Source Code Analysis Testing Technique Using SonarQube
Installing SonarQube, access to Maven, and Java 8 are the only things you'll need to get started on running source code analyses.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSource code analysis is also a software testing technique that can be used to scrutinize all code paths and data flows that a program will execute; It can be either static or dynamic.
In static analysis, debugging is done by examining the code without actually executing the program. This can reveal errors, security vulnerabilities, poorly written code that will make maintenance costly and redundant code at an early stage in application development, often eliminating the need for multiple revisions later.
We are using SonarQube with Maven to analyze application source code created in Java. Automation frameworks should also pass static code analysies to ensure that all best practices are followed. This article is focused on using SonarQube to analyse application developed in Java (Maven Java Project).
Installing SonarQube:
- Go to SonarQube community edition page and download the version you want. (I am using SonarQube 6.5, Maven 3.5.0 and JDK 1.8)
- Extract/Unzip the downloaded file in location you need.
- Go to /bin folder.
- There will be different folders for different OS platforms. (I am using this setup with 64 bit Linux system, so I selected “linux-x86-64” folder).
- There will be sonar.sh file along with other files/folders
Run the command ./sonar.sh and this will give you usage details.
sonarqube-6.5/bin/linux-x86-64 $ ./sonar.sh
Usage: ./sonar.sh { console | start | stop | restart | status | dump }To start SonarQube server
./sonar.sh startTo stop SonarQube server
./sonar.sh stopTo check whether the server is running
./sonar.sh statusFor Windows platform, there would be different *.bat files such as StartSonar.bat etc. Execute the .bat file to start server in Windows.
This will start a SonarQube server at default port of 9000.
Open a web browser and access the page, http://localhost:9000. If you see ‘about’ page, then SonarQube is successfully started. If you have performed source code analysis for multiple projects, all the results will be displayed here grouped by project and you can choose the project of your choice.
SonarQube comes with an embedded database and it is used by default. This quick setup with embedded database can be used for testing purpose and for production/real usage; please configure custom databases such as MySQL, Oracle, etc.
Configuration instructions and parameters are available in /conf/sonar.properties to configure the database settings. Templates are available for all supported databases.
Once SonarQube server is up and running, we can start scanning projects to initiate source code analysis.
Scanning a Project
Prerequisites to run scan for a project using Maven.
- Maven 3.x
- Java supported by SonarQube server (Java 8)
- Read access to source code.
- along with SonarQube installation.
Edit the settings.xml file, located in $MAVEN_HOME/conf or ~/.m2, to set the plugin prefix and optionally the SonarQube server URL.
<settings xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0"
xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/SETTINGS/1.0.0
https://maven.apache.org/xsd/settings-1.0.0.xsd">
<pluginGroups>
<pluginGroup>org.sonarsource.scanner.maven</pluginGroup>
</pluginGroups>
<profiles>
<profile>
<id>sonar</id>
<activation>
<activeByDefault>true</activeByDefault>
</activation>
<properties>
<!-- Optional value. Default value is http://localhost:9000 -->
<sonar.host.url>
http://localhost:9000
</sonar.host.url>
</properties>
</profile>
</profiles>
</settings>Start analyzing a Maven project by running a Maven goal: sonar:sonar in the directory where the pom.xml file exists for the project.
mvn clean verify sonar:sonaror
mvn sonar:sonarNow go back to the web page and check for results of source code analysis you just did.
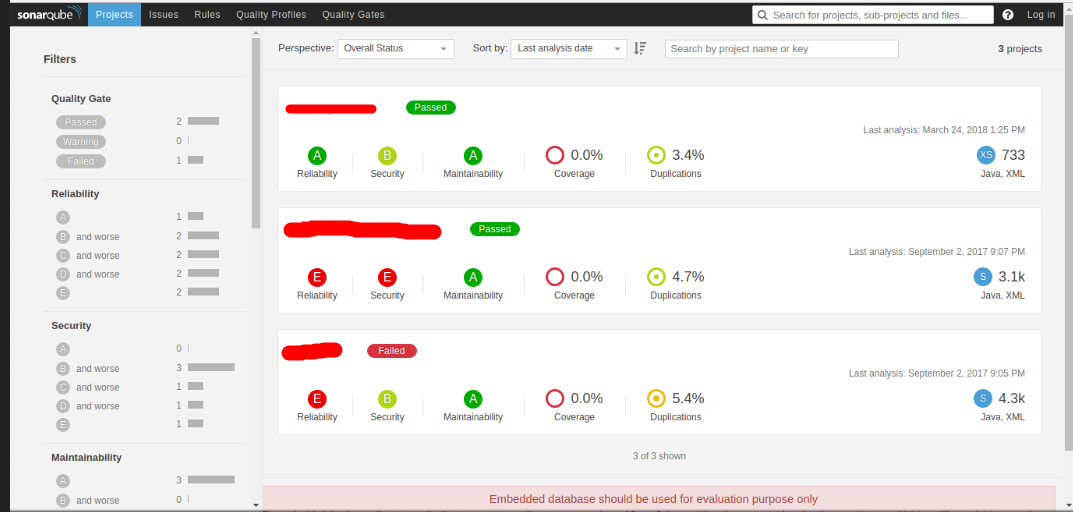
Originally posted in allselenium.info
Published at DZone with permission of Arunkumar Velusamy. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments