Spring Boot + RabbitMQ Tutorial — Retry and Error Handling Example
In this tutorial, we will be implementing a Spring Boot + RabbitMQ example to retry messages on exception.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
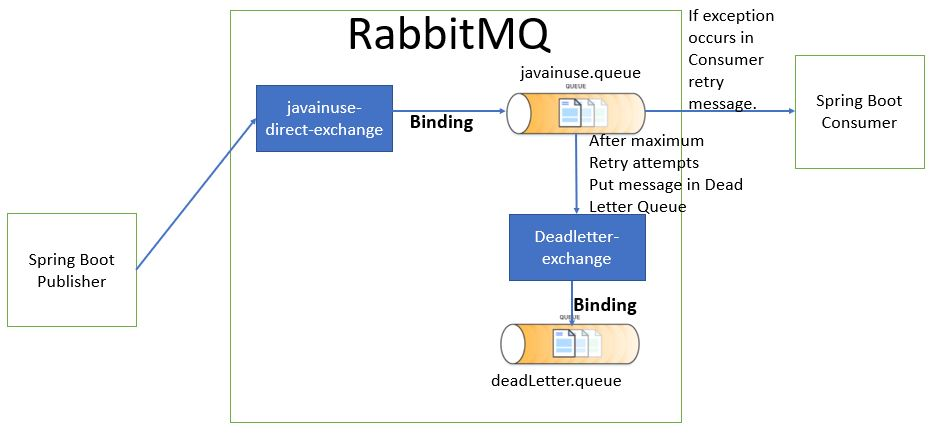
Join For FreeIn a previous tutorial, we implemented a Spring Boot + RabbitMQ example to understand the various exchange types. In this tutorial, we will be implementing a Spring Boot + RabbitMQ example to retry messages on exception. If the exception still exists after maximum retries, then we put a message in a dead letter queue where it can be analyzed and corrected later.
What Is a Dead Letter Queue?
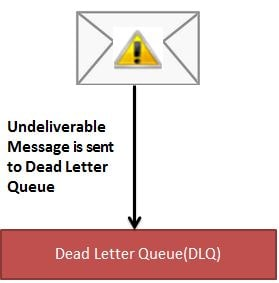
In English vocabulary, dead letter mail is undeliverable mail that cannot be delivered to the addressee. A dead-letter queue (DLQ), sometimes known as an undelivered-message queue, is a holding queue for messages that cannot be delivered to their destinations due to something.
According to Wikipedia — In message queueing the dead letter queue is a service implementation to store messages that meet one or more of the following failure criteria:
- Message that is sent to a queue that does not exist
- Queue length limit exceeded
- Message length limit exceeded
- Message is rejected by another queue exchange
- Message reaches a threshold read counter number because it is not consumed. Sometimes this is called a “back out queue”
Later on, we can analyze the messages in the DLQ to know the reason why the messages are failing.
This tutorial is explained in the below YouTube video.
We will be implementing two modules:
- Spring Boot Producer Module — It will produce a message and put it in the RabbitMQ queue. It will also be responsible for creating the required queues including the dead letter queue.
- Spring Boot Consumer Module — It will consume a message from the RabbitMQ queue. We will be throwing an exception and then retrying the message. After maximum retries, it will then be put in dead letter queue.
Spring Boot + RabbitMQ Producer Module
The Maven project will be as follows:
The pom.xml will have the following dependencies:
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>com.javainuse</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-rabbitmq-producer</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version><packaging>jar</packaging><parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath />
</parent><properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties><dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies><build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build></project>
Define the domain class Employee as follows:
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.javainuse.model;import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIdentityInfo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.ObjectIdGenerators;(generator = ObjectIdGenerators.IntSequenceGenerator.class, property = "@id", scope = Employee.class)
public class Employee { private String empName;
private String empId;
private int salary; public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
} public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
} public String getEmpId() {
return empId;
} public void setEmpId(String empId) {
this.empId = empId;
} public int getSalary() {
return salary;
} public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
public String toString() {
return "Employee [empName=" + empName + ", empId=" + empId + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
}
}
Next, define the configuration class where we:
- Create Direct Exchanges named — deadLetterExchange and javainuseExchange.
- Create Queue named javainuse and dlq. For the javainuse queue, specify the x-dead-letter-exchange argument as the deadLetterExchange. This means that any message in the javainuse queue that cannot be delivered will be sent to the deadLetterExchange.
- Bind the javainuse queue with javainuseExchange and the dlq queue with deadLetterExchange.
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.javainuse.config;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Binding;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.BindingBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.DirectExchange;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.Queue;
import org.springframework.amqp.core.QueueBuilder;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.connection.ConnectionFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.core.RabbitTemplate;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.MessageConverter;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
public class RabbitMQConfig {
DirectExchange deadLetterExchange() {
return new DirectExchange("deadLetterExchange");
}
DirectExchange exchange() {
return new DirectExchange("javainuseExchange");
}
Queue dlq() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("deadLetter.queue").build();
}
Queue queue() {
return QueueBuilder.durable("javainuse.queue").withArgument("x-dead-letter-exchange", "deadLetterExchange")
.withArgument("x-dead-letter-routing-key", "deadLetter").build();
}
Binding DLQbinding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(dlq()).to(deadLetterExchange()).with("deadLetter");
}
Binding binding() {
return BindingBuilder.bind(queue()).to(exchange()).with("javainuse");
}
public MessageConverter jsonMessageConverter() {
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
public AmqpTemplate rabbitTemplate(ConnectionFactory connectionFactory) {
final RabbitTemplate rabbitTemplate = new RabbitTemplate(connectionFactory);
rabbitTemplate.setMessageConverter(jsonMessageConverter());
return rabbitTemplate;
}
}
Create the RabbitMQWebController class where we expose API to send a message to RabbitMQ Exchange.
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.javainuse.controller;import org.springframework.amqp.core.AmqpTemplate;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.GetMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController;
(value = "/javainuse-rabbitmq/")
public class RabbitMQWebController {
private AmqpTemplate amqpTemplate; (value = "/producer")
public String producer(("empName") String empName,("empId") String empId,("salary") int salary) {
Employee emp=new Employee();
emp.setEmpId(empId);
emp.setEmpName(empName);
emp.setSalary(salary); amqpTemplate.convertAndSend("javainuseExchange", "javainuse", emp);
return "Message sent to the RabbitMQ Successfully";
}
}
Create the Spring Boot Bootstrap class with SpringBootApplication annotation.
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.javainuse;import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
public class SpringBootHelloWorldApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootHelloWorldApplication.class, args);
}
}
Spring Boot Consumer Module
The project will be as follows:
Define the pom.xml as follows: Add the spring-boot-starter-amqp dependency.
xxxxxxxxxx
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion><groupId>com.javainuse</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-rabbitmq-consumer</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<packaging>jar</packaging><name>spring-boot-rabbitmq-consumer</name><parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>2.1.1.RELEASE</version>
<relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository -->
</parent><properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<project.reporting.outputEncoding>UTF-8</project.reporting.outputEncoding>
<java.version>1.8</java.version>
</properties><dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-amqp</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-logging</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies><build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
</build><description>SpringBootRabbitMQConsumer</description>
</project>
Define the domain class Employee as follows:
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.javainuse.model;import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.JsonIdentityInfo;
import com.fasterxml.jackson.annotation.ObjectIdGenerators;(generator = ObjectIdGenerators.IntSequenceGenerator.class, property = "@id", scope = Employee.class)
public class Employee { private String empName;
private String empId;
private int salary; public String getEmpName() {
return empName;
} public void setEmpName(String empName) {
this.empName = empName;
} public String getEmpId() {
return empId;
} public void setEmpId(String empId) {
this.empId = empId;
}
public String toString() {
return "Employee [empName=" + empName + ", empId=" + empId + ", salary=" + salary + "]";
} public int getSalary() {
return salary;
} public void setSalary(int salary) {
this.salary = salary;
}
}
Define a custom checked exception named InvalidSalaryException as follows:
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.javainuse.exception;public class InvalidSalaryException extends Exception { private static final long serialVersionUID = -3154618962130084535L;}
Define the RabbitMQConsumer class, which consumes the message from RabbitMQ using RabbitListener. The RabbitMQ listener listens to the RabbitMQ queue for any incoming messages. For the basic configuration, we specify the Queue/Topic name (the name of the queue/topic where the message should be consumed). Also here we will be checking the incoming message for the salary field. If this field is negative, we will be throwing an InvalidSalaryException.
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.javainuse.service;import org.slf4j.Logger;
import org.slf4j.LoggerFactory;
import org.springframework.amqp.rabbit.annotation.RabbitListener;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;import com.javainuse.exception.InvalidSalaryException;
import com.javainuse.model.Employee;
public class RabbitMQConsumer { private static final Logger logger = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RabbitMQConsumer.class); (queues = "javainuse.queue")
public void recievedMessage(Employee employee) throws InvalidSalaryException {
logger.info("Recieved Message From RabbitMQ: " + employee);
if (employee.getSalary() < 0) {
throw new InvalidSalaryException();
}
}
}
Next, define the following properties in application.yml. Here we enable the Spring Boot RabbitMQ retry mechanism and specify some more additional parameters:
- Initial interval: The message should be retried after an interval of 3s.
- Max-attempts: The message should be retried maximum of 6 times. After which it will be sent to dead letter Queue.
- Max-interval: The maximum time interval between two retries should never exceed 10s.
- Multiplier: The interval between second retry gets multiplied by 2. But this interval can never exceed the max-interval. So the retry interval values will be 3s, 6s, 10s, 10s, 10s. As 10 sec is the max interval specified.
xxxxxxxxxx
spring:
rabbitmq:
listener:
simple:
retry:
enabled: true
initial-interval: 3s
max-attempts: 6
max-interval: 10s
multiplier: 2
server:
port: 8081
Finally, define the Spring Boot Class with @SpringBootApplication annotation:
xxxxxxxxxx
package com.javainuse;import org.springframework.amqp.support.converter.Jackson2JsonMessageConverter;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
public class SpringBootConsumerApplication { public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(SpringBootConsumerApplication.class, args);
}
public Jackson2JsonMessageConverter converter() {
return new Jackson2JsonMessageConverter();
}
}
In a previous tutorial, we have shown how to install RabbitMQ and get started.
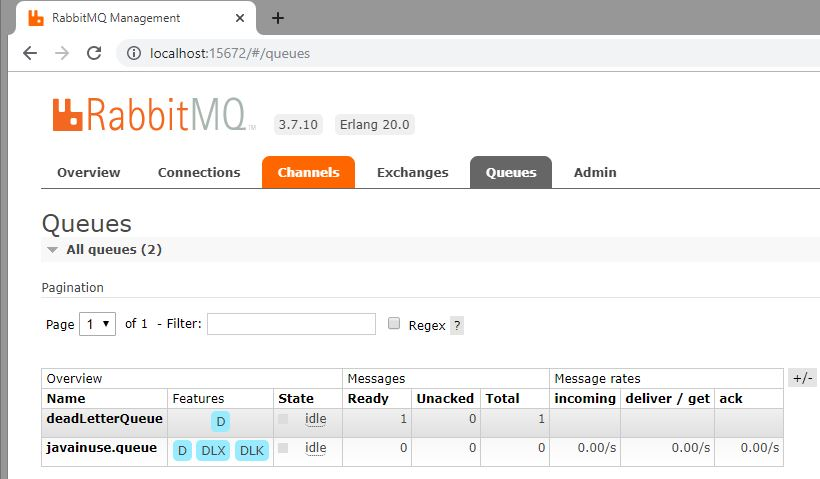
Start the Producer and Consumer applications, and go to http://localhost:8080/javainuse-rabbitmq/producer?empName=emp1&empId=emp001&salary=-50. The message will be sent to the RabbitMQ queue named javainuse.queue and consumed by the consumer application. As the salary is negative, InvalidSalaryException will be thrown. This message will be retried 6 times and then will be put in dead letter queue.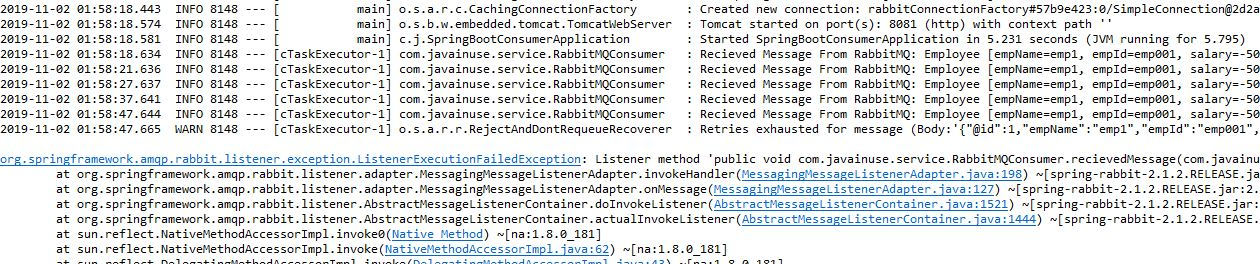
Thanks for reading!
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments