazona.com"
}
]In the next post, I will try to explain the Scatter-Gather using custom aggregation strategy.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments