Runners in Spring Boot
Know about the Runners in Spring Boot and how to implement them.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeRunners is a java class/spring beans of Spring boot Application implement the XXXRunner(I) directly or indirectly, and its auto-executable component is called by Container.
Runner classes are used to deal with one-time executing logics and those logics will be executed where SpringApplication.run(-) is about to complete all of its startup activities.
There are 2 Types of Runners
- CommandLineRunner
- ApplicationRunner
CommandLineRunner
- It's a legacy runner which was introduced in SpringBoot 1.0 version.
- It has only one abstract method “run(String… args): void”.
- It is a Functional Interface having only one abstract method i.e "void run(String… args)".
- Add one stereotype Annotation over Implementation class level (Ex:- @Component). So that container can detect the class and create the object.
ApplicationRunner(I)
- It is a new type of runner added in Spring boot 1.3 which makes it easy to access arguments.
- This will separate Option Arguments (as Map<String, List<String>>) and Non-Option Arguments (<List<String>)
NOTE:--
- If Spring Boot Application contains multiple runners like AlertRunner, EmailRunner, SecurityRunner, CloudEnvRunner, DatabaseRunner, etc…
- Spring Boot provides default execution order. i.e ApplicationRunner implemented classes will execute first based on alphabetical order(A-Z) after that CommandLineArgument implemented classes will be executed based on alphabetical order.
In case If the programmer wants to specify custom order then use the following
i) Interface: Ordered
Example:
@Component
public class CustomApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner,Ordered {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("CustomApplicationRunner.run() arguments");
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
return -15;
}
}ii) Annotation: @Order
Example:
@Component
@Order(-1)
public class AlertCammandLineRunner implements CommandLineRunner {
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("AlertCammandLineRunner.run() arguments");
}
}Here if the Order value is high then the priority is low, if the Order Value is low then priority is high
Note: Negative numbers are also allowed.
Note: If You added both @Order and Ordered(I) then the Ordered interface getOrder() return value will be taken as the priority value.
Example:
@Component
@Order(12)
public class CustomApplicationRunner implements ApplicationRunner,Ordered {
@Override
public void run(ApplicationArguments args) throws Exception {
System.out.println("CustomApplicationRunner.run() arguments");
}
@Override
public int getOrder() {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
return -15;
}
}For the above example, the priority value is -15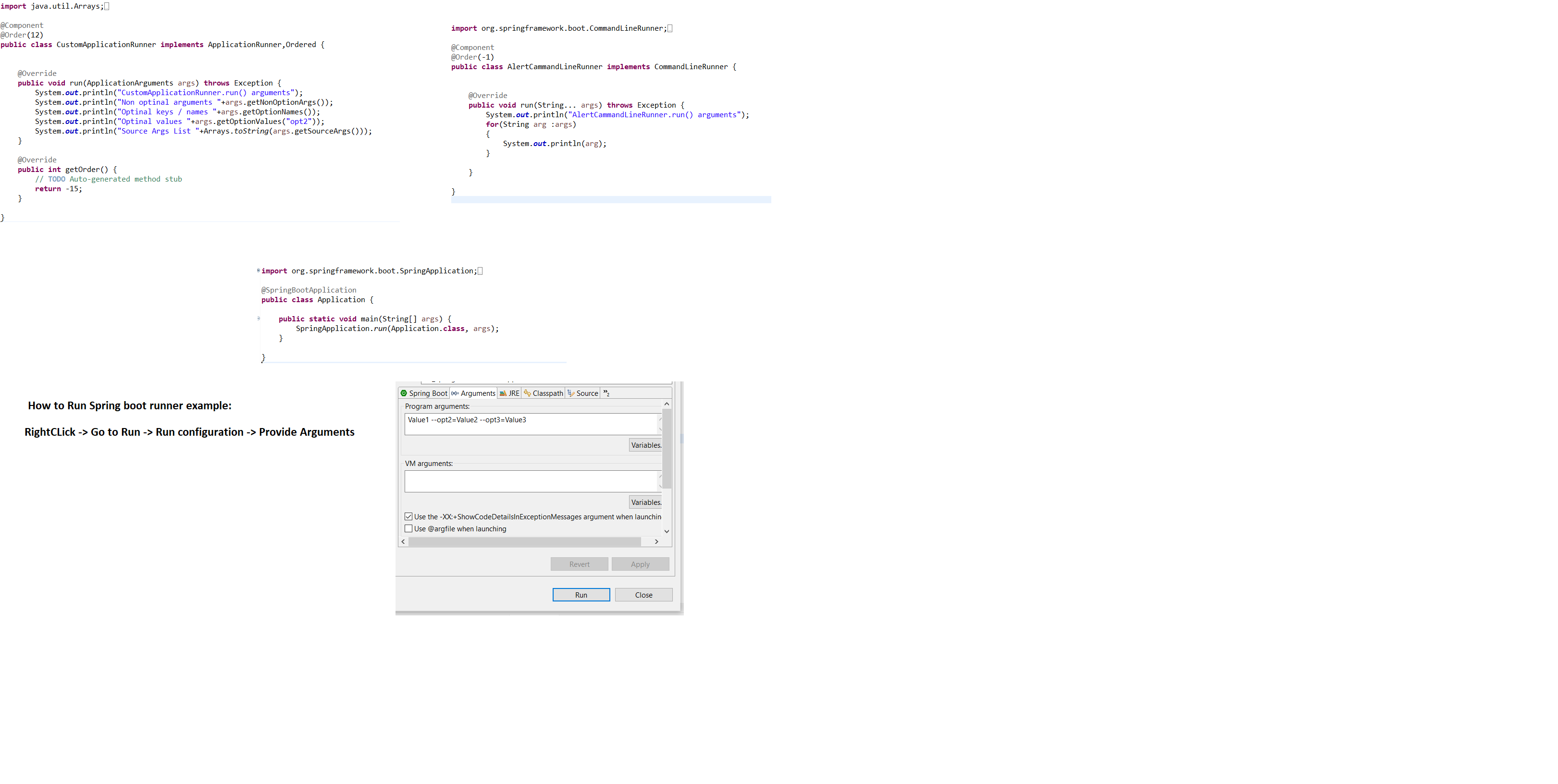
Please refer to the attached Image for Runners Example.
How To Pass Data to Runners:
We Programmers can pass data using Command Line Arguments, in two formats Option and Non-option arguments.
Syntax:
--Key = Val for optional arguments.
value for non Optional arguments.
Example's for Optional arguments:
--db=oracle, --env=prod
Example's for NonOptional arguments:
Test clean execute etc...
Arguments data will be converted to String[] and send to CommandLineRunner Classes. We can access the data based on index format.
Difference Between CommandLineRunner and ApplicationRunner
The working of both CommandLineRunner and ApplicationRunner processes is the same, but CommandLineRunner holds the data in the String[] format whereas Application (AR) holds data as ApllicationArguments as Option/Non-Option format.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments