Phases of SDLC Agile Model
In this article we will look, What is agile model, the stages of the SDLC agile model, and the pros and cons of the agile model.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAgile describes something quick to change or adapt. An "agile process model" is a software development approach focused on iterative development. Agile methodologies break projects into smaller iterations or parts, avoiding long-term planning. The project's scope and needs are specified at the outset of the development process. Each iteration's number of iterations, duration, and scope are all set ahead of time.
Agile modeling is a technique for demonstrating and documenting programming frameworks in accordance with best practices. It's a set of values and guidelines that can be used in a programming development project.
What Is Agile?
An agile paradigm is also a form of incremental development. Programming is done in short, progressive cycles. This resulted in small, progressive deliveries, each one building on the previous one's usefulness. Each delivery is thoroughly tested to ensure that programming quality is maintained. It is used in time-sensitive applications.
Phases of an Agile Process Model
The following are the steps of the agile process model:
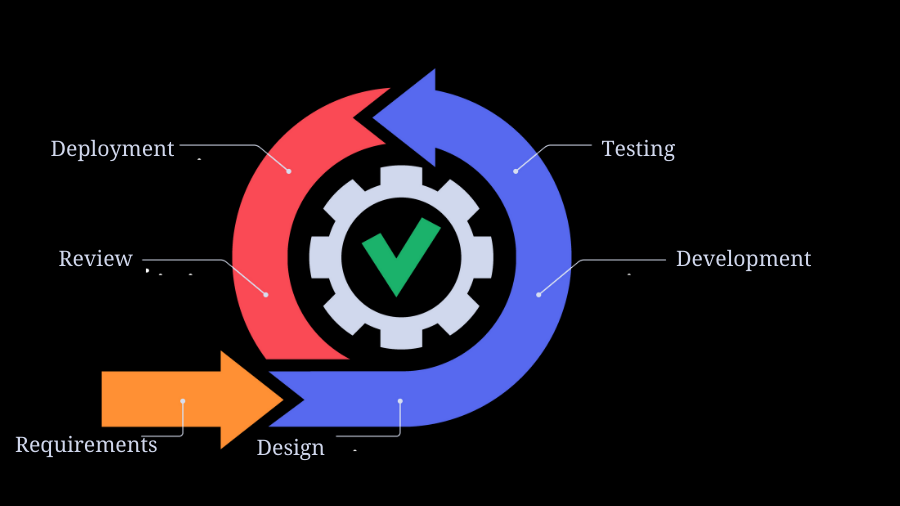
- Requirements gathering
- Design the requirements
- Construction/ iteration
- Testing
- Deployment
- Feedback
Read about the SDLC Agile process model in the following brief:
1) Gathering Requirements
The requirements should be defined at this point. Then, different business options are discussed, and efforts and time are allocated to the project's development.
2) Design the Requirements
When you've identified the task, collaborate with others to develop the requirements. You can use the client stream graph to demonstrate newly created parts and how they will fit into your existing framework.
3) Iteration/Construction
The task begins when the group defines the requirements. Then, creators and designers work on their tasks to send a working product. The item will go through many stages of development, thus it will have simple limited functionality.
4) Testing
The Quality Assurance team examines the item's presentation and looks for bugs at this step.
5) Deployment
The group now provides an item for the client's workplace.
6) Provide Feedback
The final step before a product is released is to get Feedback. The product receives Feedback, and the input is managed.
When Should an Agile Model be Used?
- To implement a new feature, developers must go back a few days, or even hours, in order to complete it.
- Agile's flexibility is critical for change when new adjustments are necessary to implement. Because new augmentations are developed on a regular basis, new alterations can be implemented at a low cost.
- In today's powerful business and IT environment, end clients' expectations are truly evolving. Changes can be observed and elements influenced. This provides the client with the whole structure they require or desire.
Pros and Cons of the Agile Model
Pros:
- Encourages collaboration and general education.
- It is possible to develop and demonstrate usefulness quickly.
- Early fractional employment agreements are described.
- For conditions that vary on a regular basis, this model is ideal.
- There are no asset requirements.
Cons:
- Not suitable for dealing with difficult situations.
- There is a lack of focus on important planning and documentation.
- If the client's requirements are unclear, the project may quickly become derailed.
- Only senior software engineers are capable of making the kinds of decisions that must be made during the improvement cycle. As a result, junior software engineers face a difficult situation unless partnered with seasoned assets.
Conclusion
The Agile Development method is a redesigned approach to programming item development that emphasizes adaptability and speed. As a result, the Agile development technique creates a significant share of today's electronic products.
Published at DZone with permission of Risha Bhat. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments