Oracle Connection Manager: Enhancing Database Connectivity in the Cloud
This article explores the various use cases, installation, configuration, and management of Oracle Connection Manager, highlighting its significance.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeIn the ever-evolving landscape of cloud computing, Oracle Connection Manager (CMAN) plays a crucial role in streamlining and optimizing database connectivity. As a proxy server, CMAN acts as a bridge between clients and databases, forwarding connection requests and managing access control. This article explores the various use cases, installation, configuration, and management of Oracle Connection Manager, highlighting its significance in the cloud environment.
1. Introduction
Oracle Connection Manager (CMAN) is a powerful software solution that facilitates database connectivity in Oracle environments. By acting as a proxy server, CMAN provides a centralized point of control for managing client connections to databases. It works on the session level, allowing for efficient routing and load balancing of requests. CMAN is compatible with Oracle Database Enterprise Edition 12c and higher.
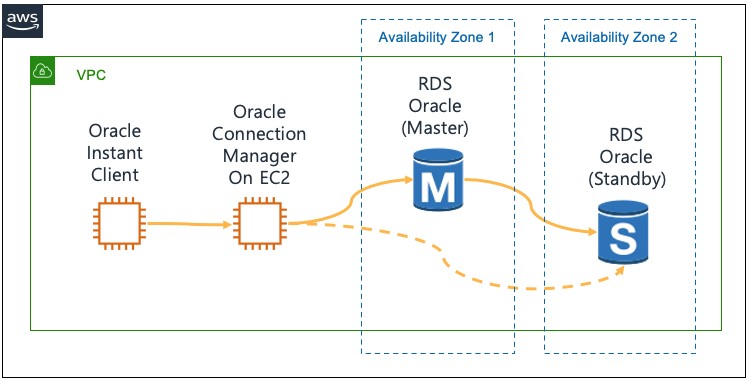
2. Use Cases of Oracle Connection Manager
CMAN offers a range of use cases that enhance database connectivity and security. Let's explore some of the key scenarios where CMAN proves invaluable:
2.1 Access Control
One of the primary use cases of CMAN is access control. By leveraging rule-based configurations, CMAN allows administrators to accept or reject specific client requests based on criteria such as client IP address. This capability adds an extra layer of security to the database environment.
2.2 Transit Routing
In scenarios where clients do not have direct access to certain databases, CMAN comes to the rescue by redirecting connection requests from clients to the appropriate databases. This ensures seamless communication and eliminates the need for complex network configurations.
2.3 Port and Protocol Mapping
CMAN enables connectivity between clients and databases that use different ports or IP protocols. For instance, if target databases use ports not open on the client side, CMAN can be configured to use a different port, ensuring successful communication. Similarly, if clients and databases use different IP protocols, CMAN serves as a network bridge, allowing for smooth interaction between IPv4 and IPv6 environments.
2.4 Database Link from Autonomous Database to Private IP
While the direct creation of database links from Autonomous Database to private IPs is still in development, CMAN presents a viable workaround. By setting up CMAN as described in this blog post, users can establish database links from Autonomous Database to private IPs. (Additional Information: Update Dec. 13, 2021 — Creating database links from Autonomous Database to private IPs is now possible, as documented in the official Oracle documentation.)
3. Installation and Setup
To leverage the power of Oracle Connection Manager, it is essential to understand the installation and setup process. Let's delve into the steps required to get CMAN up and running:
Response File (Save the response file as cman19c.rsp) |
|
Install in Silent Mode |
|
3.1 Environment Setup
Before installing CMAN, ensure that you have the necessary environment in place. This includes a server where CMAN will be installed and the required Oracle Database Enterprise Edition 12c or higher.
3.2 Installation of Connection Manager
The installation of CMAN involves downloading the Connection Manager software and following the installation steps. There are multiple modes of installation available, including the GUI mode and silent mode using a response file. Let's explore the installation process in detail.
3.2.1 Download Connection Manager
To begin the installation, download the Oracle Connection Manager software from the official Oracle website. Ensure you choose the appropriate version compatible with your Oracle Database Enterprise Edition.
3.2.2 Setup User and Group
Create a dedicated user and group for the CMAN installation. This ensures proper permissions and security for managing the CMAN instance.
3.2.3 Installation Using GUI Mode
The GUI mode installation provides a user-friendly interface to guide you through the installation process. Follow the on-screen instructions to specify the installation location, user, and group details. Once the installation is complete, you can proceed with the configuration of CMAN.
3.3 Configuration of Connection Manager
The configuration of CMAN involves setting up the cman.ora file, which contains the necessary parameters and rules for managing connections. Let's explore the key aspects of the configuration process:
3.3.1 About cman.ora File
The cman.ora file serves as the central configuration file for Oracle Connection Manager. It contains various sections, each specifying different settings such as listening addresses, rule-based access control, and connection redirection. Edit the cman.ora file to customize CMAN behavior according to your specific requirements.
oracle@ora19cdb cman19c (SID:cman19c)$ export TNS_ADMIN=/u01/app/cman19c
$ echo "IFILE=${TNS_ADMIN}/cman-test.ora" >> $TNS_ADMIN/cman.ora
oracle@ora19cdb cman19c (SID:cman19c)$ cat cman-test.ora
cman-test = (configuration=
(address=(protocol=tcp)(host=$(hostname))(port=1539))
(parameter_list =
(log_level=ADMIN)
(max_connections=1024)
(idle_timeout=0)
(registration_invited_nodes = *)
(inbound_connect_timeout=0)
(session_timeout=0)
(outbound_connect_timeout=0)
(max_gateway_processes=16)
(min_gateway_processes=2)
(remote_admin=on)
(trace_level=off)
(max_cmctl_sessions=4)
(event_group=init_and_term,memory_ops)
)
(rule_list=
(rule=
(src=*)(dst=*)(srv=*)(act=accept)
(action_list=(aut=off)(moct=0)(mct=0)(mit=0)(conn_stats=on))
) )
)
4. Managing Connection Manager Instance
Once the CMAN instance is up and running, it is essential to understand how to manage and monitor its performance. Let's explore some key management tasks:
4.1 Connect to Connection Manager Instance
To manage the CMAN instance, you need to establish a connection to it. This can be done using the Connection Manager Control utility (CMCTL). CMCTL provides a command-line interface for managing the CMAN instance, allowing you to monitor connections, view statistics, and perform various administrative tasks.
4.2 Check Connection Manager Version
Regularly checking the CMAN version is crucial to ensure you are running the latest release and taking advantage of any bug fixes or feature enhancements. The CMCTL utility provides a simple command to display the CMAN version.
oracle@ora19cdb cman19c (SID:cman19c)$ cmctl
Copyright (c) 1996, 2019, Oracle. All rights reserved.
Welcome to CMCTL, type "help" for information.
CMCTL> admin cman-test
Current instance cman-test is already started
Connections refer to (DESCRIPTION=(address=(protocol=tcp)(host=ora19cdb)(port=1521))).
The command completed successfully.
5. Integration with Amazon RDS for Oracle
Oracle Connection Manager can be seamlessly integrated with Amazon RDS for Oracle, further enhancing the database connectivity capabilities. Amazon RDS for Oracle is a managed Oracle relational database service provided by Amazon Web Services (AWS). By creating a connection asset for Amazon RDS for Oracle in CMAN, you can leverage the benefits of both solutions.
5.1 Creating a Connection Asset
To establish a connection to Amazon RDS for Oracle, you need to create a connection asset in CMAN. This involves providing the necessary connection details such as the Oracle Service name or SID, hostname or IP address of the database, and the port number. Additionally, if SSL certificate verification is required, ensure you have the relevant certificate.
5.2 Benefits of Integration
Integrating Oracle Connection Manager with Amazon RDS for Oracle offers several advantages. Firstly, it allows for centralized management and control of client connections, enhancing security and access control. Secondly, CMAN provides the flexibility to handle complex network configurations, such as port mapping and protocol conversion. Lastly, the integration simplifies the management of connections to Amazon RDS for Oracle, streamlining the overall database connectivity experience.
6. Benefits of Oracle Connection Manager
Oracle Connection Manager brings a multitude of benefits to the table, making it an indispensable component in the cloud environment. Let's explore some of the key advantages:
6.1 Enhanced Security
By acting as a proxy server, CMAN enables administrators to implement granular access control policies, ensuring that only authorized clients can establish connections to the databases. This helps prevent unauthorized access and enhances the overall security posture of the database environment.
6.2 Scalability and Load Balancing
CMAN provides the capability to distribute client connection requests across multiple databases, improving scalability and load balancing. By intelligently routing requests, CMAN optimizes resource utilization and ensures high availability of database services.
6.3 Simplified Network Configurations
In complex network environments, CMAN simplifies connectivity by handling port mapping, protocol conversions, and network bridging. It eliminates the need for intricate network configurations on client machines, allowing for seamless communication between clients and databases.
6.4 Centralized Management and Monitoring
Oracle Connection Manager offers centralized management and monitoring capabilities through tools like CMCTL. Administrators can easily track connection statistics, monitor performance, and troubleshoot issues from a single interface, streamlining the management process.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments