Store UUID in an Optimized Way
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For Free
written by karthik appigatla for
the mysql performance blog
.
a few years ago peter zaitsev, in a post titled “ to uuid or not to uuid ,” wrote: “ there is a timestamp based part in uuid which has similar properties to auto_increment and which could be used to have values generated at the same point in time physically local in btree index.”
for this post i’ve rearranged the timestamp part of uuid (universal unique identifier) and did some benchmarks.
many people store uuid as char (36) and use as row identity value (primary key) because it is unique across every table, every database and every server and allows easy merging of records from different databases. but here comes the problem, using it as a primary key causes the problems described below.
problems with uuid
- uuid has 36 characters which makes it bulky.
- innodb stores data in the primary key order and all the secondary keys also contain primary key. so having uuid as primary key makes the index bigger which can not be fit into the memory
- inserts are random and the data is scattered.
despite the problems with uuid, people still prefer it because it is unique across every table, can be generated anywhere. in this blog, i will explain how to store uuid in an efficient way by re-arranging timestamp part of uuid.
structure of uuid
mysql uses uuid version 1 which is a 128-bit number represented by a utf8 string of five hexadecimal numbers
- the first three numbers are generated from a timestamp.
- the fourth number preserves temporal uniqueness in case the timestamp value loses monotonicity (for example, due to daylight saving time).
- the fifth number is an ieee 802 node number that provides spatial uniqueness. a random number is substituted if the latter is not available (for example, because the host computer has no ethernet card, or we do not know how to find the hardware address of an interface on your operating system). in this case, spatial uniqueness cannot be guaranteed. nevertheless, a collision should have very low probability.
the timestamp is mapped as follows:
when the timestamp has the (60 bit) hexadecimal value: 1d8eebc58e0a7d7. the following parts of the uuid are set::
58e0a7d7-eebc-11d8
-9669-0800200c9a66. the 1 before the most significant digits (in 11d8) of the timestamp indicates the uuid version, for time-based uuids this is 1.
fourth and fifth parts would be mostly constant if it is generated from a single server. first three numbers are based on timestamp, so they will be monotonically increasing. lets rearrange the total sequence making the uuid closer to sequential. this makes the inserts and recent data look up faster. dashes (‘-‘) make no sense, so lets remove them.
58e0a7d7-eebc-11d8-9669-0800200c9a66 => 11d8eebc58e0a7d796690800200c9a66
benchmarking
i created three tables:
- events_uuid – uuid binary(16) primary key
- events_int – additional bigint auto increment column and made it as primary key and index on uuid column
- events_uuid_ordered – rearranged uuid binary(16) as primary key
i created three stored procedures which insert 25k random rows at a time into the respective tables. there are three more stored procedures which call the random insert-stored procedures in a loop and also calculate the time taken to insert 25k rows and data and index size after each loop. totally i have inserted 25m records.
-
data size
horizontal axis – number of inserts x 25,000
vertical axis – data size in mb
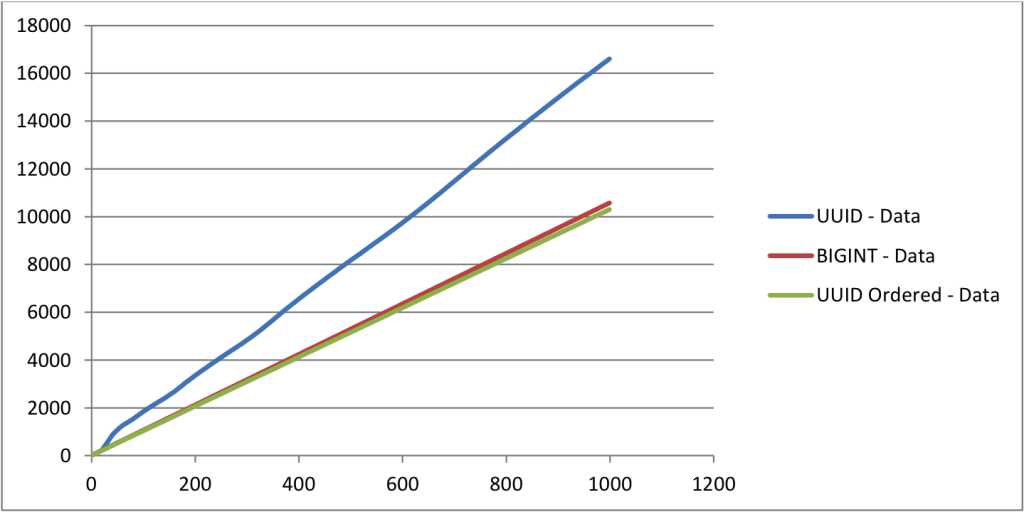
the data size for uuid table is more than other two tables. -
index size
horizontal axis – number of inserts x 25,000
vertical axis – index size in mb
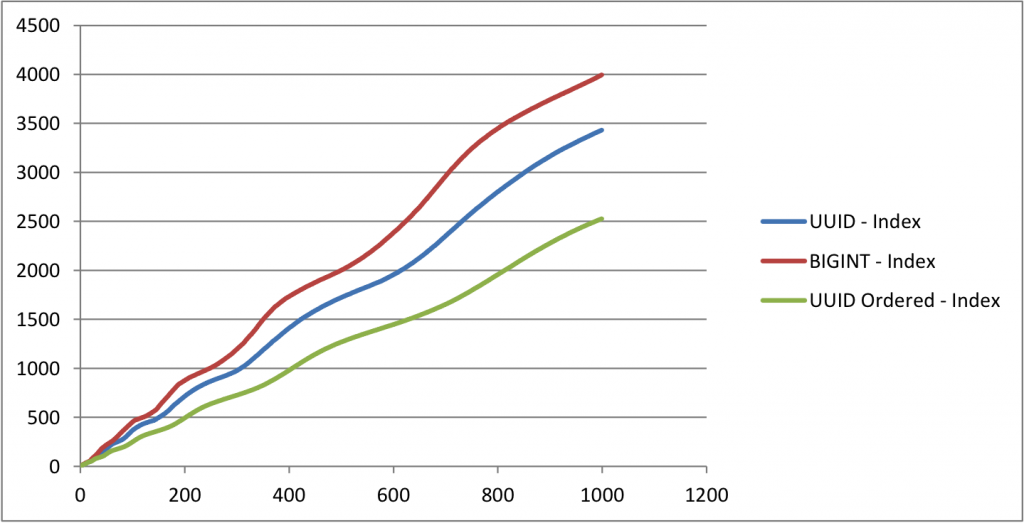
-
total size
horizontal axis – number of inserts x 25,000
vertical axis – total size in mb
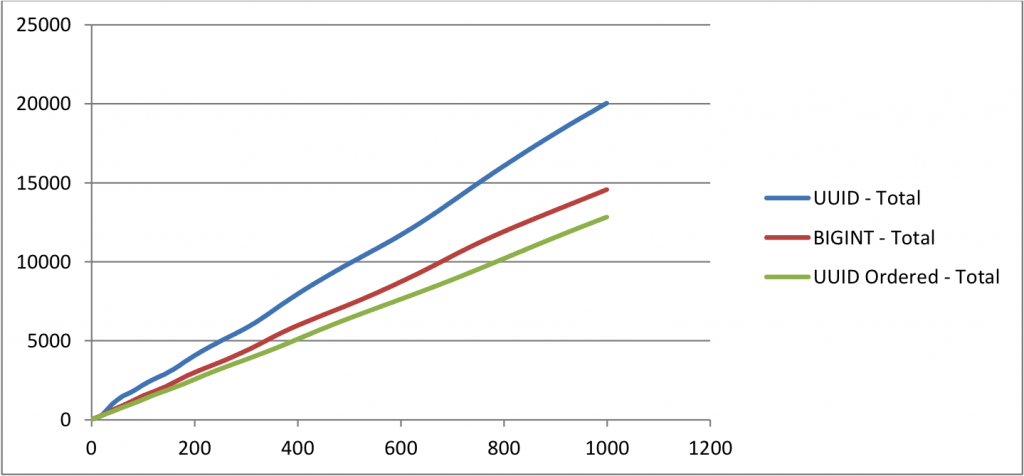
-
time taken
horizontal axis – number of inserts x 25,000
vertical axis – time taken in seconds
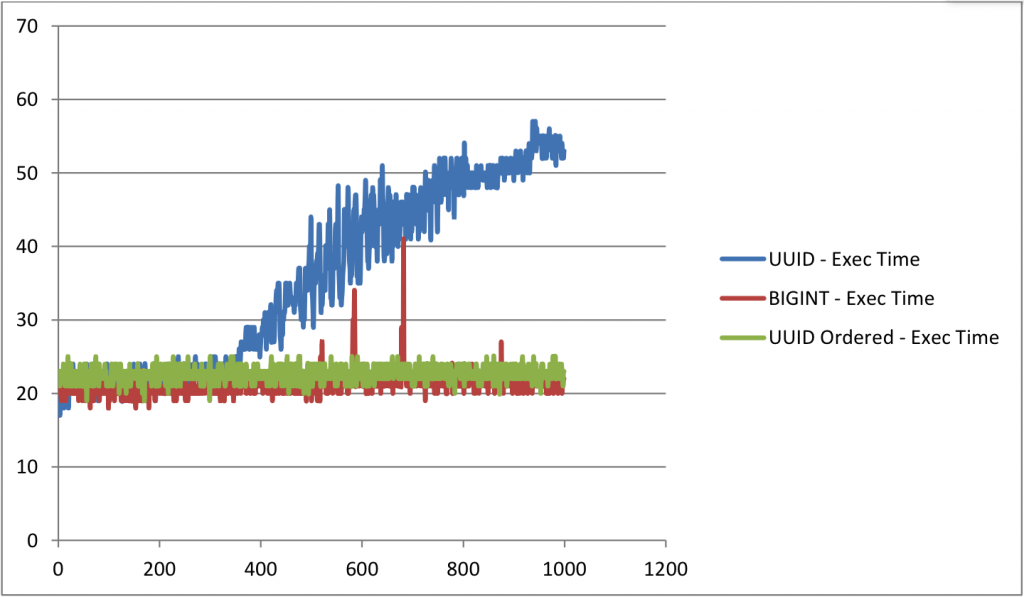
for the table with uuid as primary key, you can notice that as the table grows big, the time taken to insert rows is increasing almost linearly. whereas for other tables, the time taken is almost constant.
the size of uuid table is almost 50% bigger than ordered uuid table and 30% bigger than table with bigint as primary key. comparing the ordered uuid table bigint table, the time taken to insert rows and the size are almost same. but they may vary slightly based on the index structure.
root@localhost:~# ls -lhtr /media/data/test/ | grep ibd -rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 13g jul 24 15:53 events_uuid_ordered.ibd -rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 20g jul 25 02:27 events_uuid.ibd -rw-rw---- 1 mysql mysql 15g jul 25 07:59 events_int.ibd
table structure
#1 events_int create table `events_int` ( `count` bigint(20) not null auto_increment, `id` binary(16) not null, `unit_id` binary(16) default null, `event` int(11) default null, `ref_url` varchar(255) collate utf8_unicode_ci default null, `campaign_id` binary(16) collate utf8_unicode_ci default '', `unique_id` binary(16) collate utf8_unicode_ci default null, `user_agent` varchar(100) collate utf8_unicode_ci default null, `city` varchar(80) collate utf8_unicode_ci default null, `country` varchar(80) collate utf8_unicode_ci default null, `demand_partner_id` binary(16) default null, `publisher_id` binary(16) default null, `site_id` binary(16) default null, `page_id` binary(16) default null, `action_at` datetime default null, `impression` smallint(6) default null, `click` smallint(6) default null, `sold_impression` smallint(6) default null, `price` decimal(15,7) default '0.0000000', `actioned_at` timestamp not null default '0000-00-00 00:00:00', `unique_ads` varchar(255) collate utf8_unicode_ci default null, `notification_url` text collate utf8_unicode_ci, primary key (`count`), key `id` (`id`), key `index_events_on_actioned_at` (`actioned_at`), key `index_events_unit_demand_partner` (`unit_id`,`demand_partner_id`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8 collate=utf8_unicode_ci; #2 events_uuid create table `events_uuid` ( `id` binary(16) not null, `unit_id` binary(16) default null, ~ ~ primary key (`id`), key `index_events_on_actioned_at` (`actioned_at`), key `index_events_unit_demand_partner` (`unit_id`,`demand_partner_id`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8 collate=utf8_unicode_ci; #3 events_uuid_ordered create table `events_uuid_ordered` ( `id` binary(16) not null, `unit_id` binary(16) default null, ~ ~ primary key (`id`), key `index_events_on_actioned_at` (`actioned_at`), key `index_events_unit_demand_partner` (`unit_id`,`demand_partner_id`) ) engine=innodb default charset=utf8 collate=utf8_unicode_ci;
conclusions
- create function to rearrange uuid fields and use it
delimiter // create definer=`root`@`localhost` function `ordered_uuid`(uuid binary(36)) returns binary(16) deterministic return unhex(concat(substr(uuid, 15, 4),substr(uuid, 10, 4),substr(uuid, 1, 8),substr(uuid, 20, 4),substr(uuid, 25))); // delimiter ;
inserts
insert into events_uuid_ordered values (ordered_uuid(uuid()),'1','m',....);
selects
select hex(uuid),is_active,... from events_uuid_ordered ;
- define uuid as binary(16) as binary does not have any character set
references
Published at DZone with permission of Peter Zaitsev, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments