Spring MVC Example for User Registration and Login
This article is a step-by-step guide for setting up a User Registration and Login using a few web dev languages and databases.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeThis article is a step by step guide for User Registration and Login using the below tools and technologies.
1. Spring Framework (Core, MVC & JDBC)
2. Java 1.8
3. Maven 3.3.9
4. Eclipse IDE (Mars2)
5. MySQL 5.1
Step 1: Create a Maven Project
Using Eclipse IDE, create a Maven Project by selecting Web Archetype.
Step 2: Update Pom.xml
Update your maven dependencies.
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 http://maven.apache.org/maven-v4_0_0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<groupId>jbr</groupId>
<artifactId>SpringMvcUser</artifactId>
<packaging>war</packaging>
<version>0.1</version>
<name>SpringMvcUser Maven Webapp</name>
<url>http://maven.apache.org</url>
<properties>
<project.build.sourceEncoding>UTF-8</project.build.sourceEncoding>
<spring.version>4.3.2.RELEASE</spring.version>
<junit.version>4.12</junit.version>
<servlet.version>3.1.0</servlet.version>
<servlet.version>3.0.1</servlet.version>
<mysql.connector.version>5.1.9</mysql.connector.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<!-- Junit -->
<dependency>
<groupId>junit</groupId>
<artifactId>junit</artifactId>
<version>${junit.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<!--Servlet-Api -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>${servlet.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Spring Framework -->
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-core</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-beans</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-context</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-jdbc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-test</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
<scope>test</scope>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-webmvc</artifactId>
<version>${spring.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- Servlet API -->
<dependency>
<groupId>javax.servlet</groupId>
<artifactId>javax.servlet-api</artifactId>
<version>${servlet.version}</version>
</dependency>
<!-- MySQL database driver -->
<dependency>
<groupId>mysql</groupId>
<artifactId>mysql-connector-java</artifactId>
<version>${mysql.connector.version}</version>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<build>
<finalName>SpringMvcUser</finalName>
</build>
</project>Step 3: Update web.xml
Update the web.xml under src/main/webapp/WEB-INF as shown below:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<web-app xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/javaee/web-app_3_0.xsd" version="3.0">
<display-name>Archetype Created Web Application</display-name>
<welcome-file-list>
<welcome-file>home.jsp</welcome-file>
</welcome-file-list>
<servlet>
<servlet-name>spring-mvc</servlet-name>
<servlet-class>org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet</servlet-class>
<load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup>
</servlet>
<servlet-mapping>
<servlet-name>spring-mvc</servlet-name>
<url-pattern>/</url-pattern>
</servlet-mapping>
</web-app>DispatcherServletis the root Servlet for any Servlet defined in your application. It will redirect the request made to the application to the appropriate controller based on the URL.spring-mvcis the name of the root servlet and Spring container will look for the configuration with this name. So next step is to create a spring configuration with spring-mvc-servlet.xml.
Step 4: Create spring-mvc-servlet.xml
Create spring-mvc-servlet.xml under the src/main/webapp/WEB-INF folder and define the beans.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<import resource="classpath:jbr/config/user-beans.xml" />
<context:component-scan base-package="jbr.springmvc" />
<context:annotation-config />
<bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver">
<property name="prefix" value="/jsp/" />
<property name="suffix" value=".jsp" />
</bean>
</beans>Step 5: Create Controllers
Create Separate Controllers for User Registration and Login as below.
Create a package jbr.springmvc.controller
RegistrationController.java
package jbr.springmvc.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import jbr.springmvc.model.User;
import jbr.springmvc.service.UserService;
@Controller
public class RegistrationController {
@Autowired
public UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/register", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView showRegister(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("register");
mav.addObject("user", new User());
return mav;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/registerProcess", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ModelAndView addUser(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@ModelAttribute("user") User user) {
userService.register(user);
return new ModelAndView("welcome", "firstname", user.getFirstname());
}
}LoginController.java
package jbr.springmvc.controller;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletRequest;
import javax.servlet.http.HttpServletResponse;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.ModelAttribute;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;
import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;
import org.springframework.web.servlet.ModelAndView;
import jbr.springmvc.model.Login;
import jbr.springmvc.model.User;
import jbr.springmvc.service.UserService;
@Controller
public class LoginController {
@Autowired
UserService userService;
@RequestMapping(value = "/login", method = RequestMethod.GET)
public ModelAndView showLogin(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response) {
ModelAndView mav = new ModelAndView("login");
mav.addObject("login", new Login());
return mav;
}
@RequestMapping(value = "/loginProcess", method = RequestMethod.POST)
public ModelAndView loginProcess(HttpServletRequest request, HttpServletResponse response,
@ModelAttribute("login") Login login) {
ModelAndView mav = null;
User user = userService.validateUser(login);
if (null != user) {
mav = new ModelAndView("welcome");
mav.addObject("firstname", user.getFirstname());
} else {
mav = new ModelAndView("login");
mav.addObject("message", "Username or Password is wrong!!");
}
return mav;
}
}Step 5: Create POJO Classes
Create a package: jbr.springmvc.model
Login.java
package jbr.springmvc.model;
public class Login {
private String username;
private String password;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
}User.java
package jbr.springmvc.model;
public class User {
private String username;
private String password;
private String firstname;
private String lastname;
private String email;
private String address;
private int phone;
public String getUsername() {
return username;
}
public void setUsername(String username) {
this.username = username;
}
public String getPassword() {
return password;
}
public void setPassword(String password) {
this.password = password;
}
public String getFirstname() {
return firstname;
}
public void setFirstname(String firstname) {
this.firstname = firstname;
}
public String getLastname() {
return lastname;
}
public void setLastname(String lastname) {
this.lastname = lastname;
}
public String getEmail() {
return email;
}
public void setEmail(String email) {
this.email = email;
}
public String getAddress() {
return address;
}
public void setAddress(String address) {
this.address = address;
}
public int getPhone() {
return phone;
}
public void setPhone(int phone) {
this.phone = phone;
}
}Note: If you wanted to add any new logic, you can add another layer called service and access the DAO layer.
Step 6: Create DAO Classes
Create an interface/classes for accessing the MySQL Database.
Create a package: jbr.springmvc.dao
UserDao.java
package jbr.springmvc.dao;
import jbr.springmvc.model.Login;
import jbr.springmvc.model.User;
public interface UserDao {
void register(User user);
User validateUser(Login login);
}UserDaoImpl.java
package jbr.springmvc.dao;
import java.sql.ResultSet;
import java.sql.SQLException;
import java.util.List;
import javax.sql.DataSource;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate;
import org.springframework.jdbc.core.RowMapper;
import jbr.springmvc.model.Login;
import jbr.springmvc.model.User;
public class UserDaoImpl implements UserDao {
@Autowired
DataSource datasource;
@Autowired
JdbcTemplate jdbcTemplate;
public void register(User user) {
String sql = "insert into users values(?,?,?,?,?,?,?)";
jdbcTemplate.update(sql, new Object[] { user.getUsername(), user.getPassword(), user.getFirstname(),
user.getLastname(), user.getEmail(), user.getAddress(), user.getPhone() });
}
public User validateUser(Login login) {
String sql = "select * from users where username='" + login.getUsername() + "' and password='" + login.getPassword()
+ "'";
List<User> users = jdbcTemplate.query(sql, new UserMapper());
return users.size() > 0 ? users.get(0) : null;
}
}
class UserMapper implements RowMapper<User> {
public User mapRow(ResultSet rs, int arg1) throws SQLException {
User user = new User();
user.setUsername(rs.getString("username"));
user.setPassword(rs.getString("password"));
user.setFirstname(rs.getString("firstname"));
user.setLastname(rs.getString("lastname"));
user.setEmail(rs.getString("email"));
user.setAddress(rs.getString("address"));
user.setPhone(rs.getInt("phone"));
return user;
}
}Step 7: Create Spring Beans Configuration
Under resources , create a new xml bean configuration user-beans.xml to define the beans we created.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation=" http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd">
<context:component-scan base-package="jbr.springmvc" />
<context:annotation-config />
<bean id="userService" class="jbr.springmvc.service.UserServiceImpl" />
<bean id="userDao" class="jbr.springmvc.dao.UserDaoImpl" />
<bean id="jdbcTemplate" class="org.springframework.jdbc.core.JdbcTemplate">
<property name="dataSource" ref="datasource" />
</bean>
<bean id="datasource" class="org.springframework.jdbc.datasource.DriverManagerDataSource">
<property name="driverClassName" value="com.mysql.jdbc.Driver" />
<property name="url" value="jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/myusers" />
<property name="username" value="root" />
<property name="password" value="root" />
</bean>
</beans>Step 8: Create Tables in MySQL
CREATE DATABASE
IF NOT EXISTS myusers;USE
DROP TABLE
DROP TABLE IF EXISTS `myusers`.`users`;CREATE TABLE `myusers`.`users`
(
`username` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`password` VARCHAR(45) NULL,
`firstname` VARCHAR(45) NOT NULL,
`lastname` VARCHAR(45) NULL,
`email` VARCHAR(45) NULL,
`address` VARCHAR(45) NULL,
`phone` INT NULL,
PRIMARY KEY (`username`)
)Step 9: Create Views
Under the /src/main/webapp folder, create a home.jsp which we defined as 'welcome-file' in web.xml.
home.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Welcome</title>
</head>
<body>
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td><a href="login">Login</a>
</td>
<td><a href="register">Register</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>Under /src/main/webapp/jsp create:
register.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1" %>
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Registration</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form id="regForm" modelAttribute="user" action="registerProcess" method="post">
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="username">Username</form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:input path="username" name="username" id="username" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="password">Password</form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:password path="password" name="password" id="password" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="firstname">FirstName</form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:input path="firstname" name="firstname" id="firstname" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="lastname">LastName</form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:input path="lastname" name="lastname" id="lastname" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="email">Email</form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:input path="email" name="email" id="email" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="address">Address</form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:input path="address" name="address" id="address" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="phone">Phone</form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:input path="phone" name="phone" id="phone" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td>
<form:button id="register" name="register">Register</form:button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr></tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><a href="home.jsp">Home</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form:form>
</body>
</html>login.jsp
<%@ taglib prefix="form" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags/form" %>
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Login</title>
</head>
<body>
<form:form id="loginForm" modelAttribute="login" action="loginProcess" method="post">
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="username">Username: </form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:input path="username" name="username" id="username" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td>
<form:label path="password">Password:</form:label>
</td>
<td>
<form:password path="password" name="password" id="password" />
</td>
</tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td align="left">
<form:button id="login" name="login">Login</form:button>
</td>
</tr>
<tr></tr>
<tr>
<td></td>
<td><a href="home.jsp">Home</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</form:form>
<table align="center">
<tr>
<td style="font-style: italic; color: red;">${message}</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>welcome.jsp
<%@ page language="java" contentType="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1" pageEncoding="ISO-8859-1" %>
<!DOCTYPE html PUBLIC "-//W3C//DTD HTML 4.01 Transitional//EN" "http://www.w3.org/TR/html4/loose.dtd">
<html>
<head>
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=ISO-8859-1">
<title>Welcome</title>
</head>
<body>
<table>
<tr>
<td>Welcome ${firstname}</td>
</tr>
<tr>
</tr>
<tr>
</tr>
<tr>
<td><a href="home.jsp">Home</a>
</td>
</tr>
</table>
</body>
</html>Step 10: Run the Application
Right-click the application and Maven->clean.
Right-click the application and Maven->install.
Right-click the application and Run As->Run on Server->Run using Tomcat.
You will see the below outputs.
Home Page:
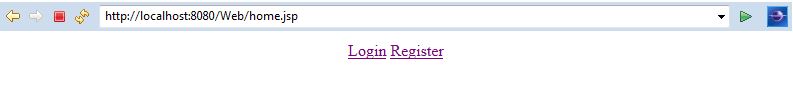
User Registration:
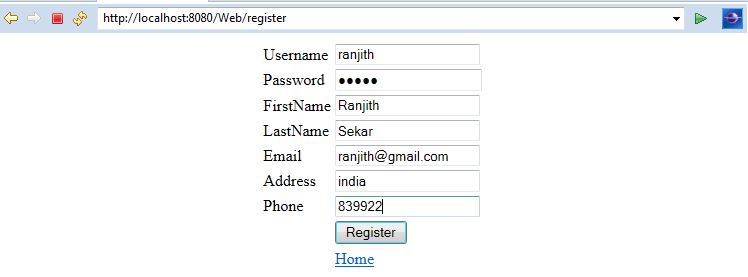
User Registration Success:
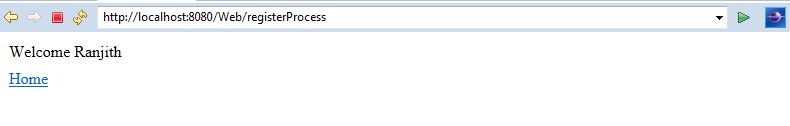
Login:
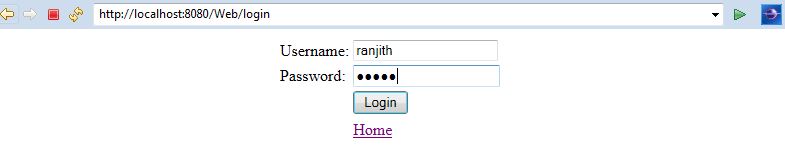
Login Success:

Summary
This tutorial helps to create a Maven Project for a Spring MVC and develop a small application for User Registration and Login.
Download the code from my git repo:
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments