Queue in Data Structures and Algorithms
In this blog, we further discuss queue implementation, how it is related to data structures, and its real-time applications.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeQueue, for example, is a sequence of people who are standing for buying a metro ticket or ordering food at a store. The first person entering the queue leaves first. Similarly, the last person entering the queue leaves at the last. These queues help in managing the flow of customers and lower the chances of rush while buying.
In this blog, we further discuss queue implementation, how it is related to data structures, and its real-time applications.
What Is Queue in DS?
A Queue is a linear type data structure that follows the principle of FIFO ( First-in-First-out ). The elements are added to the queue from one side and deleted from the other side. The side where elements are added is called the rear, and where deleted is called the front. 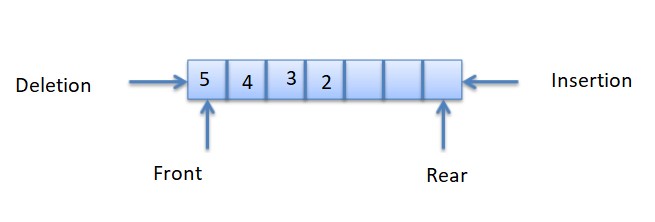
Firstly, the initial condition for the queue is front and rear should be equal to -1.
As discussed in the previous blog on the stack, let us understand the ADT of the queue now.
1. enqueue(): We can add or insert elements from the rear side.To implement this operation, first, we must check whether the queue is full or not.
The pseudo-code is shown below:
void enqueue()
{
if(rear == MAXSIZE -1) //initially rear = -1
//Overflow!
else{
rear = rear + 1;
//store element
}
}
2. dequeue(): We can delete or remove elements from the front side.
To implement this operation, first, we must check, the queue is not empty.
The pseudo-code for dequeue is:
void dequeue()
{
if(front == -1 || front > rear)
//Underflow!
else{
//store element
front = front + 1;
}
}
3. peek(): We can access the value pointed by the front.
Implementation of queue using c program:
#include<stdio.h>
#define MAXSIZE 20
int queue[MAXSIZE];
int front =-1,rear =-1,val,i;
void enqueue();
void dequeue();
void display();
void main()
{
int choice;
while(choice != 4)
{
printf("Enter a choice\n");
printf("\n1.Enqueue\n2.Dequeue\n3.Display\n4.Exit");
scanf("%d", &choice);
switch(choice)
{
case 1:
enqueue();
break;
case 2:
dequeue();
break;
case 3:
display();
break;
case 4:
printf("Exiting...\n");
break;
default:
printf("Invalid\n");
}
}
}
void enqueue()
{
printf("Enter val:");
scanf("%d", &val);
if(rear == MAXSIZE -1)
printf("Overflow\n");
else if(front == -1 && rear == -1)
{
front = 0;
rear = 0;
queue[rear] = val;
}
else
{
rear = rear + 1;
queue[rear] = val;
}
}
}
void dequeue()
{
if(front == -1 || front > rear)
printf("Underflow\n");
else if(front == rear)
{
val = queue[front];
front = -1;
rear = -1;
}
else
{
val = queue[front];
front = front + 1;
}
}
}
void display()
{
if(rear == -1)
printf("queue is empty");
else
{
printf("values in queue:\n");
for(i=front;i<=rear;i++)
{
printf("%d", queue[i]);
}
}
}When we run the program, we get the output:

Types of Queues
We can find different types of queues, and they are as followed:
- Linear queues: These are linear queues that are discussed already in the blog.
- Circular queues: In these, the last element is connected to the first element and forms a circular loop.
- Double-ended queues: These are also called Deque, where insertion and deletion can take place on both sides, i.e., both rear and front.
Conclusion
In the end, queues are one of the important concepts in data structures. I hope you like this blog, do leave a comment and share it.
Also, visit my other blog on Stack in data structures and algorithms.
Thank you.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments