CAFEBABE: Java's Magic Word
Java compilers make Java source code into bytecode. Did you know all Java classes start with the word CAFEBABE? Check out this awesome look at the Java magic word.
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeA Java compiler compiles a Java Source code into bytecode and stores it in a .class file which is then get executed by the JVM.
Well, we all know this, but do you know that all Java classes start with a magic word called – CAFE BABE?
In case you’re curious and interested to know why bear with my attempt to inform you something interesting.
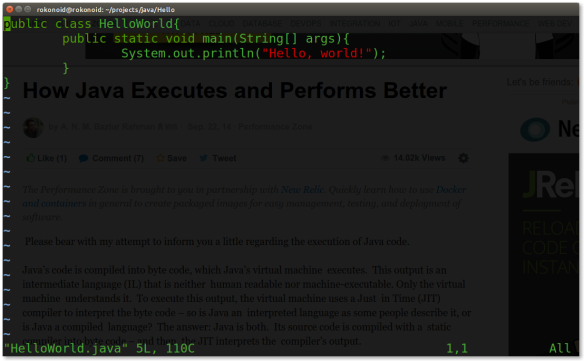
Go to the vim (whatever editor you like to) and with the simple following Java code.
public class HelloWorld{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Hello, world!");
}
}
Now compile it and open the HelloWorld.class in a hex editor –
$ javac HelloWorld.java
$ xxd HelloWorld.class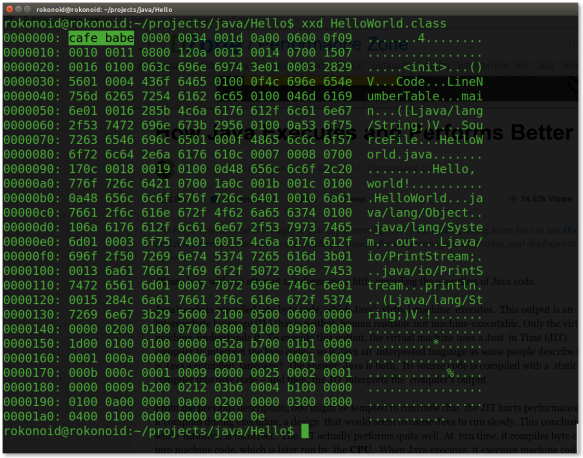
Did you notice the CAFE BABE part? If you open any java .class file with a hex editor, you will find this magic word at the beginning.
Well it's just a hexadecimal number which is 3405691582 in decimal.
(CAFEBABE)16 = (3405691582)10
But why it is so magical that it has to add in each class file is probably the most important question to be asked.
Well, James Gosling explained why: –
We used to go to lunch at a place called St Michael’s Alley. According to local legend, in the deep dark past, the Grateful Dead used to perform there before they made it big. It was a pretty funky place that was definitely a Grateful Dead Kinda Place. When Jerry died, they even put up a little Buddhist-esque shrine. When we used to go there, we referred to the place as Cafe Dead. Somewhere along the line, it was noticed that this was a HEX number. I was re-vamping some file format code and needed a couple of magic numbers: one for the persistent object file, and one for classes. I used CAFEDEAD for the object file format, and in grepping for 4 character hex words that fit after “CAFE” (it seemed to be a good theme) I hit on BABE and decided to use it. At that time, it didn’t seem terribly important or destined to go anywhere but the trash can of history. So CAFEBABE became the class file format, and CAFEDEAD was the persistent object format. But the persistent object facility went away, and along with it went the use of CAFEDEAD – it was eventually replaced by RMI.
Published at DZone with permission of A N M Bazlur Rahman, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments