Understanding Supervisor in Apache Druid
A supervisor is a built-in part of Druid, making it easier to ingest, analyze, and monitor data in real-time. Learn more!
Join the DZone community and get the full member experience.
Join For FreeAlthough both Apache Druid and Apache Kafka are potent open-source data processing tools, they have diverse uses. While Druid is a high-performance, column-store, real-time analytical database, Kafka is a distributed platform for event streaming. However, they can work together in a typical data pipeline scenario where Kafka is used as a messaging system to ingest and store data/events, and Druid is used to perform real-time analytics on that data. In short, indexing is the process of loading data in Druid, and Druid reads the data from a streaming source system like Kafka and eventually stores it in data files called segments. Druid includes an Apache Kafka Indexing Service that enables Druid to accept data streams from Apache Kafka, analyze the data in real time, and index the data for querying and analysis.
A supervisor is a built-in part of Druid, making it easier to ingest, analyze, and monitor data in real-time. The data ingestion lifecycle is managed by druid supervisors. They handle jobs like reading information from a streaming source (like Kafka topics), indexing it into Druid segments, and keeping track of the ingestion procedure. The data ingestion for Kafka streaming ingestion is configured by the supervisor's specification. A JSON specification (often referred to as the supervisor spec) that specifies how the supervisor should consume data from Kafka and how it should process and index that data into Druid must be provided when configuring an Apache Kafka supervisor. Kafka indexing tasks read events using Kafka’s own partition and offset mechanism to guarantee exact-once ingestion. The Kafka supervisor in Druid reads the data in real time from the mentioned topic name and converts them into Druid events based on the submitted supervisor spec. The supervisor applies any necessary transformations or aggregations on the data before indexing it into Druid segments. These segments are essentially Druid’s way of storing and organizing data for efficient querying.
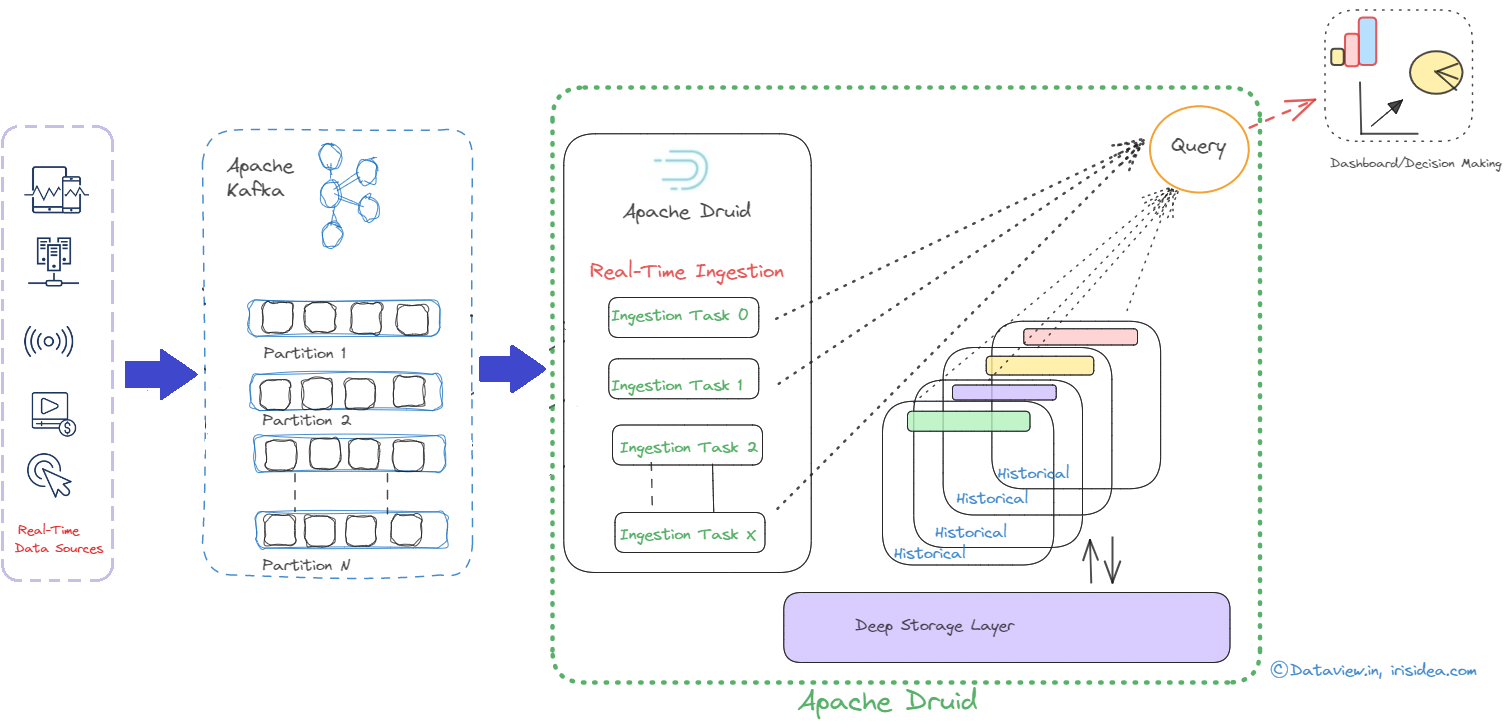
If a segment fails to build or if there are issues with the ingestion process, supervisors can be configured to take corrective actions, like retrying the ingestion or alerting administrators. Supervisors can be configured to handle scalability requirements. In order to spread out the workload and balance the ingestion process, more supervisor jobs may be added as the volume of data grows. The key sections typically found in a Kafka supervisor spec in Druid are:
type: Specifies the type of supervisor, which, in this case, is “Kafka.”dataSchema: Specify the Druid data source name to which the data will be ingested, primary timestamp, dimensions, metrics, transforms, and any necessary filters.ioConfig: to explain the configure details of Kafka connection settings like a topic name from which the supervisor will consume data, input format of event/data type, and bootstrap server IP address with a port for establishing the initial connection to Kafka brokers. and configure how Druid parses the data.tuningConfig: to control various tuning parameters specific to each ingestion method, like- Task Count: The number of parallel tasks used to ingest data. Increasing this number can enhance parallelism and increase ingestion throughput.
- Window Period: The duration of time for each window during which events are collected before they are ingested and indexed into Druid.
- Shard Spec: Defines how the data is partitioned into Druid segments.
tuningConfig is not mandatory to be added in the supervisor spec. by leveraging supervisor specification with these above options, we can give Druid instructions on how to take data from Kafka, process it, and index it into Druid segments. You can read here how to integrate Kafka with Druid to transport messages/data from topic to view on Druid.
Here is the sample supervisor spec to enable smooth integration between Apache Kafka and Druid for real-time data intake and analytics. This JSON specification serves as a model for the Kafka supervisor.
{
"type": "kafka",
"dataSchema": {
"dataSource": "your_druid_data_source_name",
"parser": {
"type": "string",
"parseSpec": {
"format": "json",
"timestampSpec": {
"column": "timestamp",
"format": "auto"
},
"dimensionsSpec": {
"dimensions": ["dimension1", "dimension2"],
"dimensionExclusions": [],
"spatialDimensions": []
}
}
},
"metricsSpec": [
{
"name": "count",
"type": "count"
},
{
"name": "sum",
"type": "doubleSum",
"fieldName": "metricField"
}
],
"granularitySpec": {
"type": "uniform",
"segmentGranularity": "hour",
"queryGranularity": "minute",
"intervals": ["2010-01-01T00:00:00.000Z/2025-01-01T00:00:00.000Z"]
}
},
"tuningConfig": {
"type": "kafka",
"taskCount": 1,
"replicas": 1,
"maxRowsPerSegment": 5000000,
"maxRowsInMemory": 1000000,
"intermediatePersistPeriod": "PT10m",
"windowPeriod": "PT5m"
},
"ioConfig": {
"topic": "your_kafka_topic",
"consumerProperties": {
"bootstrap.servers": "kafka-broker1:9092,kafka-broker2:9092",
"group.id": "druid-kafka-ingestion"
}
},
"filter": null,
"tuning": {
"type": "kafka",
"maxRowsPerSegment": 5000000
}
}
In conclusion, Apache Druid supervisors, more especially Kafka supervisors, enable the seamless and real-time intake of data from Kafka topics into Druid, providing data processing that is reliable, fault-tolerant, and effective.
I hope you have enjoyed this read. Please like and share if you feel this composition is valuable. Thank you for reading this tutorial, and I hope it was helpful in getting you started with Kafka and Druid!
Published at DZone with permission of Gautam Goswami, DZone MVB. See the original article here.
Opinions expressed by DZone contributors are their own.

Comments