Secure Spring REST API Using OAuth2 + MySQL
REST easy knowing your APIs are secure after this tutorial.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
Let’s secure our Spring REST API with OAuth2 and MySQL. We will store user credentials in the MySQL database, and client credentials will be stored in the in-memory database. Every client has its own unique client ID.
To secure our REST API, we will have to do the following things:
Configure Spring Security and the database.
Configure the authorization server and resource server.
Get an access token and a refresh token.
Get a protected Resource (REST API) using an access token.
Before we start, let's look at some basic concepts related to Spring Security OAuth2.
You may also like: Spring Security Authentication.
OAuth2 Roles
Resource Owner
A resource owner is a person (like an end-user) in an application that owns the service or security policy.
Resource Server
This is the resource server hosting the protected resource or service.
Client Application
The client application is the application requesting access to resources stored on the resource server. The client application also obtains authorization from the resource owner.
Authorization Server
The authorization server is the server authorizing the client app to access the resources of the resource owner.
Application
Let's start to secure our REST API endpoints.
First, we need to enable Spring Security to add the security feature in the application. To configure and enable Spring Security, the @EnableWebSecurity annotation is used.
By using @EnableGlobalMethodSecurity, we can easily secure our methods with Java configurations. Global method security will activate @PreFilter, @PostFilter , @PreAuthorize, and the @PostAuthorize annotations if we want to use them.
@EnableWebSecurity
@EnableGlobalMethodSecurity(securedEnabled = true)
public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
UserDetailsServiceImpl userDetailsService;
@Override
protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.csrf().disable().sessionManagement().sessionCreationPolicy(SessionCreationPolicy.STATELESS)
.and().authorizeRequests().antMatchers("/oauth/token")
.permitAll().anyRequest().authenticated();
}
@Bean
public DaoAuthenticationProvider authenticationProvider() {
DaoAuthenticationProvider provider = new DaoAuthenticationProvider();
provider.setPasswordEncoder( bCryptPasswordEncoder() );
provider.setUserDetailsService(userDetailsService);
return provider;
}
@Bean
public BCryptPasswordEncoder bCryptPasswordEncoder() {
return new BCryptPasswordEncoder();
}
@Override
@Bean
public AuthenticationManager authenticationManagerBean() throws Exception {
return super.authenticationManagerBean();
}
@Autowired
public void configureGlobal(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception {
auth.authenticationProvider(authenticationProvider());
}
}Note:
Here,
WebSecurityConfigurerAdapteris used to customize security implementation.Endpoint /OAuth/tpkenis used to request a token (access or refresh).We inject a custom implementation of
UserDetailsServicein order to retrieve user details from the database.We use the defined
BCryptPasswordEncoderbean for password encoding.
Now, we need to configure the authorization server. The @EnableAuhtorizationServer annotation enables an authorization server. AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter implements the AuthorizationServerConfigurer, which provides all the necessary methods to configure an Authorization server. It also contains information about registered clients and possible access to scopes and grant types.
@Configuration
@EnableAuthorizationServer
public class OAuthConfiguration extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter {
@Autowired
@Qualifier("authenticationManagerBean")
private AuthenticationManager authenticationManager;
@Autowired
UserDetailsService userDetailsService;
@Override
public void configure(final AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer oauthServer) throws Exception {
oauthServer.tokenKeyAccess("permitAll()").checkTokenAccess("isAuthenticated()");
}
@Override
public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception {
clients.inMemory()
.withClient("fooClientId").secret("secret")
.authorizedGrantTypes("password", "authorization_code", "refresh_token").scopes("read","write")
.autoApprove(true);
}
@Override
public void configure(final AuthorizationServerEndpointsConfigurer endpoints) throws Exception {
endpoints.tokenStore(tokenStore()).authenticationManager(authenticationManager).accessTokenConverter(defaultAccessTokenConverter())
.userDetailsService(userDetailsService);
}
@Bean
public TokenStore tokenStore(){
return new JwtTokenStore(defaultAccessTokenConverter());
}
@Bean
public JwtAccessTokenConverter defaultAccessTokenConverter() {
JwtAccessTokenConverter converter = new JwtAccessTokenConverter();
converter.setSigningKey("123");
return converter;
}
}
Notes on the above configuration:
Registers a client with client-id ‘
fooClientId’ and password ‘secret’ and the roles and scope they are allowed.Specifies authorized grant types (password, authorization_code, refresh_token).
Specifies the
JwtTokenStoreto store tokens.
Next, we need to configure the resource server. The @EnableResourceServer annotation, applied on OAuth2 Resource Servers, enables a Spring Security filter that authenticates requests using an incoming OAuth2 token.
The class ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter implements the ResourceServerConfigure, providing methods to adjust the access rules and paths that are protected by OAuth2 security.
@Configuration
@EnableResourceServer
public class ResourceServerConfiguration extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter {
private static final String RESOURCE_ID = "resource-server-rest-api";
@Override
public void configure(ResourceServerSecurityConfigurer resources) {
resources.resourceId(RESOURCE_ID);
}
@Override
public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception {
http.antMatcher("/**").authorizeRequests().anyRequest().authenticated();
}
}Next, we need to update the application.properties to configure the MySQL database. Create the user_management schema in MySQL and add the user table to store user credentials with roles.
spring.datasource.url = jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/user_management
spring.datasource.username = root
spring.datasource.password = root
# Hibernate ddl auto (create, create-drop, update)
spring.jpa.hibernate.ddl-auto = update
# Naming strategy
spring.jpa.hibernate.naming-strategy = org.hibernate.cfg.ImprovedNamingStrategy
# Use spring.jpa.properties.* for Hibernate native properties (the prefix is
# stripped before adding them to the entity manager)
# The SQL dialect makes Hibernate generate better SQL for the chosen database
spring.jpa.properties.hibernate.dialect = org.hibernate.dialect.MySQL5Dialect
spring.datasource.driver-class-name=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
server.port = 8080Test Application
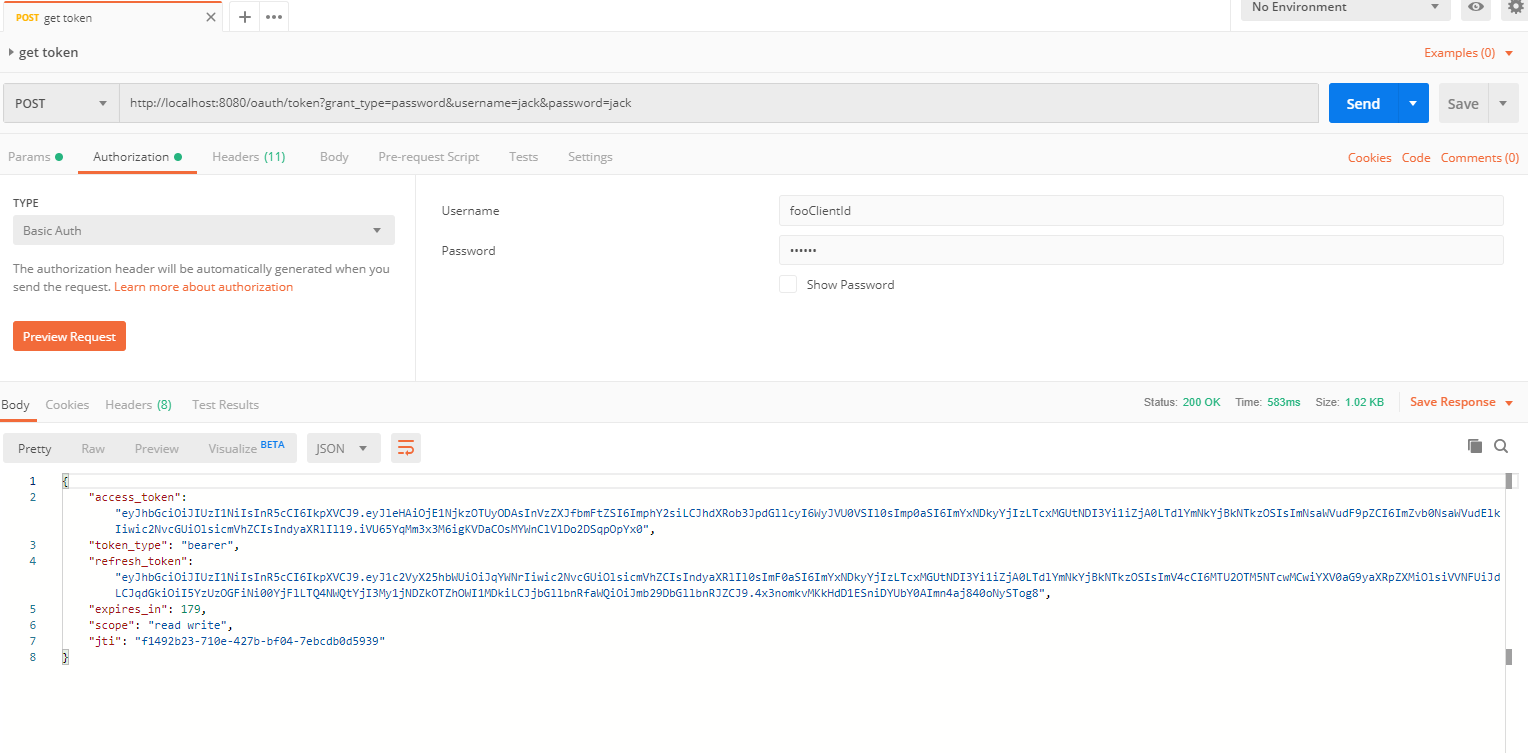
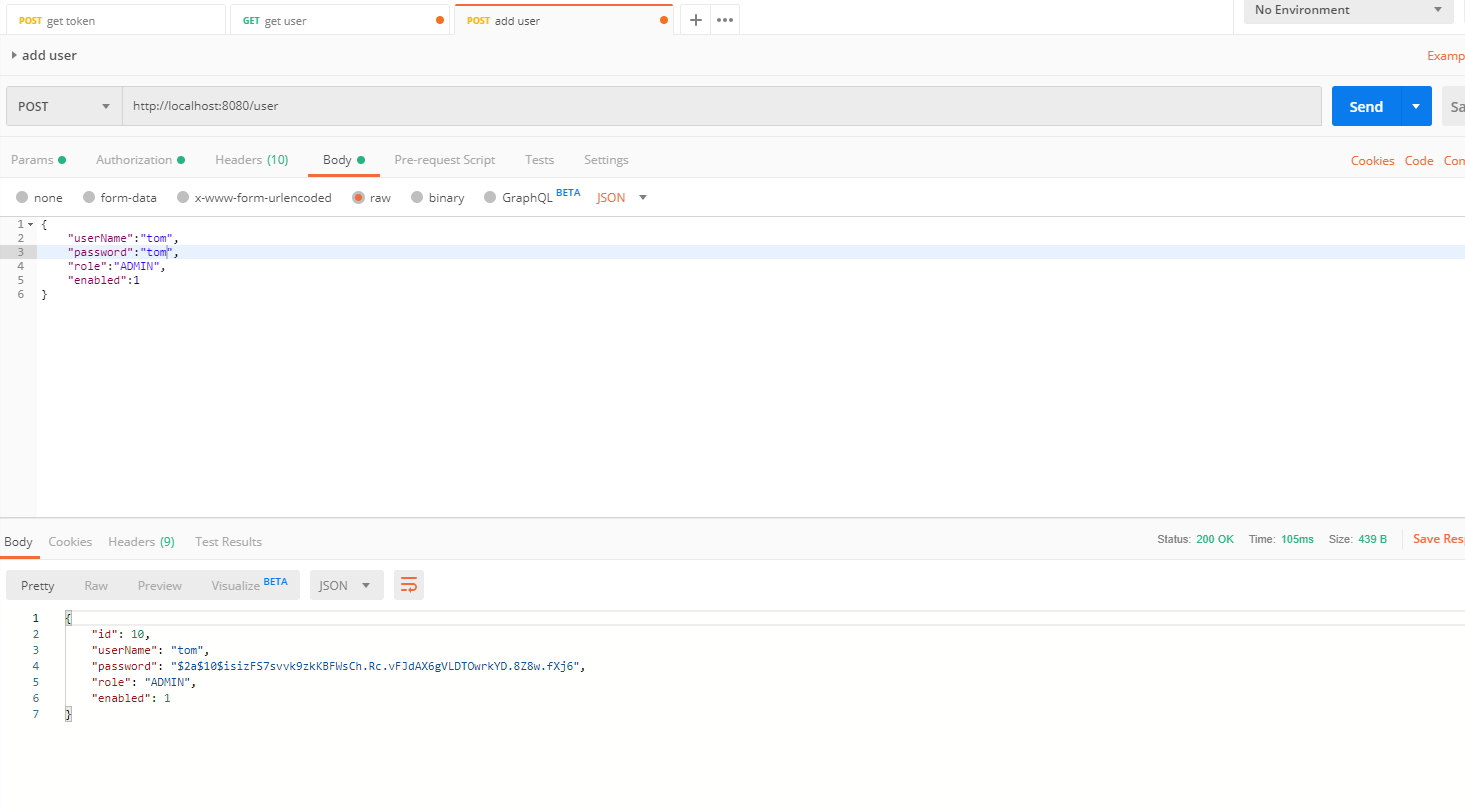
To access any secured REST API endpoint, first, we will have to get the access token. To get the access token, we will need to add an authorization header with client credentials and add the request body with user credentials in postman.
After receiving the access token and refresh token, we can access any secured REST API endpoints using access token. When the access token expired, the refresh token is used to get a new access token.
I have attached some of postmen request responses
# getToken
# getUser

# addUser
You can refer to the whole project on GitHub.
Related Articles
- Spring Security in Action.
- Getting Started With Spring Boot and Microservices.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments