Spring Boot WebClient: Performance Optimization and Resilience
In this post, you'll find out how to optimize Spring WebClient using Reactor Netty, with features like connection pooling, resilience, compression, and more.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeSpring WebClient is a reactive, non-blocking HTTP (HyperText Transfer Protocol) client designed for making requests to external services. It belongs to the Spring WebFlux framework and provides advanced, scalable handling of HTTP requests more efficiently than the RestTemplate.
WebClient also supports parallel and reactive programming, making it suitable to perform a large volume of operations without blocking requests. It is ideal when you want to build high-performance applications, either by making external API calls or having thousands of concurrent requests.
It improves debugging and blends well with Spring Boot and third-party products like Resilience4j and Spring Cloud. It is best suited for the development of superior, adaptable, and microservices running in the cloud.
WebClient needs proper configuration to effectively deliver optimal performance and manage resource utilization and durability against short-term errors. The following guide covers advanced features for better tuning of WebClient.
The following features are important for the improvement of the WebClient in microservices:
Performance Improvement
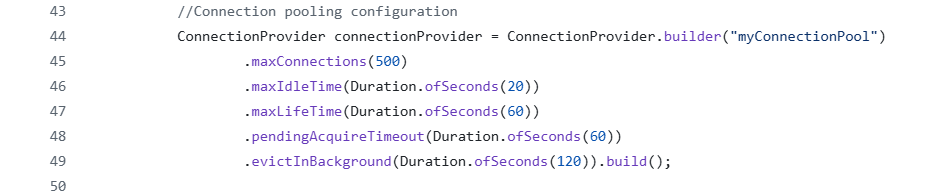
Configuring how many requests will be managed, also known as connection pooling, and setting timeouts for WebClient play a vital role in handling a large number of concurrent requests. By default, WebClient uses Reactor Netty, which calls for connection pooling and timeout options out of the box. A well-configured connection pool ensures that simultaneous requests are processed efficiently and safeguards against resource exhaustion.
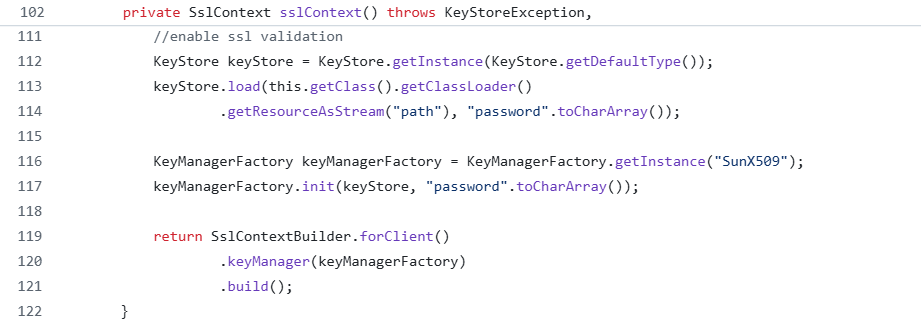
Enable SSL/TLS Validation
WebClient can be configured to make secure connections between microservices by validating SSL/TLS client certificates. This configuration is essential when interacting with servers that require client certificates for mutual TLS authentication.
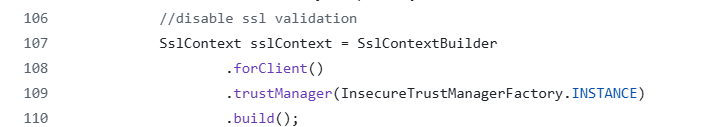
Disable SSL Verification
Disabling SSL verification is not a good practice as it can introduce security weaknesses. It should only be used for testing purposes.
Add Resilience and Retry Mechanism to WebClient
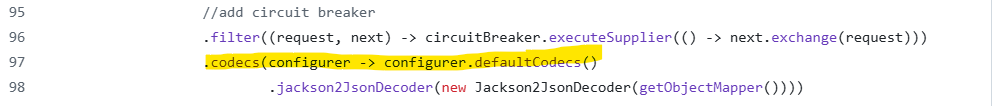
Circuit breakers are often used in distributed systems to stop cascading failures if a dependent service is down or not able to perform. Incorporating a circuit breaker filters bad requests and prevents them from affecting the rest of the application. Here, the Resilience4j library is being used as a circuit breaker, and WebClient is configured along with it.
Transient errors may appear, which may result in failed HTTP requests. On this note, one can set up a retry mechanism so as to allow WebClient to automatically retry requests based on a policy. This will increase the likelihood of receiving a successful response in subsequent attempts.

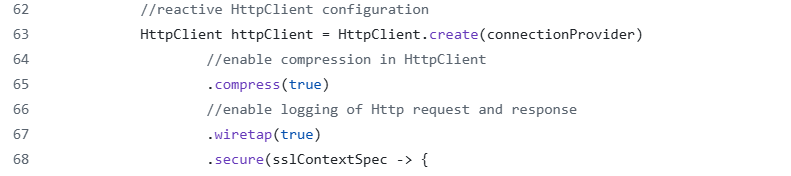
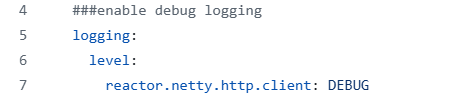
Enable Logging for HTTP Requests and Responses
In microservices, one can get detailed logs, which may be useful for finding the root cause of actual issues with HTTP requests. The wiretap feature of WebClient can be used to log all request and response data. This is particularly useful when a root cause is required to be found.
Serialization/Deserialization Configuration
The built-in feature within WebClient has a powerful way of writing or reading a response in a specific data format. Custom serializer helps developers to implement their own serializers that can better handle the domain-specific data structures. Post this, WebClient helps in improving response time for microservices.

Enable Error Handling
WebClient makes it easier to handle HTTP errors due to the availability of HTTP status codes in response. It is displayed in the following example whether the status code is of type client error (4xx) or server error (5xx), allowing us to perform targeted error responses or retry mechanisms as needed.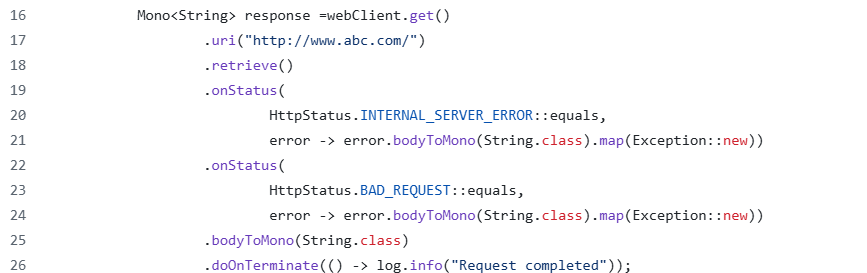
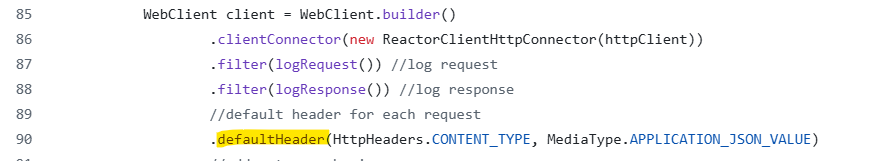
Default Header
All HTTP requests in WebClient will have default headers. To avoid duplicated work for each request, it can be added globally.
Compression
GZIP compression provides higher performance, while microservices carry large request payloads.
Conclusion
Spring Boot's WebClient provides many features, such as connection pools, request timeouts, and retry policies, improving performance to a great extent. Circuit breaker functionality adds immunity to WebClient against failures. Error handling and compression features streamline data movement and reduce network usage.
These configurations transform WebClient into a robust, high-performance HTTP client suitable for modern, reactive applications. By applying these strategies, applications will be better equipped to handle traffic surges, ensure fault tolerance, and provide a responsive experience for end-users.
The code examples mentioned above are available in the GitHub repository.
Further Reading
To read more about optimizing Spring Boot’s WebClient for better performance, refer to the Spring Framework WebClient Documentation, and the broader insight is provided by the Spring Framework Reference Guide.
Advanced netty configurations are documented in the Reactor Netty Documentation, while the Resilience4j Documentation elaborates on the circuit breakers and retry mechanisms.
The common challenges and practical strategies are highlighted in Maximizing Performance with Netty and Reactive Programming in Java.
Finally, the hands-on guide to integrating resilience patterns into spring boots is available in Baeldung's guide on Resilience4j. When used together, all these references provide a comprehensive guide to building scalable, efficient applications using WebClient.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments