Creating Microservices on the Pivotal Platform
Using the Pivotal platform gives you an easy way to deploy, scale, and monitor your microservices. Learn how to get it set up and running.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeImagine you have multiple microservices running on different machines as multiple instances. It seems natural to think about the tools that help you in the process of monitoring and managing all of them. If we add that our microservices like most people are created based on the Spring Cloud framework obviously seems to look at the Pivotal platform. Here is a figure with the platform's architecture downloaded from the main Pivotal site.
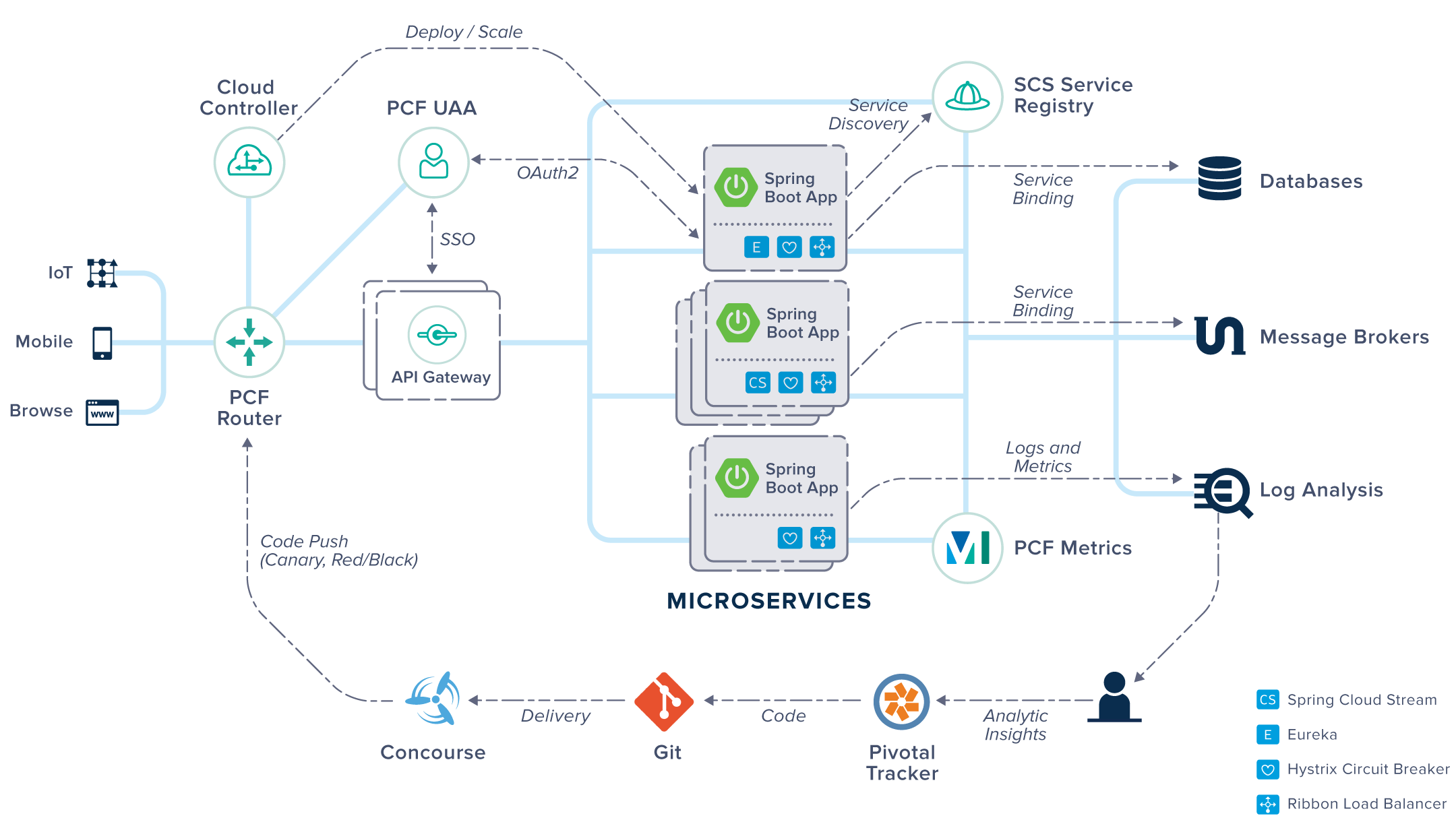
Although the Pivotal platform can run applications written in many languages, it has the best support for Spring Cloud Services and Netflix OSS tools, like you see in the figure above. From the possibilities offered by Pivotal, we can take advantage in three ways:
Pivotal Cloud Foundry - this solution can be run on public IaaS or a private cloud like AWS, Google Cloud Platform, Microsoft Azure, VMware vSphere, or OpenStack.
Pivotal Web Services - a hosted cloud-native platform available at the pivotal.io site.
PCF Dev - this instance can be run locally as a single virtual machine. It offers the opportunity to develop apps using an offline environment which basic services installed like Spring Cloud Services (SCS), MySQL, Redis databases and RabbitMQ broker. If you want to run it locally with SCS you need more than 6GB RAM free.
As Spring Cloud Services, Circuit Breaker (Hystrix), Service Registry (Eureka) and standard Spring Configuration Server are available based on the git configuration.
That’s all I wanted to say about the theory. Let’s move on to practice. On the Pivotal website, we have detailed materials on how to set up, create, and deploy a simple microservice based on Spring Cloud solutions. In this article, I will try to present the essence collected from these descriptions based on one of my standard examples from the previous posts. As always, the sample source code is available on GitHub. If you are interested in a detailed description of the sample application, microservices, and Spring Cloud, read my previous articles: Creating microservice using Spring Cloud, Eureka and Zuul and Creating Microservices: Circuit Breaker, Fallback and Load Balancing with Spring Cloud.
If you have a lot of free RAM, you can install PCF Dev on your local workstation. You need to have Virtual Box installed. Then, download and install Cloud Foundry Command Line Interface (CF CLI) and PCF Dev. All this is described here. Finally, you can run the command below and take a small break for coffee. The virtual machine needs to be downloaded and started.
cf dev start -s scsFor those who do not have RAM enough (like me), there is the Pivotal Web Services platform. It is available here. Before using it, you have to register on Pivotal's site. The rest of the article is identical for both options.
In comparison to previous examples of Spring Cloud-based microservices, we need to make some changes. There is one additional dependency inside every microservice’s pom.xml.
<properties>
...
<spring-cloud-services.version>1.4.1.RELEASE</spring-cloud-services.version>
<spring-cloud.version>Dalston.RELEASE</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.pivotal.spring.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-services-starter-service-registry</artifactId>
</dependency>
...
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>io.pivotal.spring.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-services-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud-services.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>We also use the Maven Cloud Foundry plugin cf-maven-plugin for application deployment on the Pivotal platform. Here is a sample for account-service. We run two instances of that microservice with max memory 512MB. Our application name is piomin-account-service.
<plugin>
<groupId>org.cloudfoundry</groupId>
<artifactId>cf-maven-plugin</artifactId>
<version>1.1.3</version>
<configuration>
<target>http://api.run.pivotal.io</target>
<org>piotrminkowski</org>
<space>development</space>
<appname>piomin-account-service</appname>
<memory>512</memory>
<instances>2</instances>
<server>cloud-foundry-credentials</server>
</configuration>
</plugin>Don’t forget to add credentials configuration into the Maven settings.xml file.
<server>
<id>cloud-foundry-credentials</id>
<username>piotr.minkowski@gmail.com</username>
<password>***</password>
</server>Now, when building a sample application, we append cf:push command.
mvn clean install cf:pushHere is a circuit breaker implementation inside customer-service.
@Service
public class AccountService {
@Autowired
private AccountClient client;
@HystrixCommand(fallbackMethod = "getEmptyList")
public List<Account> getAccounts(Integer customerId) {
return client.getAccounts(customerId);
}
List<Account> getEmptyList(Integer customerId) {
return new ArrayList<>();
}
}There is a randomly generated delay on the account’s service side, so 25% of circuit breaker calls should be activated.
@RequestMapping("/accounts/customer/{customer}")
public List<Account> findByCustomer(@PathVariable("customer") Integer customerId) {
logger.info(String.format("Account.findByCustomer(%s)", customerId));
Random r = new Random();
int rr = r.nextInt(4);
if (rr == 1) {
try {
Thread.sleep(2000);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
return accounts.stream().filter(it -> it.getCustomerId().intValue() == customerId.intValue())
.collect(Collectors.toList());
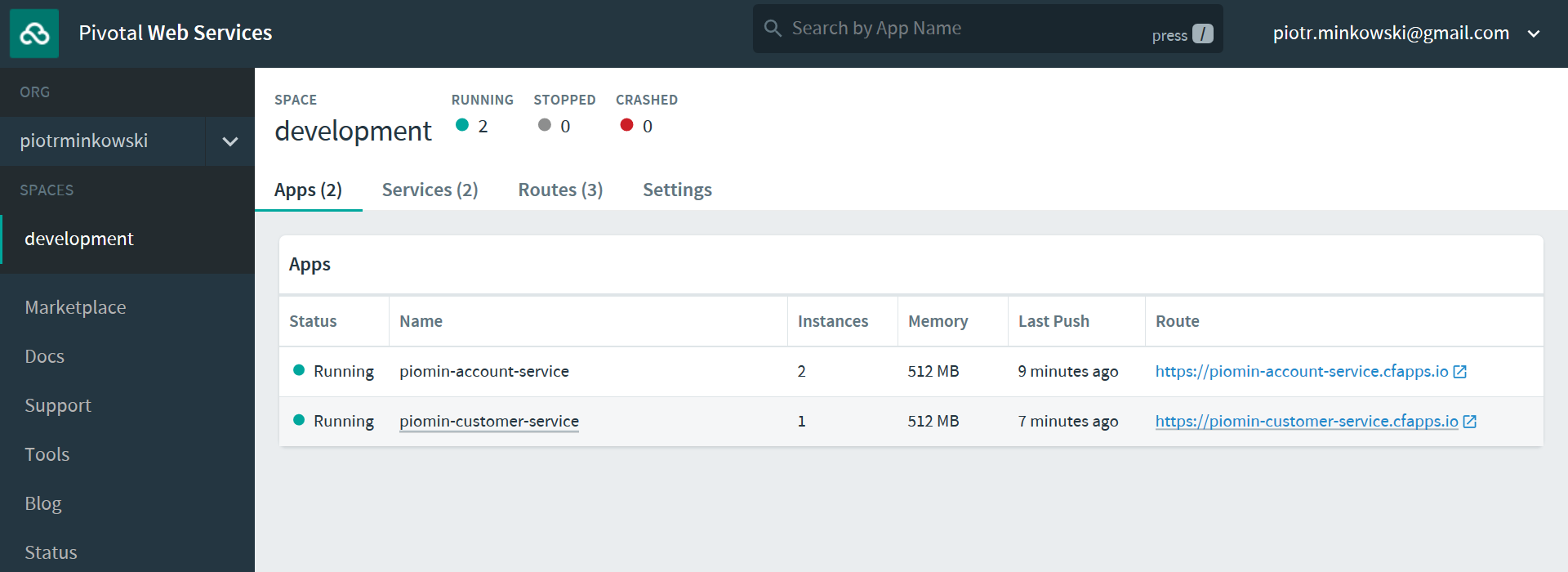
}After successfully deploying the application using the Maven cf:push command, we can go to the Pivotal Web Services console available here . Here are our two deployed services: two instances of piomin-account-service, and one instance of piomin-customer-service.
I have also activated Circuit Breaker and Service Registry from the Marketplace.
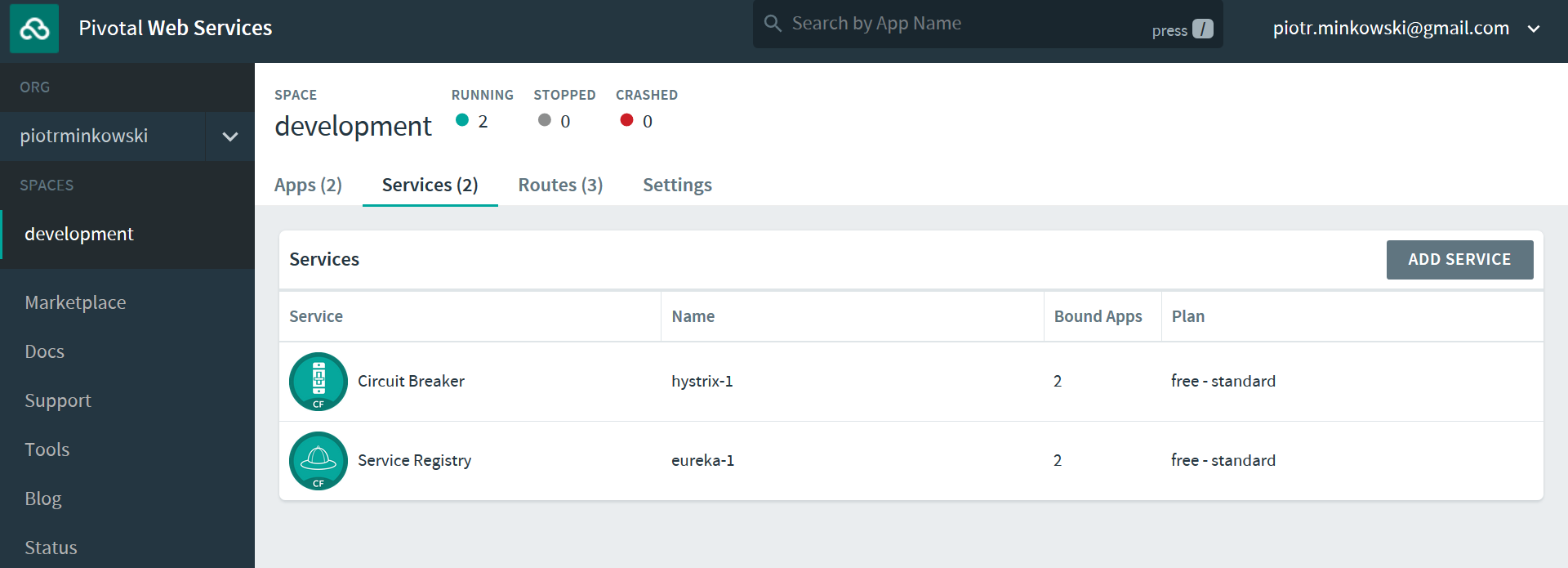
Every application needs to be bound to a service. To enable it, select service, then expand Bound Apps overlap and select the checkbox next to each service name.
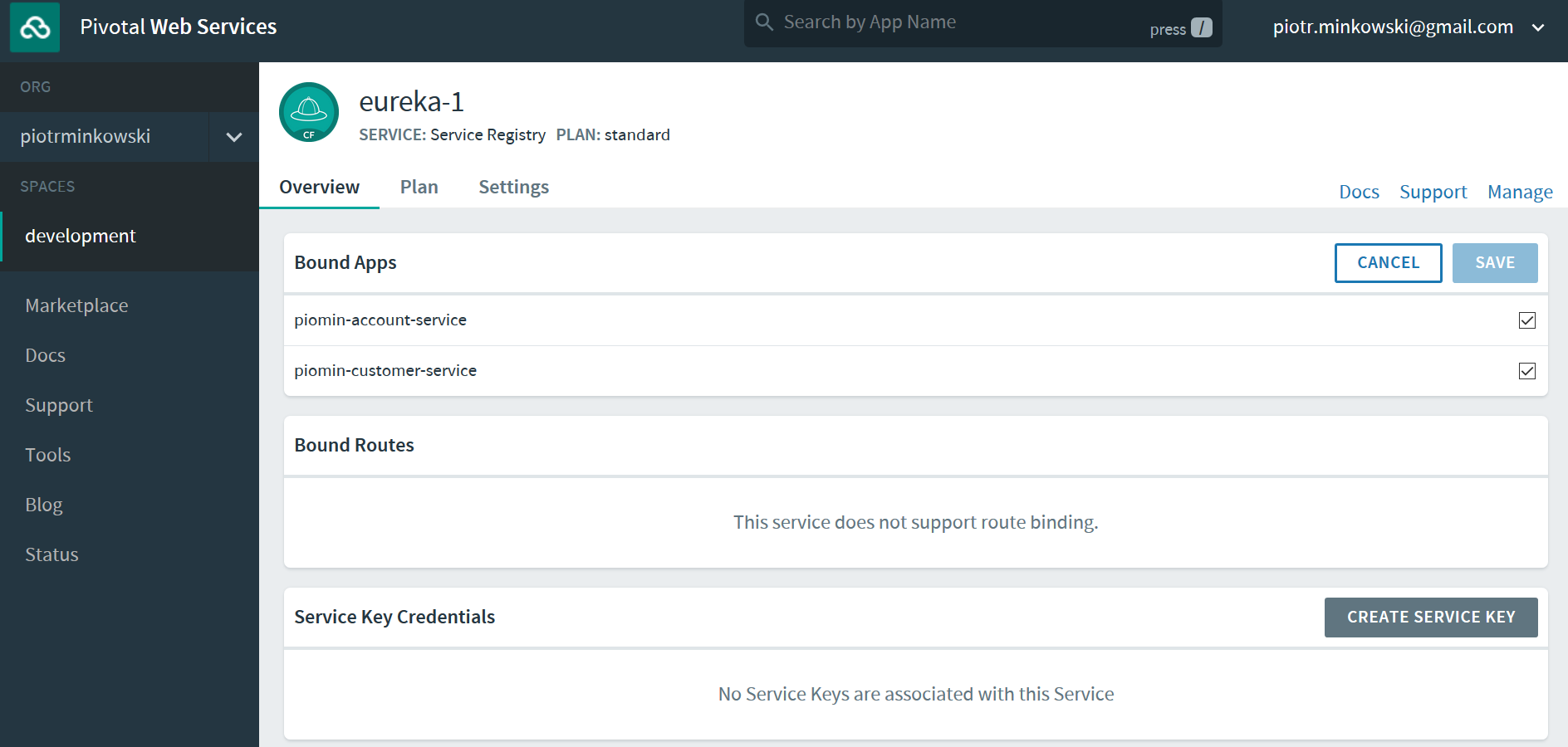
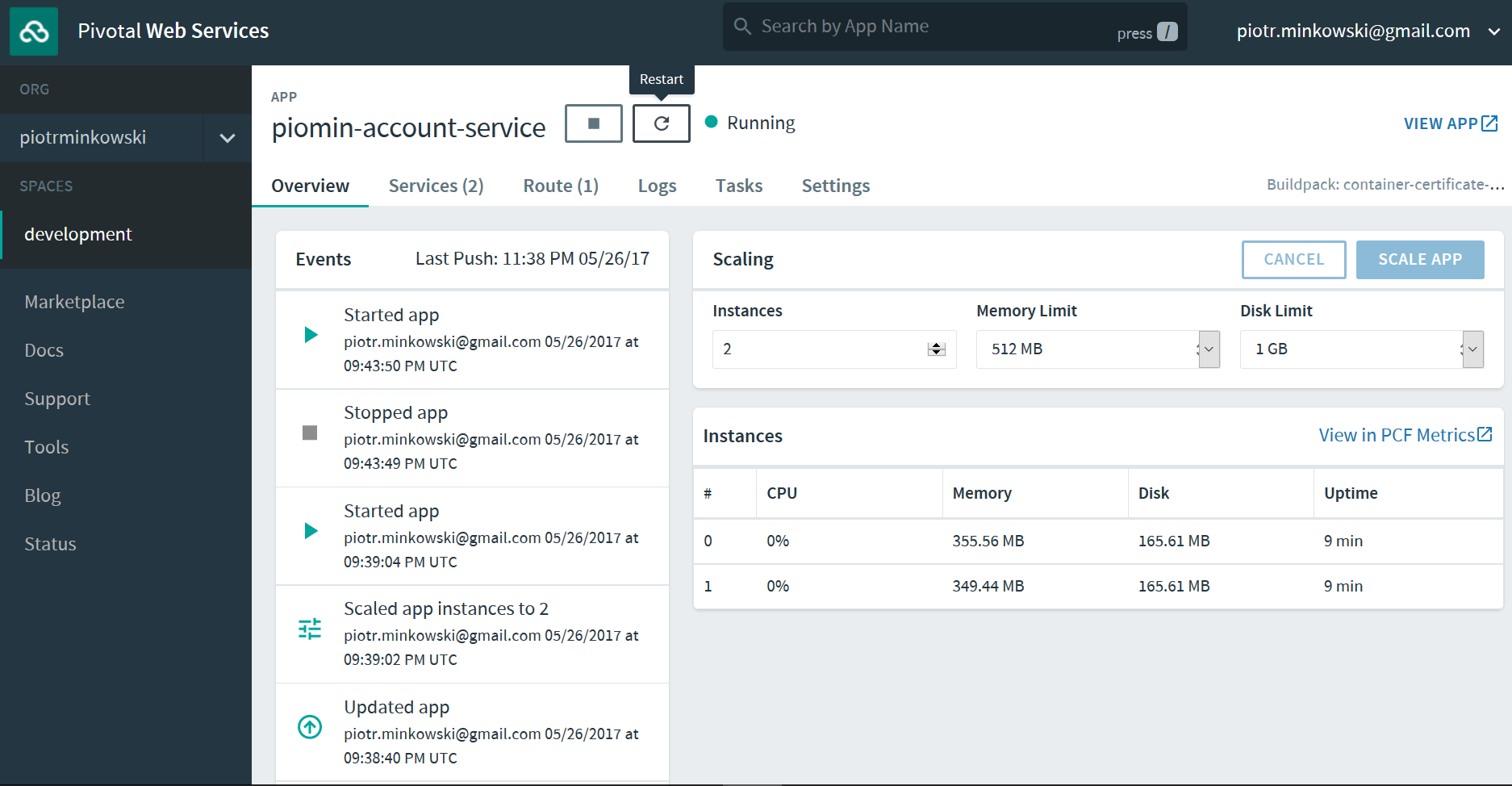
After this step, the application needs to be restarted. It also can be done using the web dashboard inside each service.
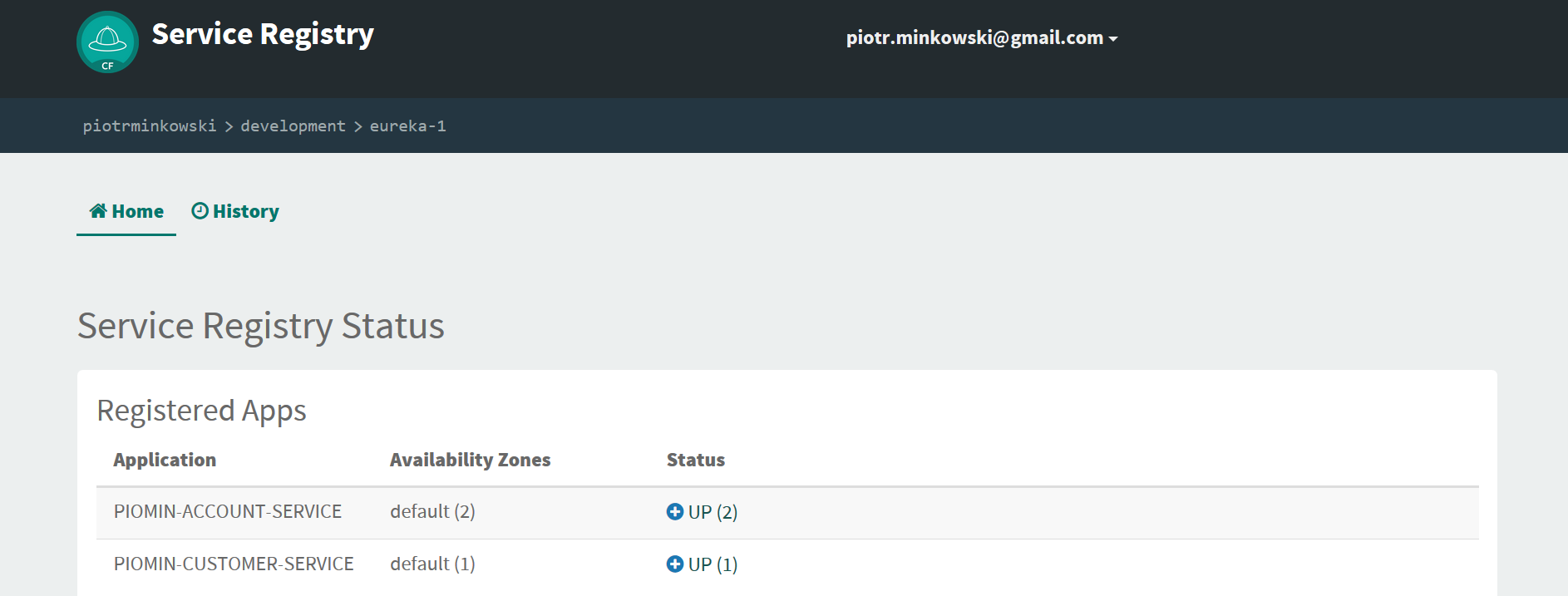
Finally, all services are registered in Eureka and we can perform some tests using customer endpoint https://piomin-customer-service.cfapps.io/customers/{id} .
With the Pivotal solution, we can easily deploy, scale, and monitor our microservices. Deployment and scaling can be done using Maven plugin or via web dashboard. There are also available some services prepared especially for microservices needs like service registry, circuit breaker and configuration server. Pivotal is the competition for such solutions like Kubernetes which based on Docker containerization (more about this tools here). Pivotal is useful if you are creating a microservices based on Spring Boot and Spring Cloud frameworks.
Published at DZone with permission of Piotr Mińkowski, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments