Spring Boot: Reading Resources
Learn how to read files from the resources folder in a Spring Boot application.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Reading files from a Spring Boot application is possible through Java 8 NIO API. This article demonstrates how to read files from the resources folder in a Spring Boot application, which is running as a standalone application or inside the Docker container.
You may also like: Working With Resources in Spring
Create a Project
Generate a Gradle or Maven project using the Spring Initializer. Create folder and files inside the resources folder as required.
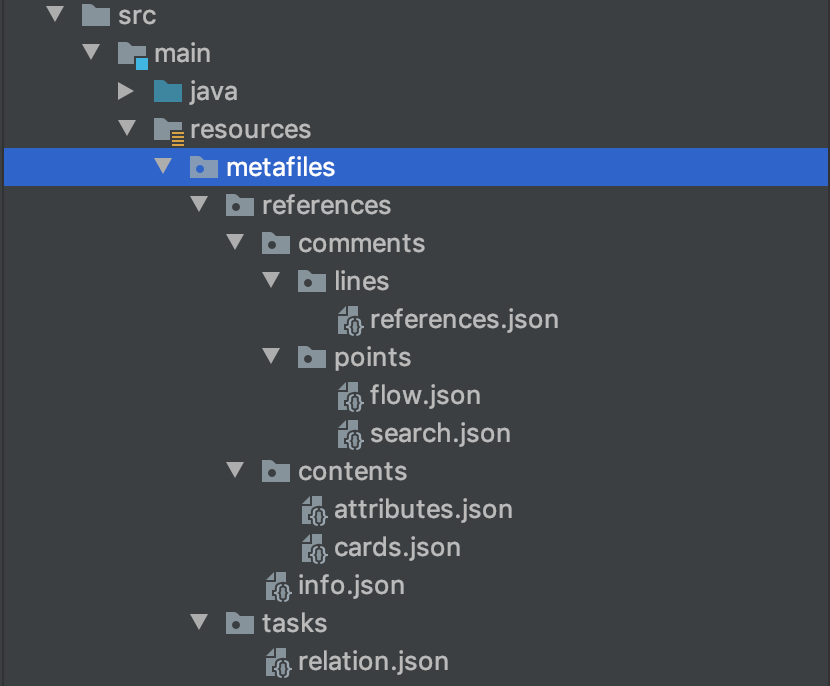
Create a Pseudo File System
We are trying to read metafiles folder contents from the above structure. We need to convert the file path to URI resource. Create a new file system for URI resource. Since FileSystem is Closable, we are able to place initialize the jarFileSystem within the try block.
xxxxxxxxxx
public void readFolderFromJar() throws Exception {
String relativePath = "metafiles";
URI resource = getClass().getClassLoader().getResource(relativePath).toURI();
try (FileSystem jarFileSystem = FileSystems.newFileSystem(resource, Collections.emptyMap())) {
String[] jarPath = resource.toString().split("!", 2);
String jarReference = jarPath[1].replace("!", "");
readContent(jarFileSystem.getPath(jarReference));
}
}
Recursively Traverse
If the path is a directory, then recursively call readContent function until we encounter the individual files. Let us use NIO API Files. Files.list lists would list out paths lazily.
xxxxxxxxxx
public void readContent(Path path)
{
try
{
Stream<Path> list = Files.list(path);
List<Path> paths = list.parallel().collect(Collectors.toList());
paths.stream().parallel().forEach(filePath -> {
if (Files.isDirectory(filePath))
{
readContent(filePath);
}
else
{
try
{
String fileName = filePath.toString().split("classes")[1];
String content = readFile(filePath);
logger.debug("File: "+fileName+": Content: "+content);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
logger.error("Unable to read file " + e.getMessage());
}
}
});
}
catch (Exception e)
{
logger.error("Unable to read file " + e.getMessage());
}
}
Read content
Read content of files from path using Files.readAllBytes.
private String readFile(Path path) throws IOException
{
byte[] encoded = Files.readAllBytes(path);
return new String(encoded, Charset.forName("UTF-8"));
}
Test Run
Run your Spring Boot project using the traditional approach shown below. Here, resources/metafiles will be part of "jar," and still, we will be able to read the contents of these files.
java -jar demo-0.0.1-SNAPSHOT.jar
Hope you enjoyed!
Further Reading
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments