Rate Limiter Internals in Resilience4j
In this article, we look at how this open source framework can help you boost the performance of your web application by making rate limiting easier.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis is the third article of a short series about the Resilience4j library. If you are not familiar with the library itself, please read this introduction article first. There is also a similar write-up about circuit breaker implementation.
What Is Rate Limiting and When Is it Useful?
So, let's talk about another core component of the Resilience4j called the Rate Limiter. Unlike circuit breaking, the impact of rate limiting on your application resilience is not so obvious and comes into the game only after a certain scale. If you've ever worked with APIs for some huge products you know that they have rate limiting applied to almost any operation. Examples: Facebook, Twitter, Google Analytics...
But it doesn't mean that this pattern can be useful only for giants. In reality, it's the opposite - the smaller production environment you have, the more you should think about incoming traffic and your ability to handle possible request spikes. In practice, there are also situations when you're integrating with some legacy API and it doesn't have any rate limiters applied, so you can unintentionally perform a DoS attack on your partners. In such cases, you should of course tune this API usage and enforce rate limits on your side.
In general, rate limiting is an imperative technique to prepare your API for scale and establish high availability and reliability of your service. But also, this technique comes with a whole bunch of different options of how to handle a detected limits surplus, or what type of requests you want to limit. You can simply decline this over limit request, or build a queue to execute them later or combine these two approaches in some way. You can also limit concurrent requests by allowing only a certain amount of parallel executions (Resilience4j has a separate component for such limits, called Bulkhead). Another option would be to categorize all requests by priority and apply different limits for each category.
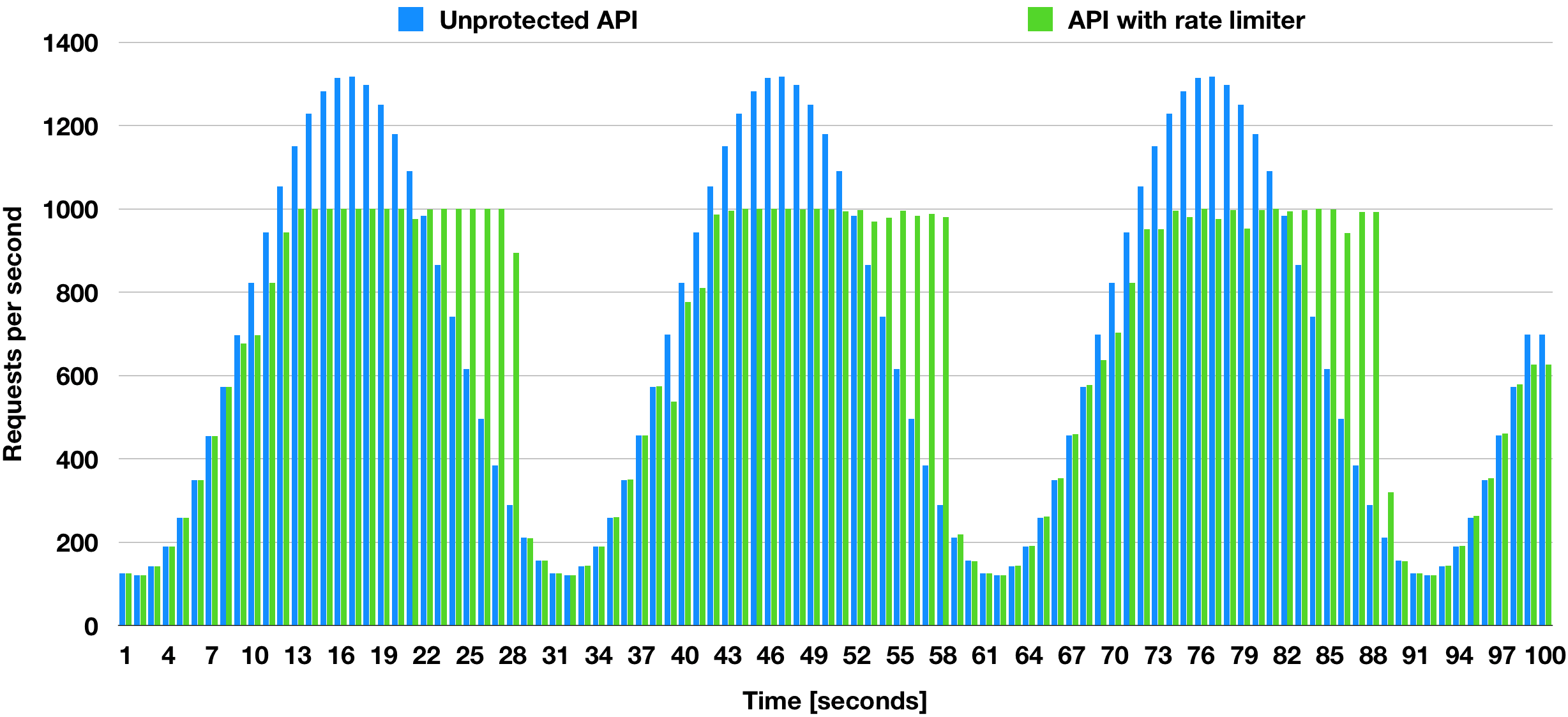
Impact of queueing rate limiter on application throughput.
Rate Limiter Implementations
Resilience4j has a simple interface called RateLimiter (obviously) and the main method within it is
boolean getPermission(java.time.Duration timeoutDuration);where timeoutDuration is a period you're ready to wait for permission if it's not there yet. This method returns true if a permission was acquired and false if while waiting timeoutDuration elapsed before a permit was acquired.
Currently, we have de-facto standard rate limiting algorithm called "token-bucket," but it comes with different variations and in Resilience4j you can find two implementations: SemaphoreBasedRateLimiter and AtomicRateLimiter.
Semaphore-Based Rate Limiter
Let's talk about SemaphoreBasedRateLimiter first, because it is actually the simplest and most performant implementation at the same time.
It's based on the simple idea that we can have one java.util.concurrent.Semaphore to store current permissions and all user threads will call semaphore.tryAcquire method, while we will have an additional internal thread and it will call semaphore.release when new limitRefreshPeriod starts.
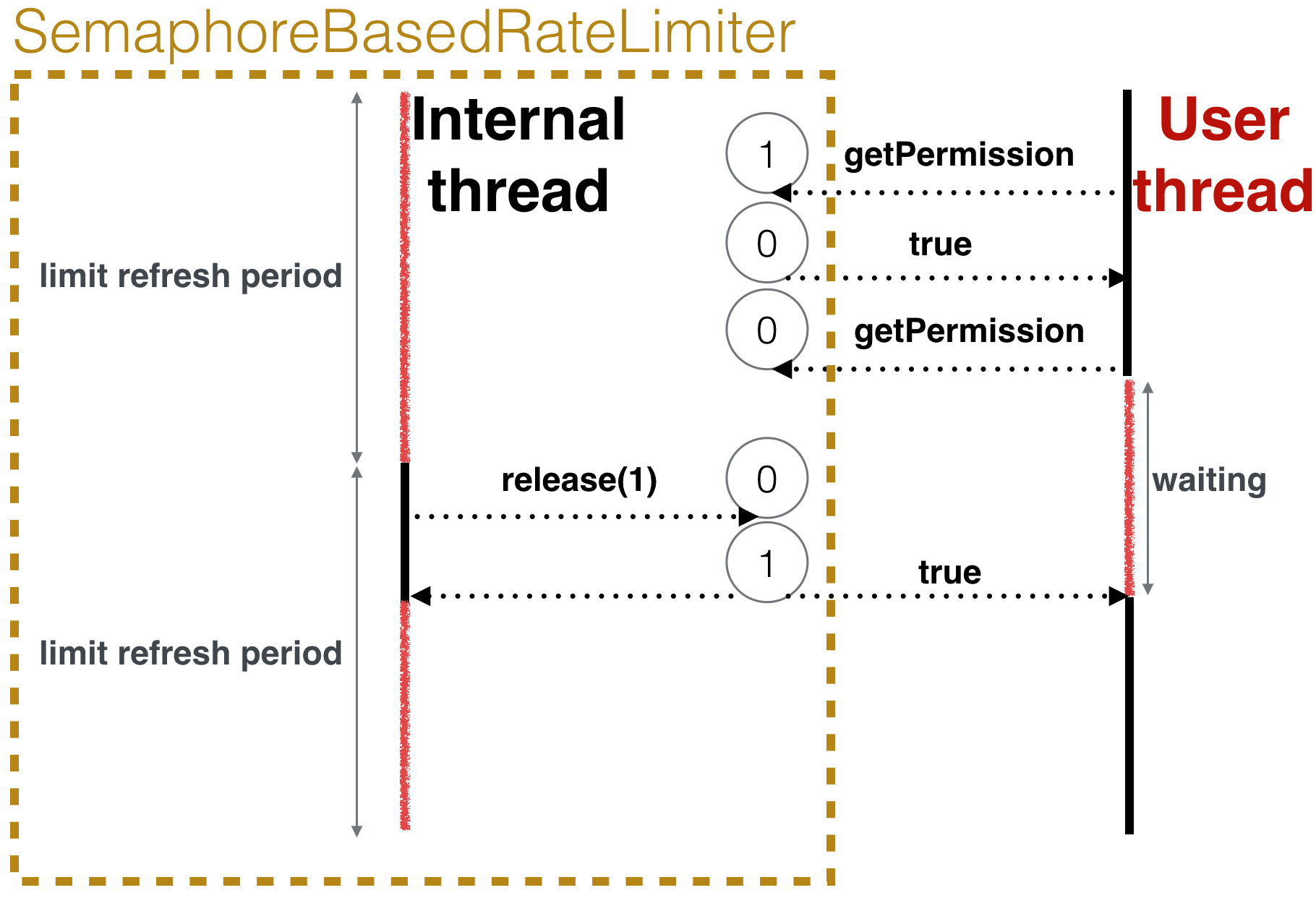
Permission acquire and waiting sequence diagram
This simple approach is actually really performant because user threads have very small hot paths and don't care about any other required calculations; all permission refreshment is handled by an internal thread. So, my relatively small laptop can perform up to 30 permission checks within a microsecond. In the end, this implementation has only one drawback: you should have this internal thread in place and it looks like a bit of overhead. We know about that issue and provide our users with some ways to share this management thread with a whole bunch of limiters, so overall overhead can be really low. We also have another implementation called AtomicRateLimiter and it has no need of such management threads because all permission recalculation logic is executed by user threads themselves.
Atomic Rate Limiter
This rate limiter has a bit of tricky logic, and a sequence diagram for it would be hard to understand, so I'll just describe the main ideas behind it:
- We can virtually split time into equal pieces called cycles. In any time, we can determine the current cycle by calculating currentTime/cyclePeriod.
- If we know the current cycle number and cycle when the limiter was in use last, we can actually calculate how many permissions should've appeared in the limiter.
- After this calculation, if available permissions aren't enough, we can perform permission reservation, by decreasing current permissions and calculating the time we should wait for it to appear.
- After all calculations, we can produce a new limiter state and store it in AtomicReference, to propagate these changes across all user threads.
Of course, real implementation has some nuances to handle corner cases, deal with thread interrupts, maintain consistent limiter throughput under contention, etc. After all, this implementation is also very performant and much easier to configure. On my laptop, this limiter is capable to maintain 10 limiter checks per microsecond even under big contention. This is more than enough for almost any load you have, that's why this limiter is our default implementation. But if you really need to check permissions more than 2 million times per second, then I think it will be more beneficial to spend some time and configure semaphore based limiter for this high load operation.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments