MuleSoft API Lifecycle Management
Learn about the lifecycle of an API managed with MuleSoft, from the design and build stages, to implementation and management.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free1. Introduction
In today’s competitive landscape, businesses need to make decisions quickly; whether it’s a new marketing campaign, a new product enhancement, a new partner portal, or an employee productivity app, businesses are competing on speed. What is needed is flexibility. And what better way to do this than to create purposeful, agile application building blocks that can be easily pieced together with well-designed, well-managed APIs to quickly create what is needed. Connecting these building blocks results in a network of interchangeable functionality — a network of sub-functions, or applications. We call it the application network.
Let's future-proof ourselves and hedge against uncertainty by creating these building blocks, and then allow for the flexibility to rapidly piece them together on an on-demand basis.
1.1 Welcome to the Application Network
The application network is the future. It emerges from the creation of multiple API-enabled microservices; connecting these microservices with a strategic API approach results in a composable network. The network allows the flexibility to rapidly piece together different services for multiple functionalities an on-demand basis, providing business agility and a robust platform for innovation.
1.2 The Anatomy of an Application Building Block
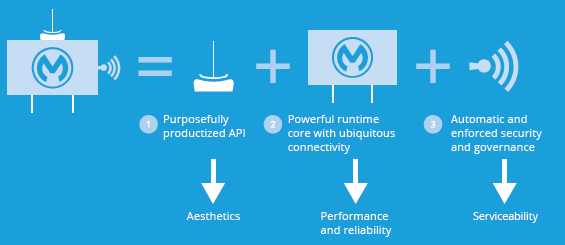
An application network is composed of application building blocks. These have multiple elements. and it's critical to separate the concerns between each. The API interface, the API implementation, and the API management aspects all have their own specific, unique lifecycles to follow. This building block should itself be treated as a product since these characteristics are common to what a good product should also have. Therefore, it makes sense to treat a building block from a product-centric approach.
We see this product-centric lifecycle as having three distinct stages: design, implementation, and management.
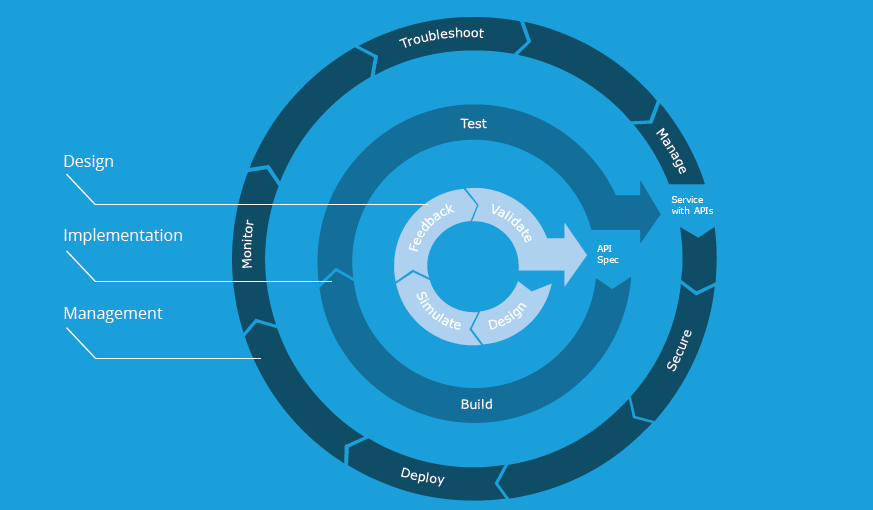
 1.3 The Lifecycle of an Application Building Block
1.3 The Lifecycle of an Application Building Block
2. Design
2.1 How to Design an API
Designing an API starts with an acknowledgment ahead of time that the API production process will start from an outside-in perspective, beginning with the “interface/contract” of the API. That is to say, let us first decide what the API will look and behave like before we actually begin to code the backend logic.
Often, developers build APIs without knowing the API has been validated and accepted. As a result, there is always this air of uncertainty: “Is this what my consuming developers want?”
2.2 “Outside-In” Done Right
API developers must design the user interface of the API first – this is also known as the API contract. This approach is typically known as a “design-first” approach, and it should follow a deliberate API design lifecycle in order to optimize for the best API experience. As a result, it is important to be able to do this in a human-readable fashion — to specify the contract in a way that humans can easily digest.
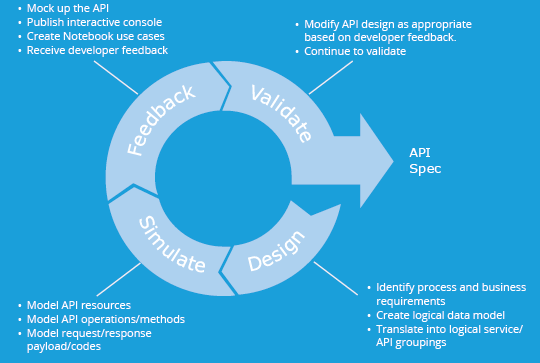 2.3 Soliciting Feedback on the API's Design
2.3 Soliciting Feedback on the API's Design
At this point in the process, the API designer (i.e. the designer of the API contract) is ready to have the API validated and tested by the API consumers (i.e. a client mobile app/website developer, or another API provider in some cases).
The currency of conversation between both parties will be interactive tools such as the API Notebook and interactive documentation, to name a few. There are many other tools that can be referenced from the raml.org site. This process of validation may be brief or extended over numerous iterations.
2.4 Repeatable Design
Any well-designed API will have repeatability, as well as repeatability across other APIs. This can easily be encapsulated into best practice patterns both at the structural level of the API (nouns/resources), as well as at the method level (verbs). So as API developers go about the design process, it is important to be able to discover and share repeatable patterns.
3. Implementation
3.1 Connect Systematically, Not in an Ad-Hoc Fashion
API implementation is a critical piece in enabling a next-generation enterprise. Enabling for dozens, potentially even hundreds or thousands of APIs to be connected down to a backend and connected to each other will be key. This must be done in a systematic manner (as opposed to point-to-point code).
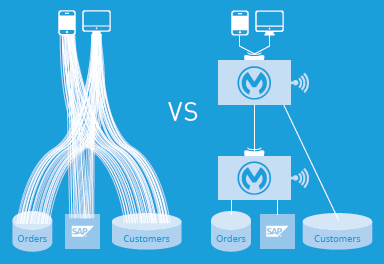 3.2 Put API Design Principles and Best Practices in a Common Repository
3.2 Put API Design Principles and Best Practices in a Common Repository
Benefits of a best practices repository:
• Increase business agility.
• Share best practices with reusable templates and logic.
• Leverage best practice patterns.
• Rapidly deploy APIs: fail fast, succeed faster.
• Minimize point-to-point logic and future-proof for stability.
3.3 Testing the API Implementation
At this point in the process, the API provider (i.e. the developer behind the API implementation) is ready to have the "guts" of the API tested. MUnit is MuleSoft’s testing solution, which is incorporated into the full application building block lifecycle. Test automation tools are critical here, as this integrates into the DevOps processes of continuous
delivery and deployment.
4 Management
4.1 Embrace DevOps
Embracing modern DevOps-centric processes and tooling is critical to reducing mean time-to-production, and this should apply to your application building blocks as well.
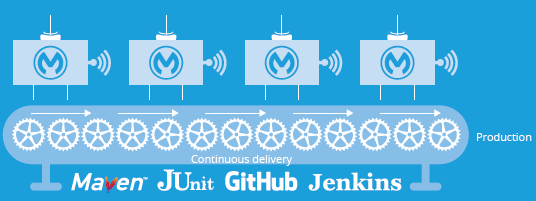
Once the application building block has been assembled and tested, deployment should be as easy as the click of a button.
The use of a hybrid integration platform that is lightweight, easy to install, and suitable for CI/CD workflows is key. The ability to have seamless support for dependency management, testing, version control, and automated deployment tooling should be an assumption.
4.2 Govern and Secure All Traffic
It is critical to ensure your application building blocks are following best practices in security and
architectural governance by applying policies to them at runtime. Monitoring all traffic is equally critical because it just takes just one weak link to bring the ship down.
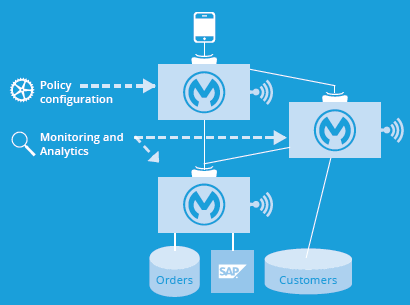
4.3 Don’t Forget About the Discoverability and On-Ramp
Imagine your company with hundreds — if not thousands — of APIs in your expansive application network. Imagine you're adding several new ones every day.
Being able to appropriately publish them so the consuming developer can find, research, and understand them easily could make or break your entire program. There is no point in building something that won’t ever be found, let alone used.
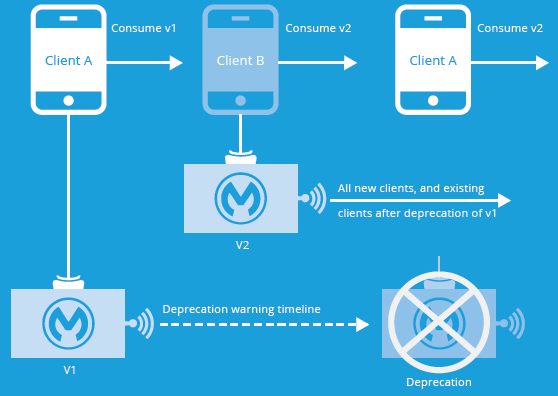
4.4 Just Like Any Product, Application Building Blocks Change
Building blocks will change. It’s a WHEN, not an IF, so be ready for it, which requires a carefully planned set of policies, procedures and the right platform to seamlessly migrate clients across new versions of APIs.
Getting this migration wrong will affect your customers. That’s not a risk worth taking.
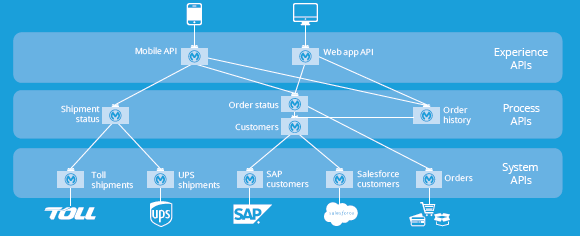
It takes a village to have an application network.
So, Now What?
For more background on full lifecycle API management, take a look at the Gartner Magic Quadrant, in which MuleSoft is a Leader. You can also take a look at their further resources on API strategy and API development.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments